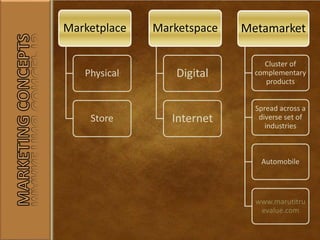
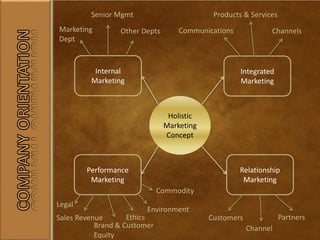
The document outlines various definitions and concepts of marketing in the 21st century, emphasizing the importance of societal processes that allow individuals and groups to fulfill their needs and wants through exchanges of valuable goods and services. It discusses the role of marketing management in targeting markets and enhancing customer value, along with different marketing strategies such as the production, product, selling, and marketing concepts. Additionally, it highlights the significance of holistic marketing that integrates customer relationships, brand equity, and ethical considerations in developing effective marketing plans.