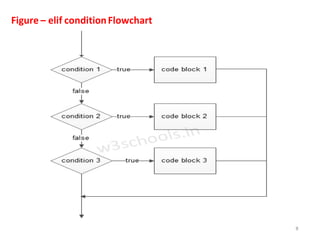
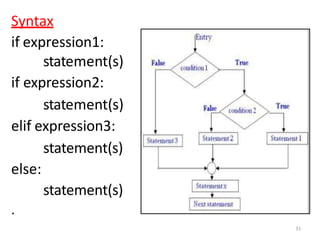
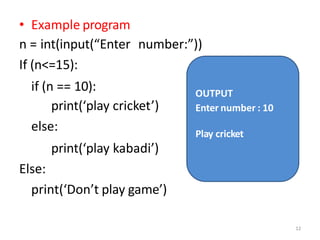
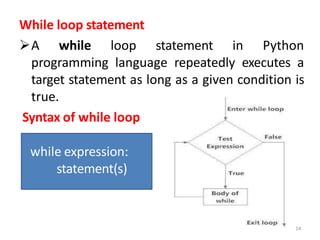
The document discusses different types of conditional and control statements in Python programming. It describes if, if-else, if-elif-else statements for decision making or conditional execution. It also covers while and for loops as control structures for repetitive execution of code. Nested if statements allow conditional blocks within other conditional blocks. While and for loops can have optional else blocks that execute after the loop completes without breaking.









![For loop flow chart
Addition of number using for loop
numbers = [6, 5, 3, 8, 4, 2, 5, 4]
sum1 = 0
for val in numbers:
sum1 = sum1+val
print("The sum is", sum1)
OUTPUT
The sum is 37
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/loops-230630101937-ec546add/85/loops-pdf-18-320.jpg)
![for Loop and for Loop with else
EX-01:
genre = ['pop', 'rock', 'jazz']
for i in range(len(genre)):
print("I like", genre[i])
EX-02:
genre = ['pop', 'rock', 'jazz']
for i in range(len(genre)):
print("I like", genre[i])
else:
print("No items left.")
OUTPUT
I like pop
I like rock
I like jazz
OUTPUT
I like pop
I like rock
I like jazz
No items left.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/loops-230630101937-ec546add/85/loops-pdf-19-320.jpg)