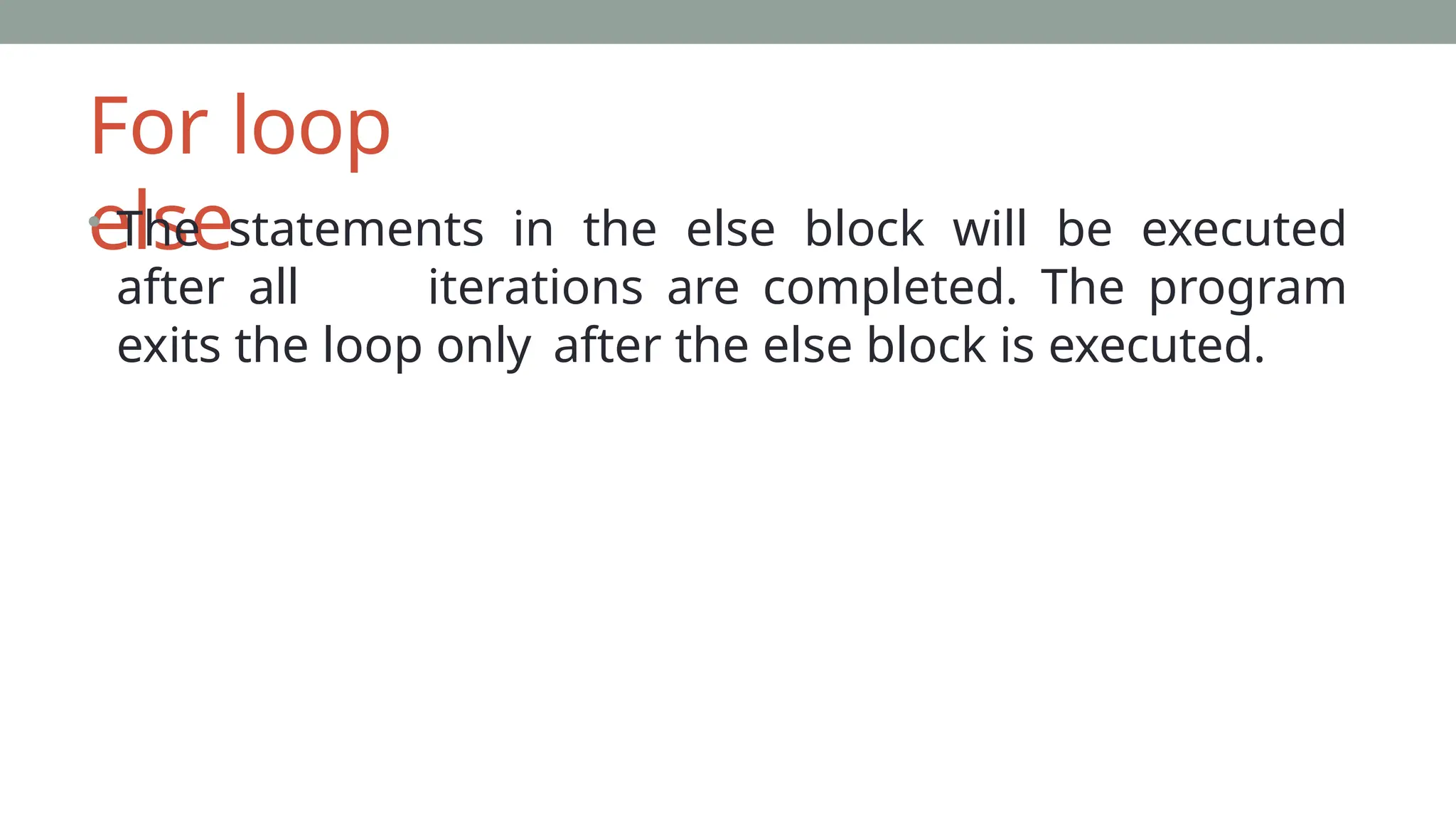
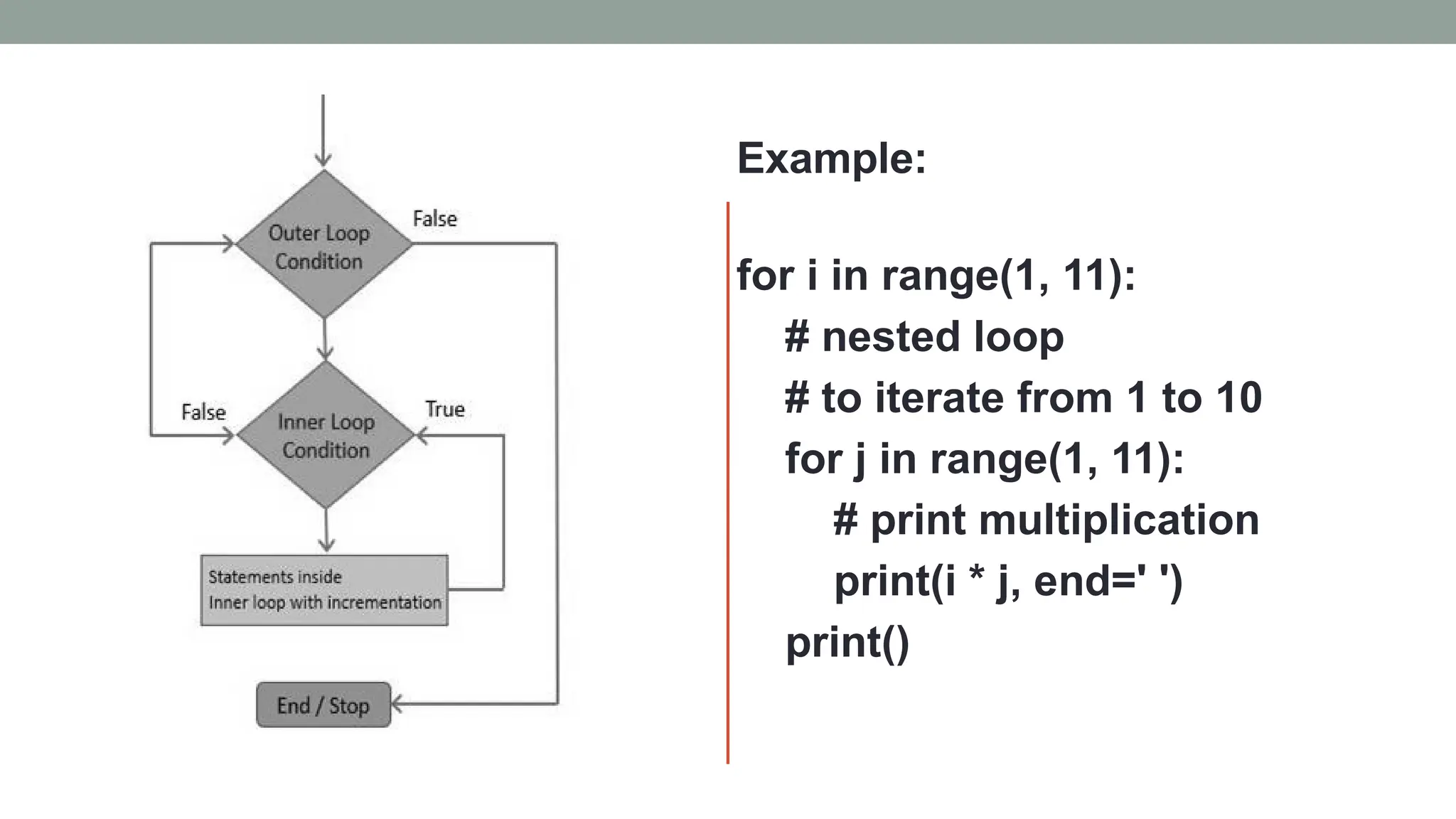
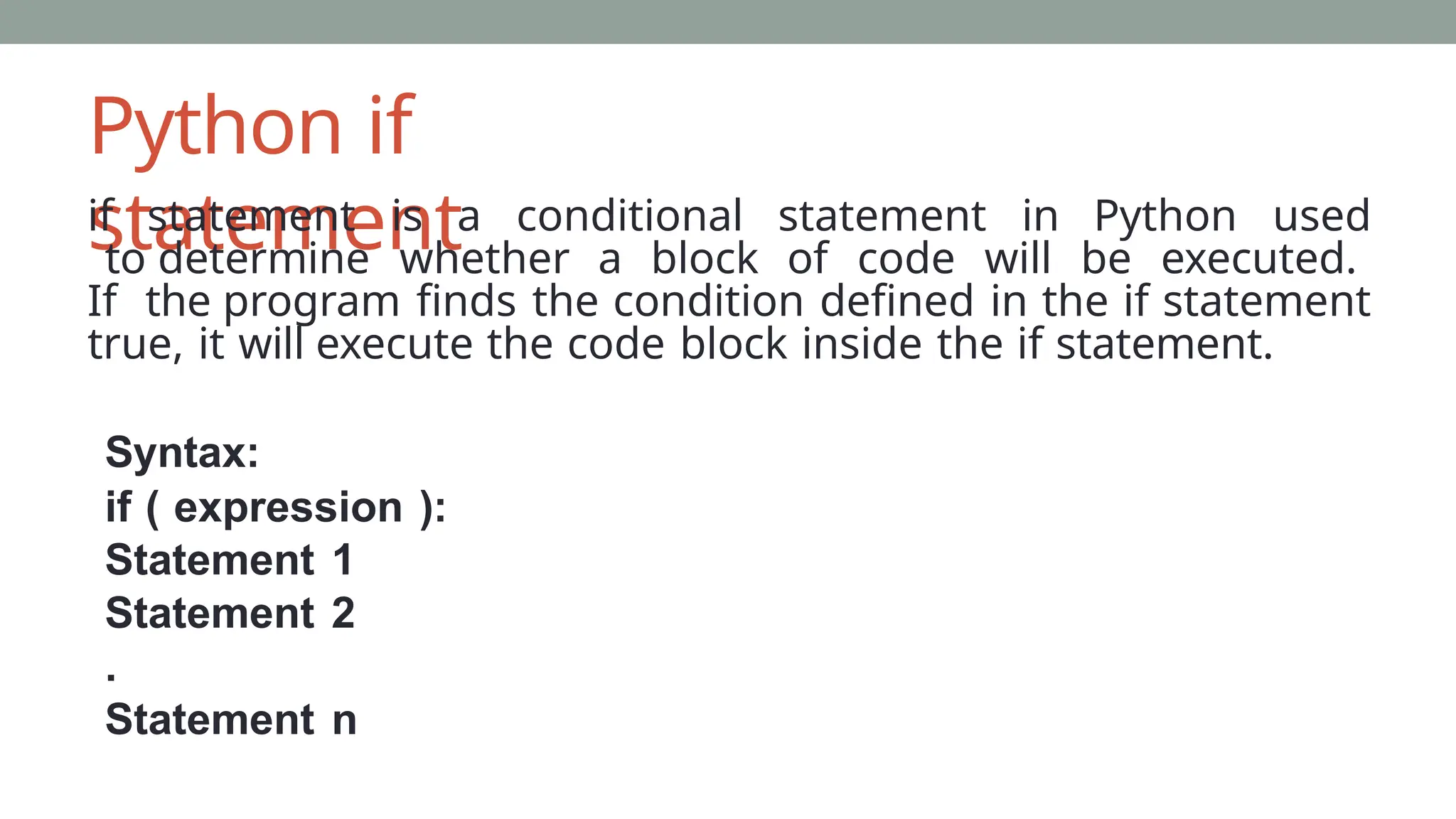
The document covers the fundamentals of Python programming, including sequential statements, data types, conditionals (if, if-else, if-elif-else), loops (for, while), and functions. It explains the syntax and use-cases of various control flow statements such as break, continue, and pass, as well as nested loops and functions. The document provides numerous examples to illustrate how these concepts are implemented in Python.


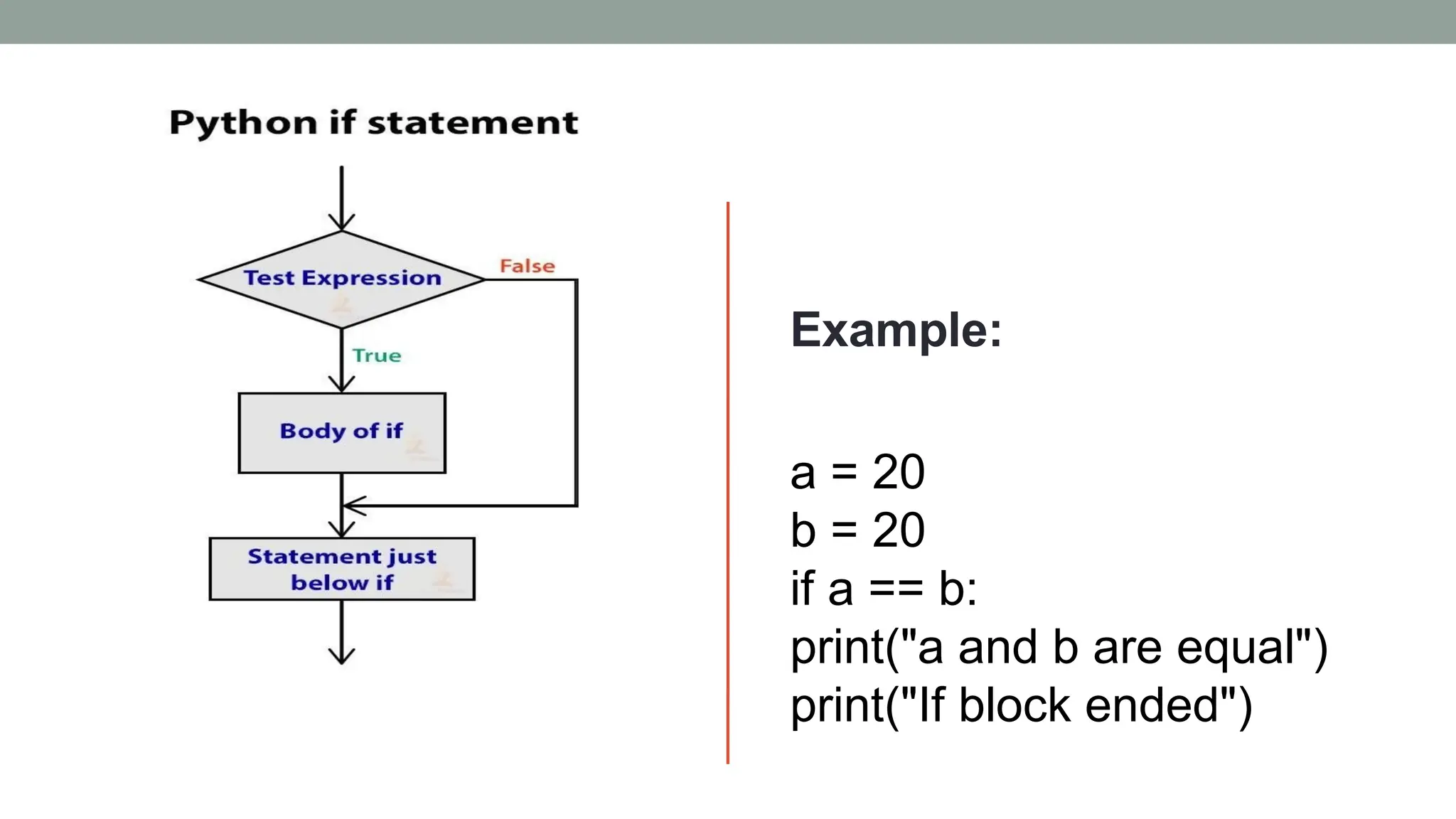

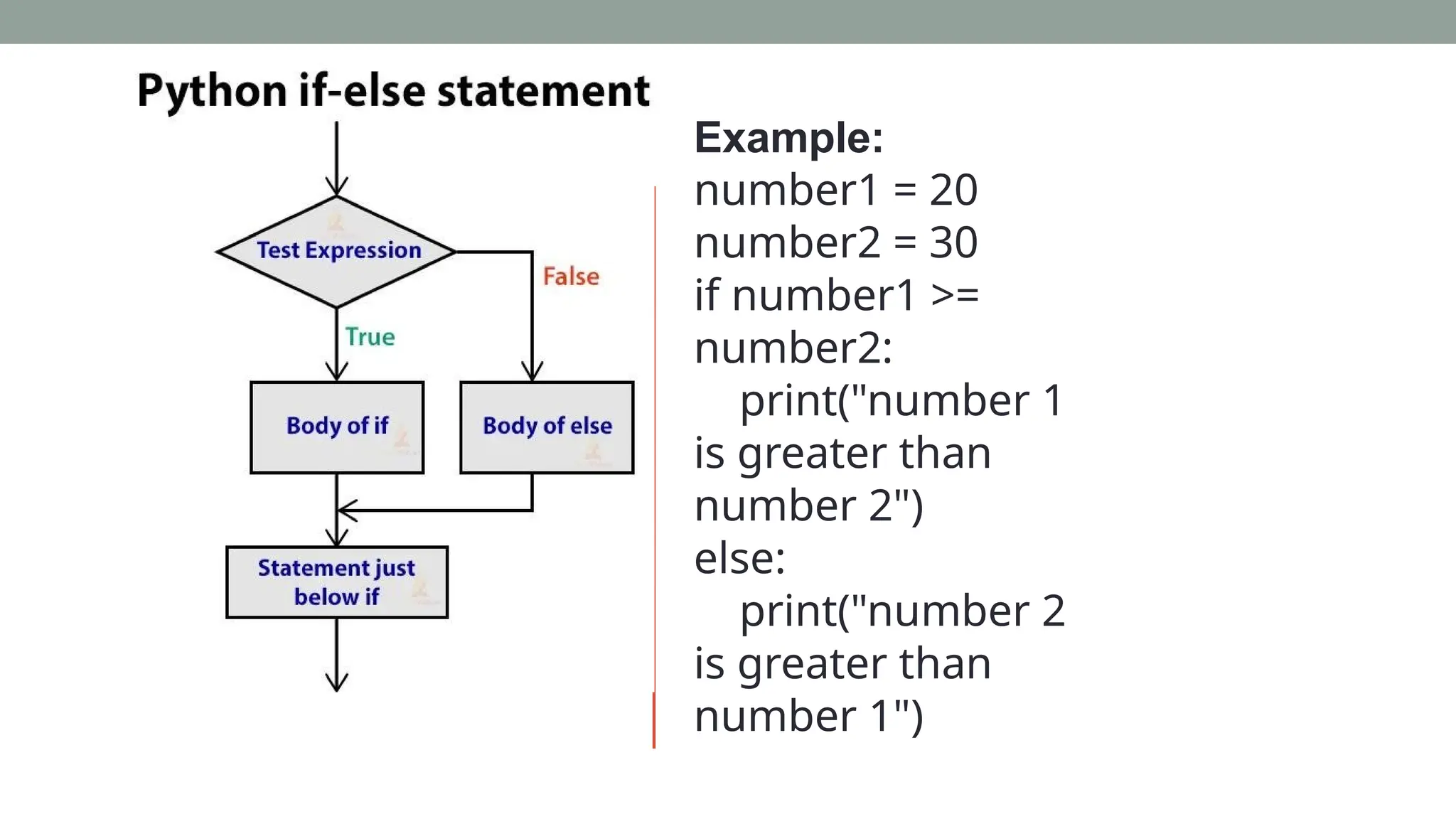

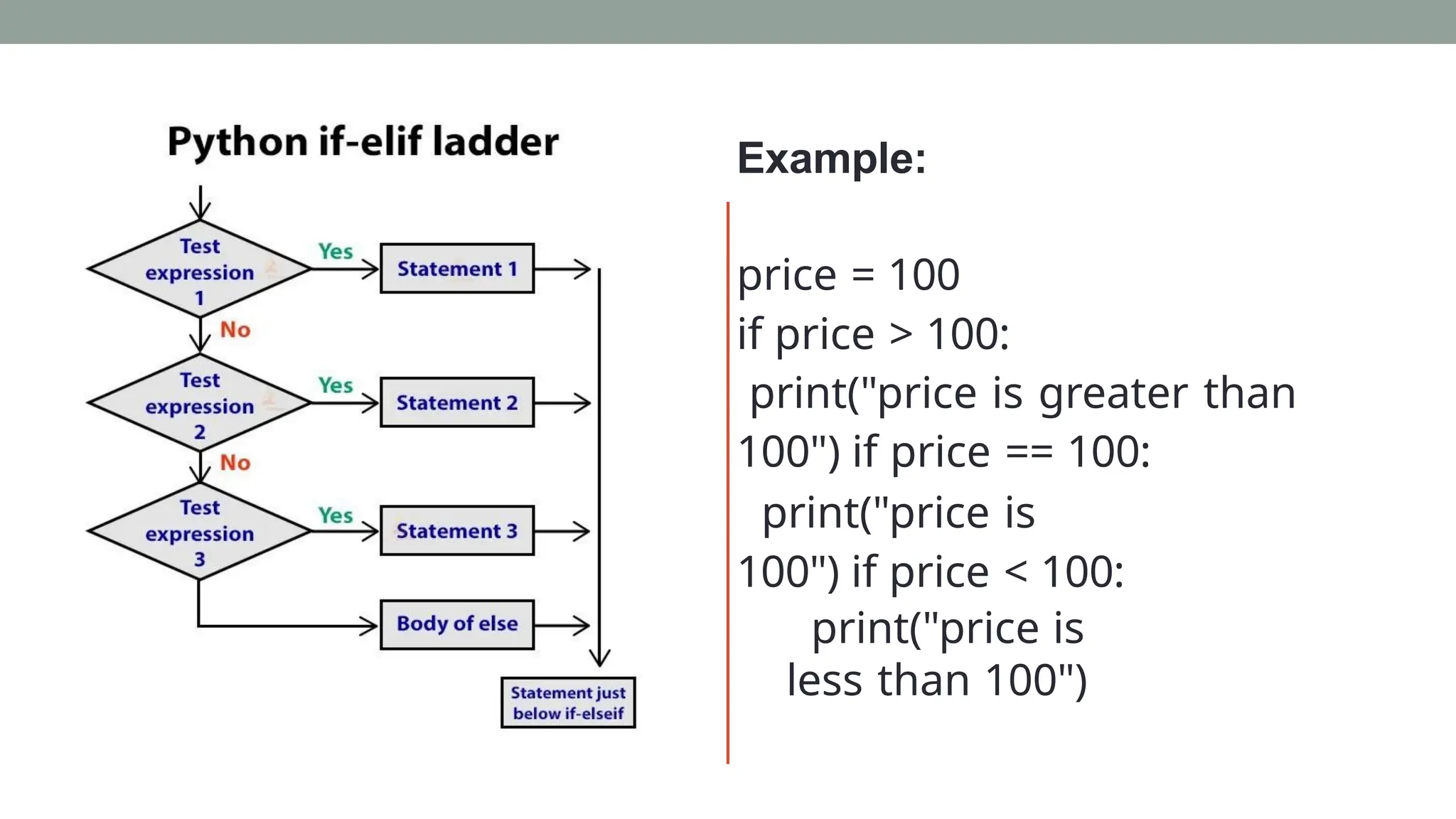
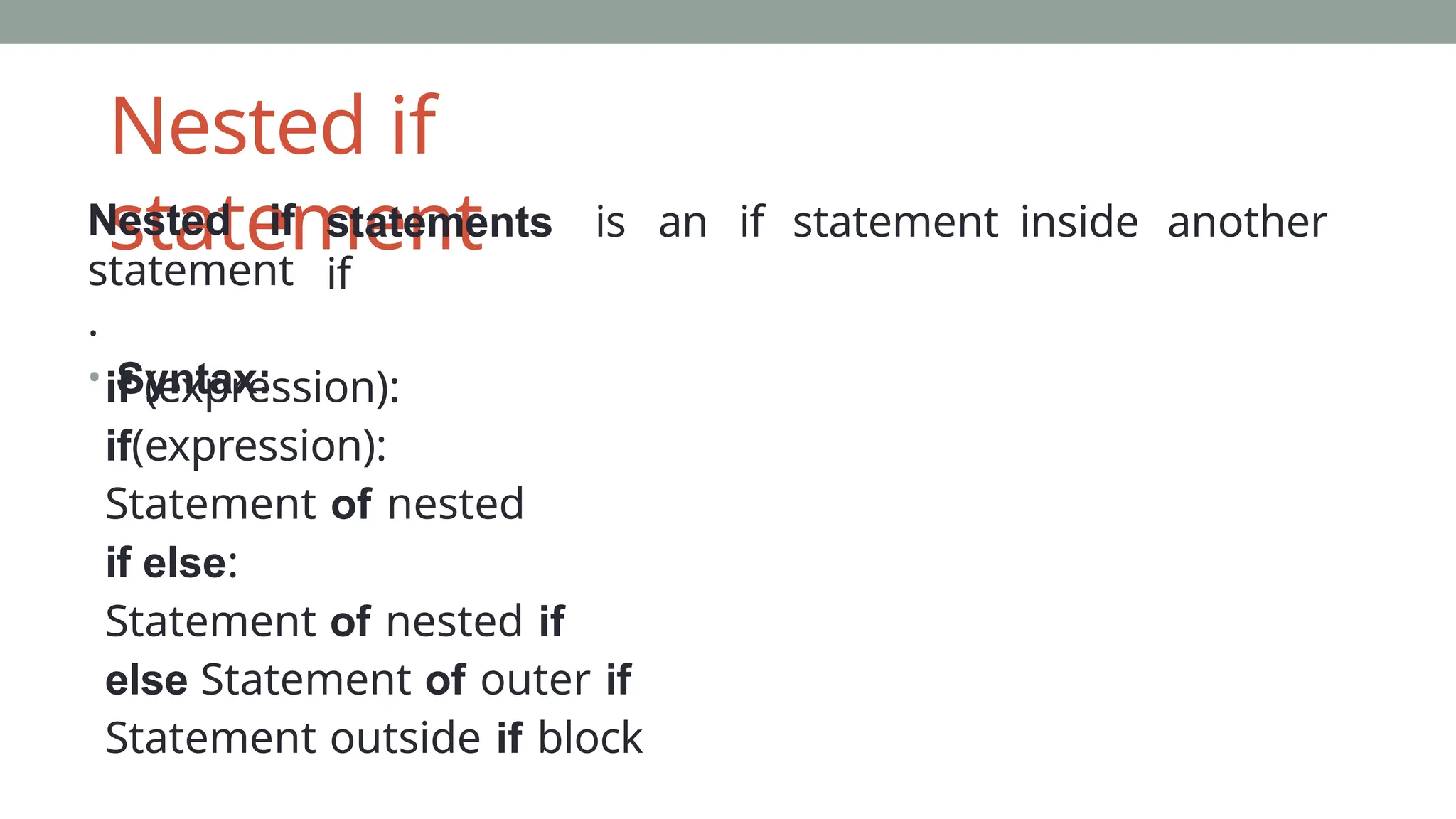



![Example:
fruits = ["apple",
"banana", "cherry"]
for x in fruits:
print(x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdsfirstunitmodule2ppt-240925062830-fa99c914/75/pds-first-unit-module-2-MODULE-FOR-ppt-pptx-18-2048.jpg)