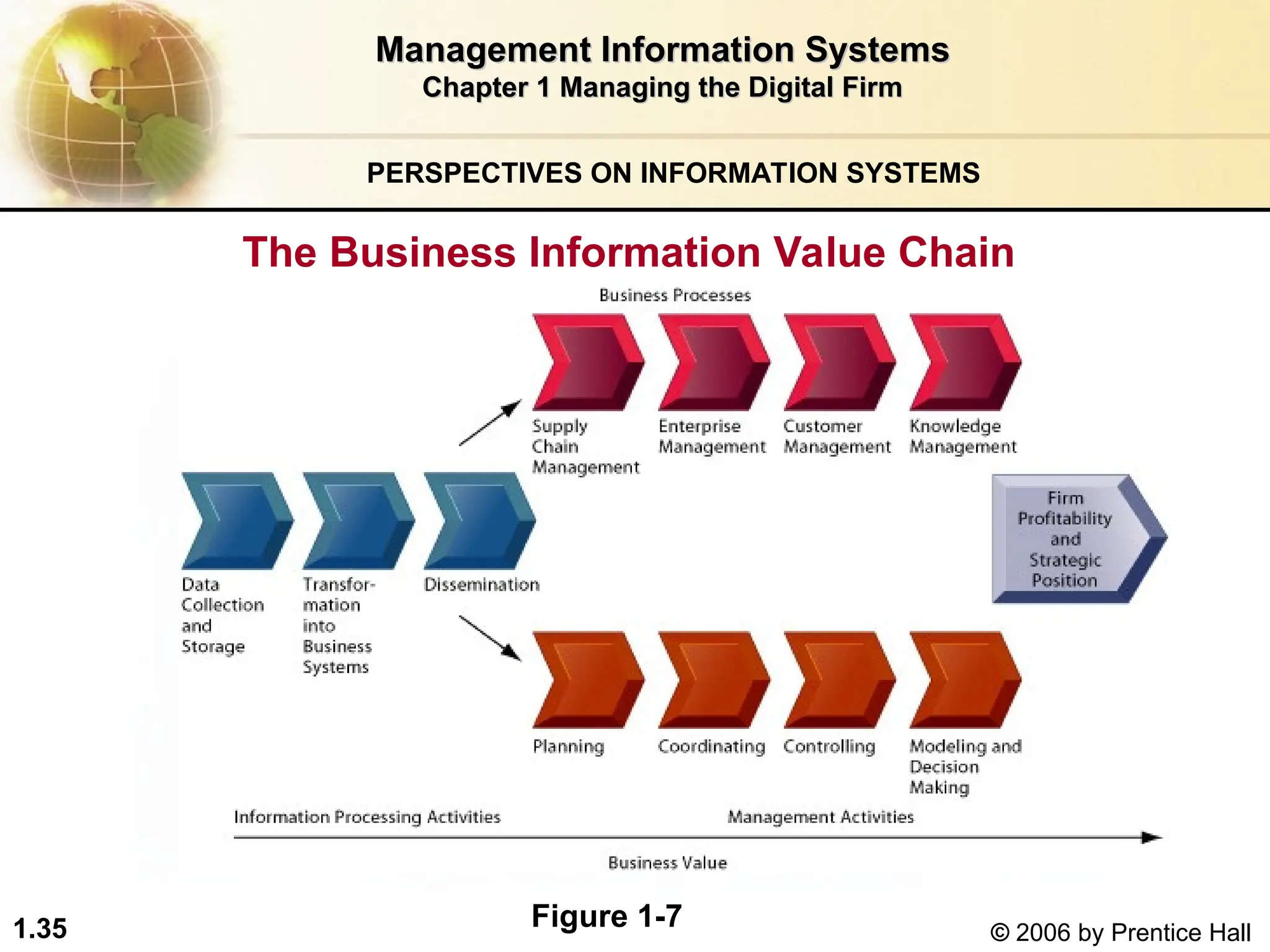
The document discusses the critical role of information systems in modern business management and their significance in enhancing productivity, strategic advantage, and competitive edge. It highlights the integration of technology and information systems to optimize operations, improve decision-making, and facilitate innovation. Key challenges and the importance of understanding both technical and management aspects of information systems for effective capital investment are also emphasized.