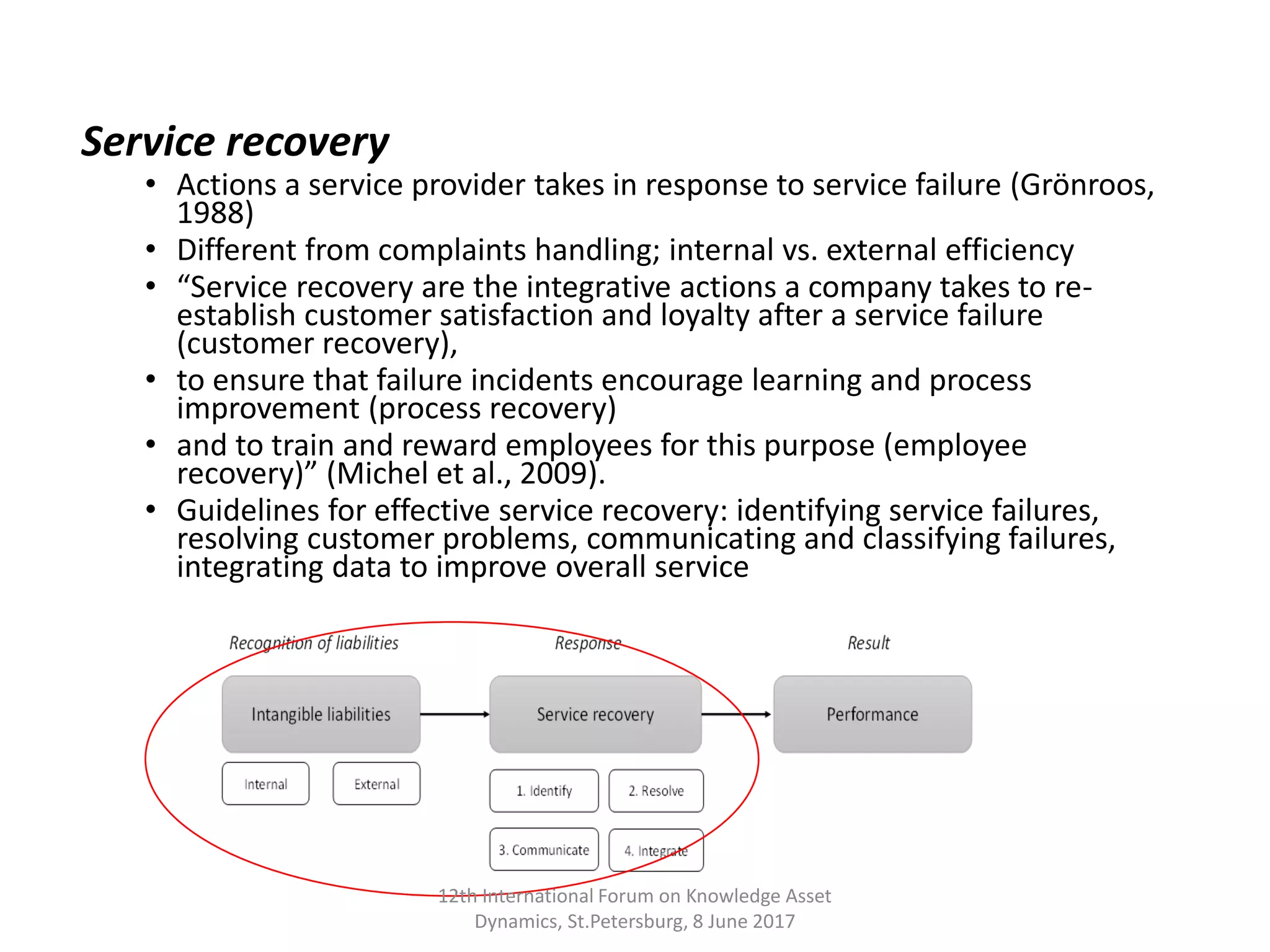
This study explores the management of intellectual liabilities in customer encounters, particularly in the construction industry, by integrating service recovery strategies and theoretical frameworks from literature. Key findings highlight the importance of addressing customer expectations, enhancing communication, and implementing effective service recovery practices to mitigate these liabilities. The research identifies specific challenges in the customer journey and provides practical guidelines for organizations to improve their management of intangible assets.