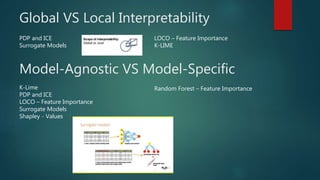
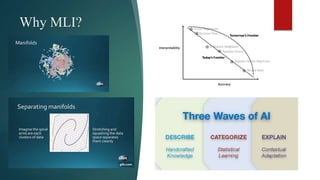
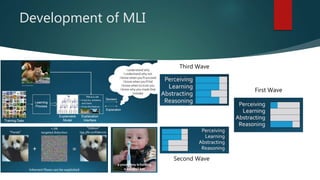
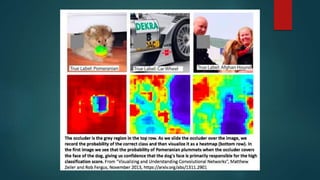
The document discusses machine learning interpretability, explaining concepts like global vs local interpretability, model-agnostic vs model-specific methods, and various techniques for assessing feature importance. It outlines linear and non-linear model hypotheses, along with tools like SHAP values and surrogate models. Additionally, it touches on the evolution of machine learning interpretability in the context of driverless AI.