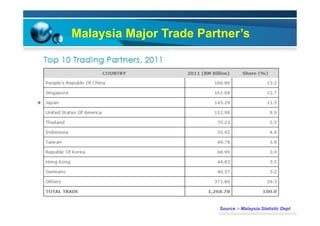
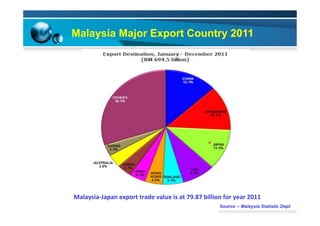
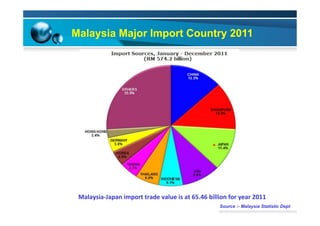
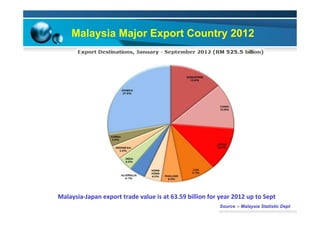
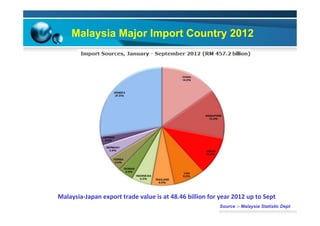
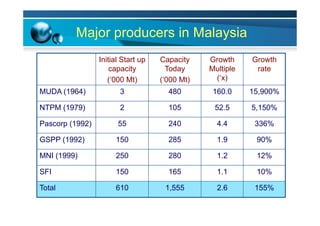
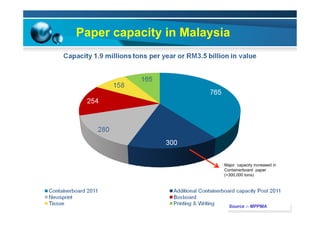
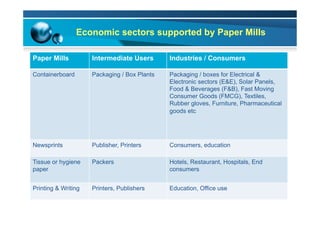
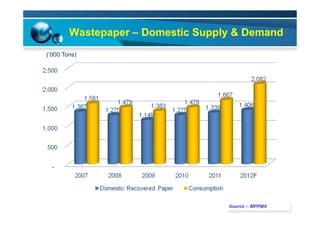
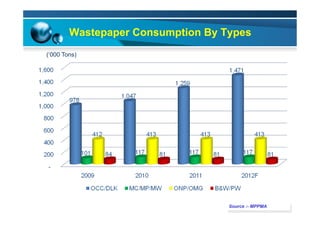
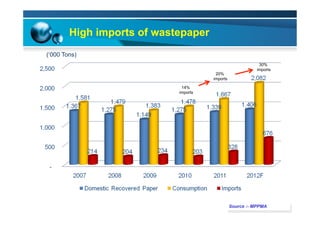
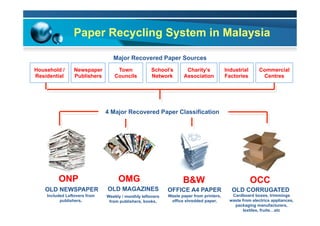
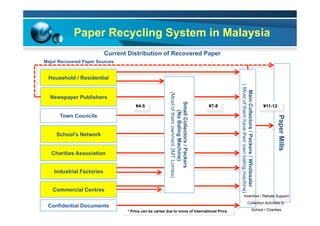
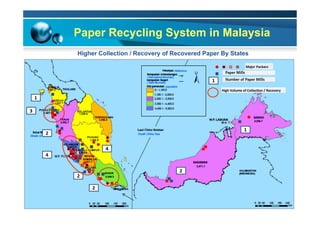
This document provides information on the paper industry and recycling system in Malaysia in 2012. It summarizes data from the Malaysian Pulp and Paper Manufacturer Association (MPPMA) report. It outlines key facts about Malaysia, its major trade partners, paper mills and production capacities. It also describes Malaysia's paper recycling system, sources of recovered paper, and challenges around increasing domestic wastepaper supply and quality. The document advocates for improving public awareness of recycling and expanding recovery efforts in underserved states to develop a more robust recycling system in Malaysia.