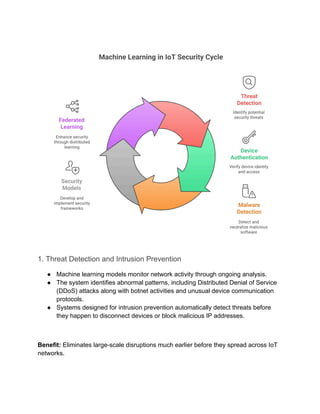
Machine learning in IoT security is transforming how connected devices are protected from evolving cyber threats. By analyzing patterns, detecting anomalies, and predicting risks, ML-powered IoT security solutions enable real-time monitoring, intrusion detection, and proactive threat prevention. Current applications include device authentication, network traffic analysis, and predictive maintenance for enhanced reliability. However, challenges such as data privacy, scalability, and handling vast, diverse IoT data remain critical concerns. As IoT adoption accelerates, leveraging machine learning for security will be key to ensuring resilience. Explore current solutions, limitations, and the future of ML-driven IoT security in safeguarding enterprise ecosystems.