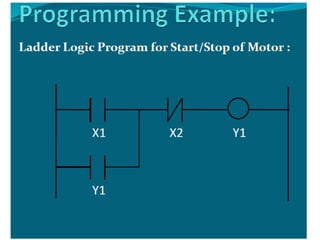
This document provides an overview of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), describing their architecture, major components, input/output processing, and programming methods, particularly ladder logic. It outlines key functionalities such as timing, counting, latching, and sequencing operations, while also emphasizing the importance of understanding sinking and sourcing for input/output modules. Additionally, it highlights various applications of PLCs across different industries, including robotics, manufacturing, and food processing.