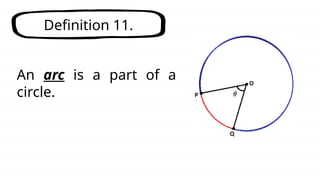
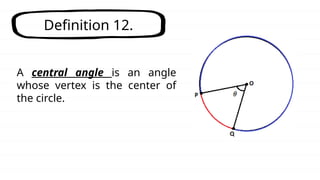
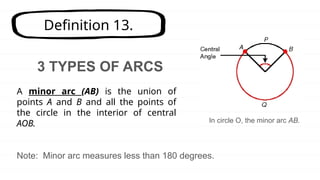
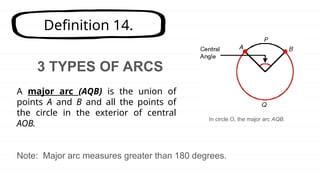
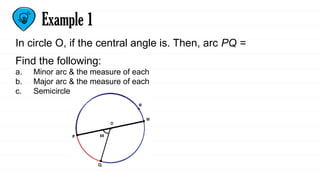
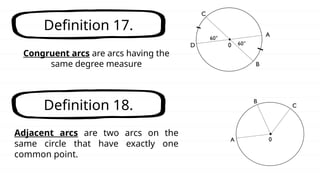
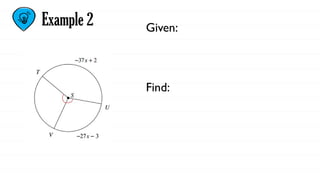
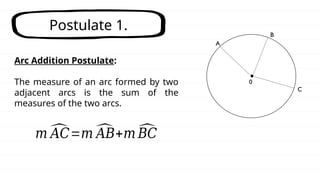
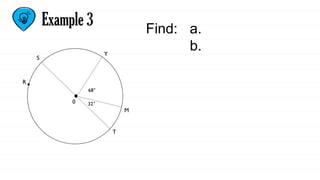
The document defines key concepts related to circles, including arcs, central angles, and types of arcs such as minor, major, and semicircles. It explains how the measures of these arcs relate to their central angles and discusses properties like congruent and adjacent arcs. Additionally, it introduces the concepts of theorems, postulates, and provides an example of the arc addition postulate.