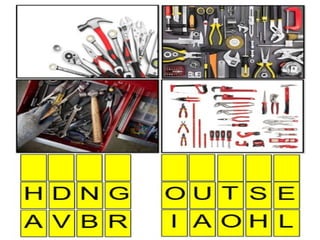
The document outlines activities and objectives for teaching students proper maintenance and storage of hand tools. It includes discussions on routine maintenance, repair procedures, and benefits of organized tool storage, emphasizing safety and efficiency. Students are encouraged to reflect on their learning through a graphic organizer and written assignment.