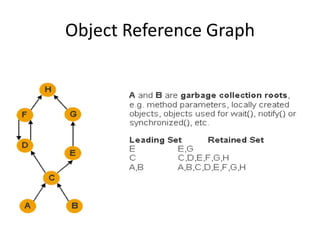
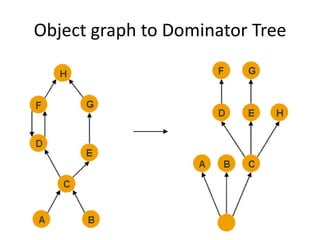
The document details a memory analyzer tool presented by Mohammad Samiullah Farooqui, covering essential concepts of memory analysis, such as heap dumps, shallow and retained heaps, and memory leak identification methods. It outlines how to analyze memory leaks by examining the dominator tree and provides specific strategies to optimize memory usage. Additionally, it includes resources for further learning on memory analysis techniques.