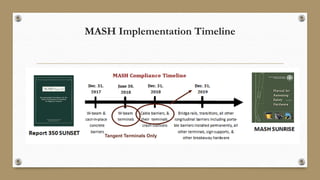
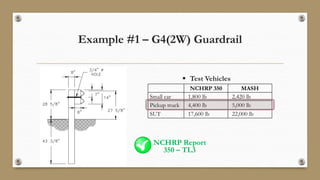
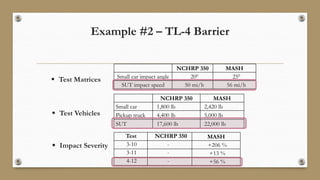
This document discusses the Manual for Assessing Safety Hardware (MASH) requirements for roadside safety hardware. MASH provides uniform crash testing guidance for safety features to improve safety. By December 31, 2019, only hardware evaluated using MASH 2016 is allowed for new permanent installations on the National Highway System. Key changes in MASH include increased weights and sizes of test vehicles to better represent current vehicles. Examples discussed include increased requirements for W-beam guardrails, higher barriers required for Test Level 4, and new roof crush and pickup truck tests for sign supports. States like Texas are conducting research to evaluate existing hardware and ensure compliance with MASH by the deadline.