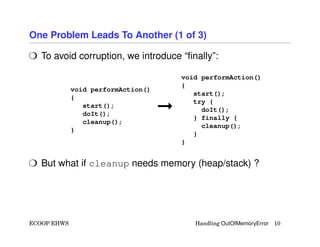
The document discusses methods for handling 'Out of Memory' errors, particularly in Eclipse, emphasizing the need for recovery techniques such as the 'hedge' technique, which involves pre-allocating memory to help manage low memory situations. It highlights the difficulties in implementing these strategies due to potential memory inconsistencies and compiler behaviors. The author suggests that while hedge recovery can be effective, improvements are necessary in language specifications and compiler behavior to ensure safer memory management.










![One Problem Leads To Another (2 of 3)
H So we pre-allocate some memory:
void performAction()
{
start();
int[] space = new int[1000];
// Point A
try {
doIt();
} finally {
// Point B
space = null;
cleanup();
}
}
H But what if the compiler . . .
– moves the allocation later (B)?
– moves the deallocation earlier (A)?
ECOOP EHWS Handling OutOfMemoryError 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memory-error-talk-140714045514-phpapp01/85/Memory-error-talk-12-320.jpg)
![One Problem Leads To Another (3 of 3)
H Fake uses force early allocation.
H Fake tests force late deallocation.
void performAction()
{
start();
int[] space = new int[1000];
space[45] = 1+space[fact(6)];
try {
doIt();
} finally {
if (space[45] > space[44]) {
space = null;
cleanup();
}
}
}
H We have obfuscated our program.
ECOOP EHWS Handling OutOfMemoryError 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memory-error-talk-140714045514-phpapp01/85/Memory-error-talk-13-320.jpg)


