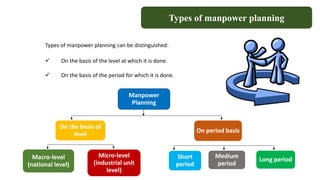
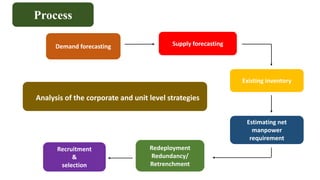
Manpower planning involves forecasting staffing needs, acquiring the right employees, and ensuring the optimal allocation of human resources. It aims to have the proper number and type of employees in the right places at the right time. The document outlines the objectives, types, factors, advantages, and processes of manpower planning. It also discusses job analysis, which identifies the tasks, skills, and attributes required for roles. Job analysis data is used for recruitment, performance management, training, and other human resource activities.