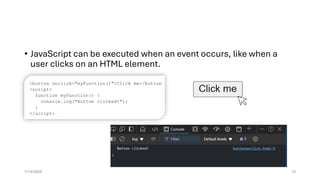
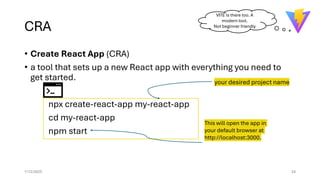
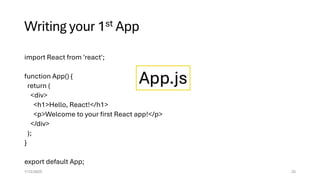
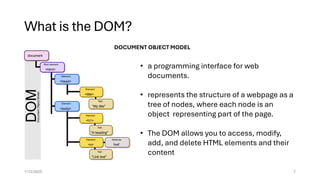
The document provides an overview of JavaScript, highlighting its popularity in web development and job market demand, along with its versatility across frontend, backend, and mobile applications. It explains key concepts like the Document Object Model (DOM) and JavaScript libraries, particularly React, which enhances UI development by enabling component-based architecture. It also outlines the setup process for using Node.js and React, and emphasizes the advantages of using React for building single-page applications with efficient updates using a virtual DOM.






![2. getElementsByClassName()
Access all elements with a specific class name.
<div class="box">Box 1</div>
<div class="box">Box 2</div>
<script>
var boxes = document.getElementsByClassName("box");
document.write(boxes[0].innerHTML); // Outputs: Box 1
</script>
1/12/2025 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/masteringjsanddom-250112023742-2880211a/85/Mastering-JavaScript-and-DOM-A-Gateway-to-Web-Development-9-320.jpg)
![3. getElementsByTagName()
Access all elements with a specific tag name.
<div>First</div>
<div>Second</div>
<script>
var divs = document.getElementsByTagName("div");
console.log(divs[1].innerHTML); // Outputs: Second
</script>
1/12/2025 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/masteringjsanddom-250112023742-2880211a/85/Mastering-JavaScript-and-DOM-A-Gateway-to-Web-Development-10-320.jpg)