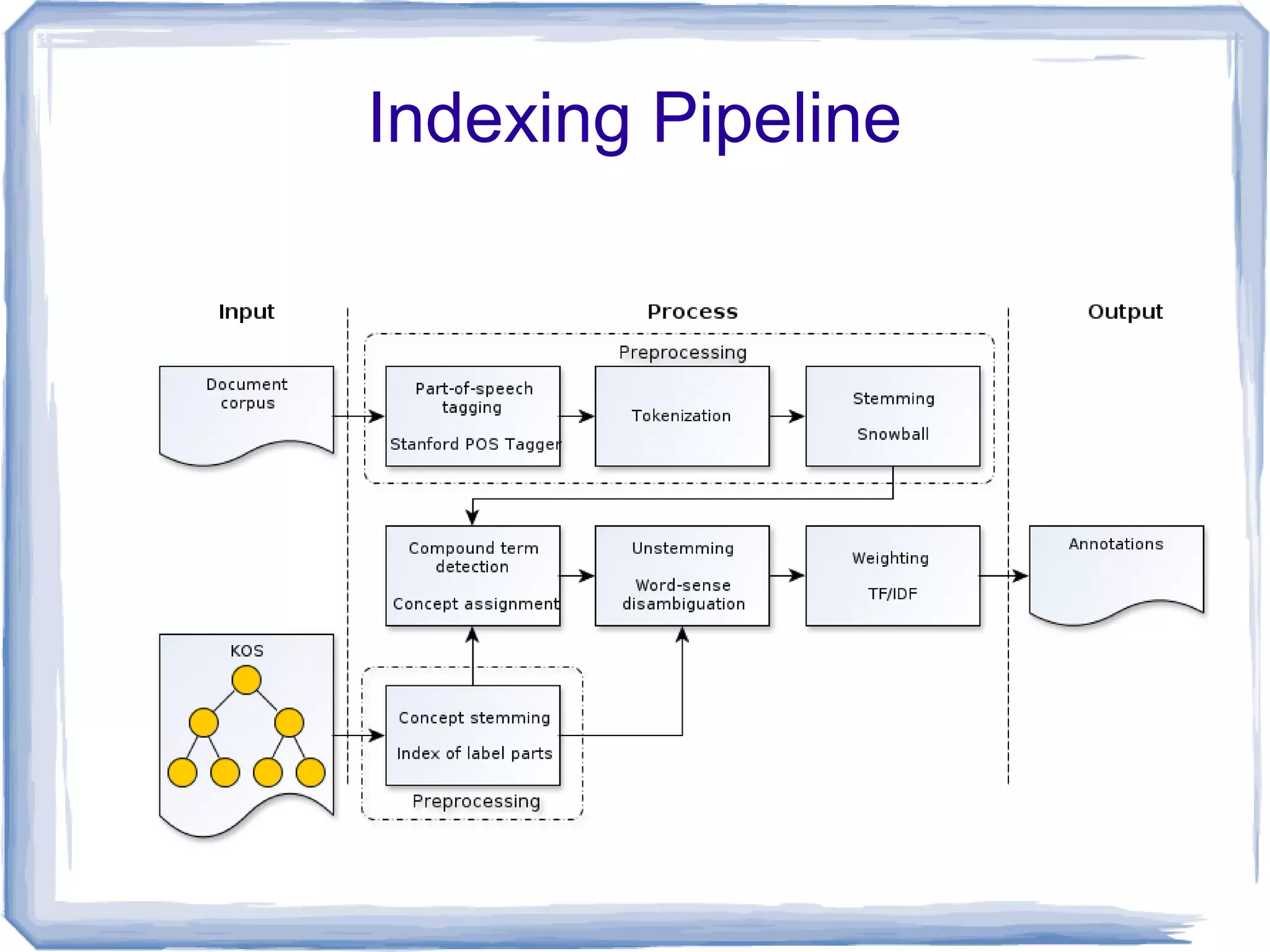
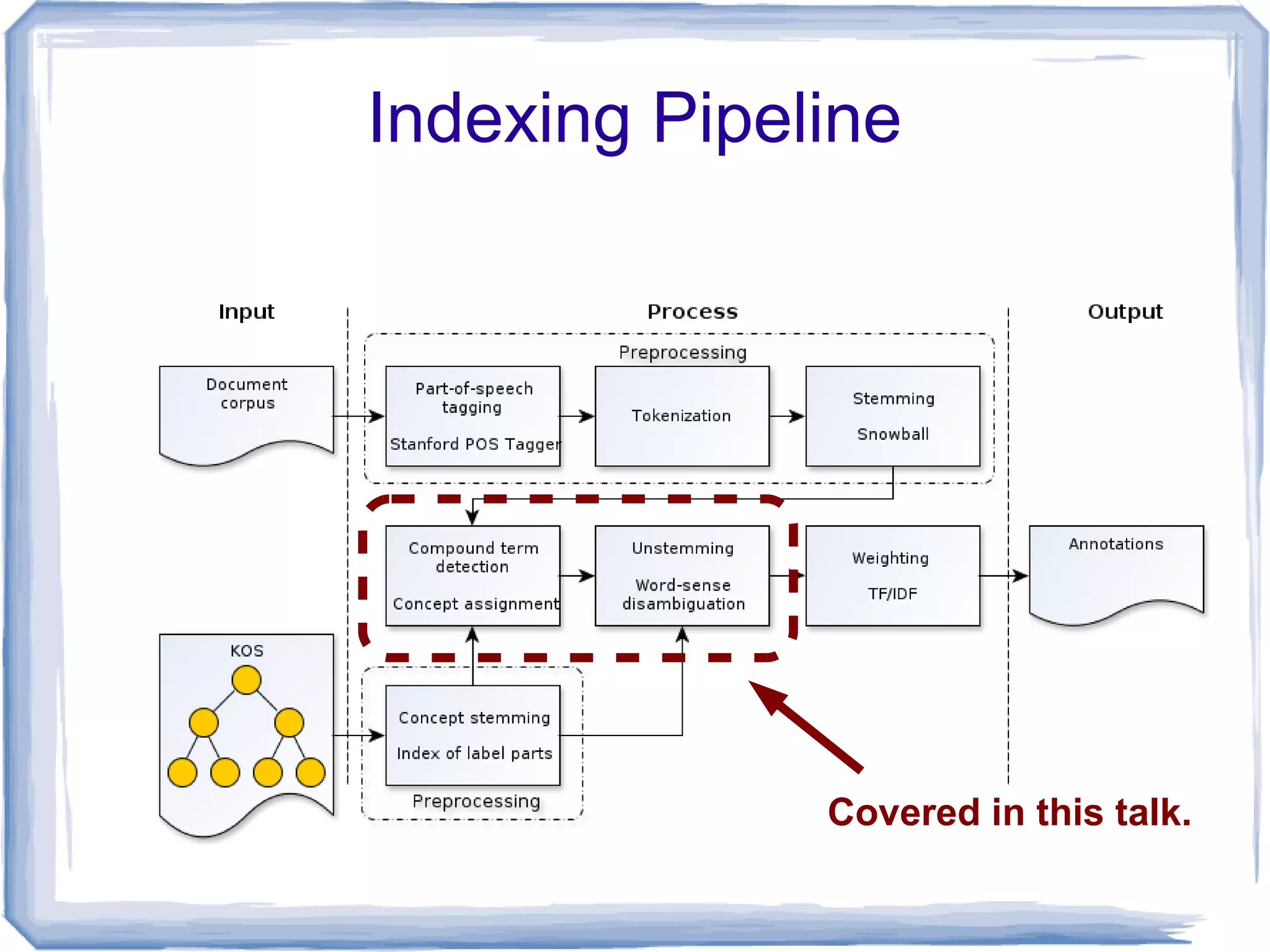
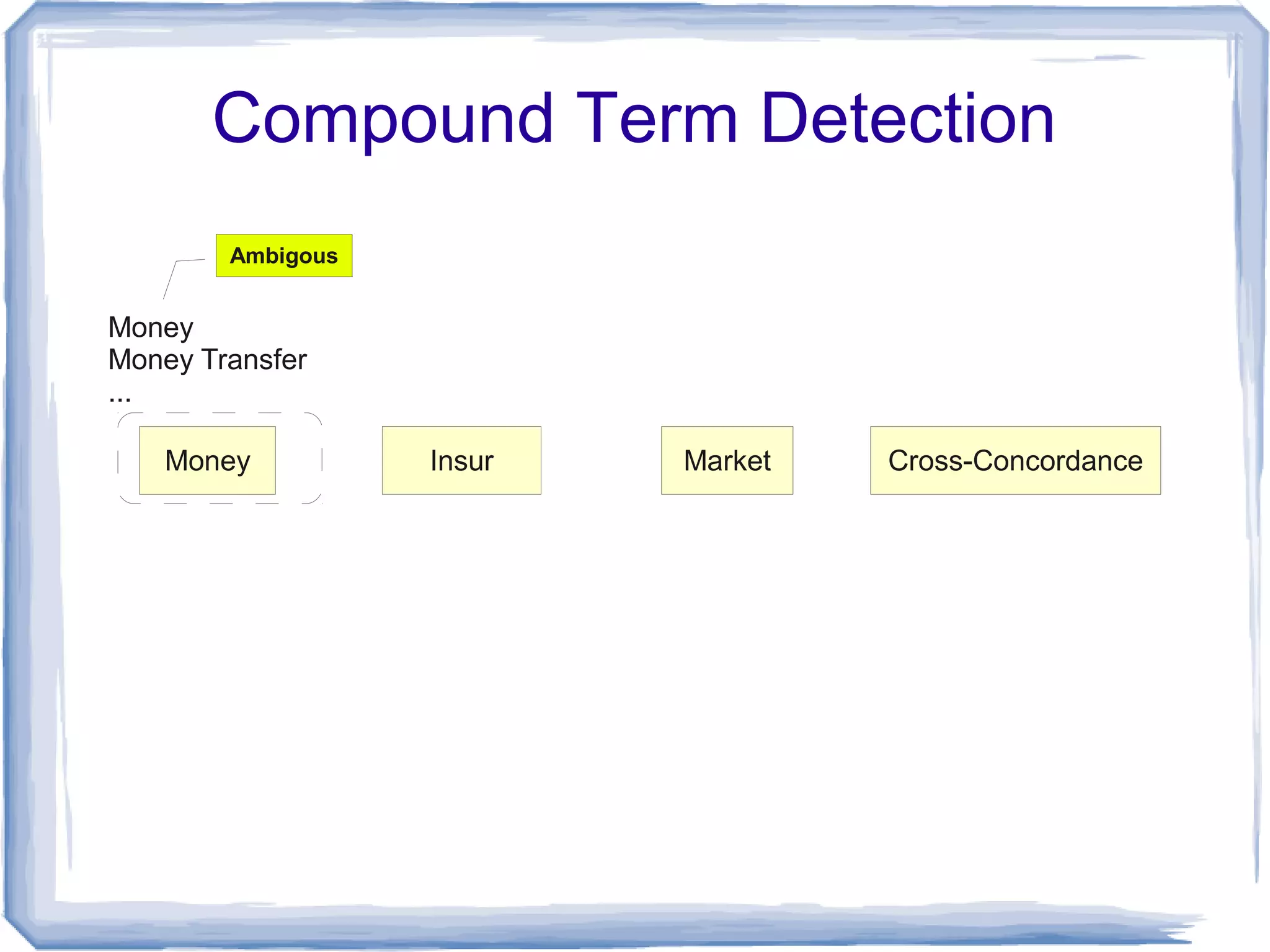
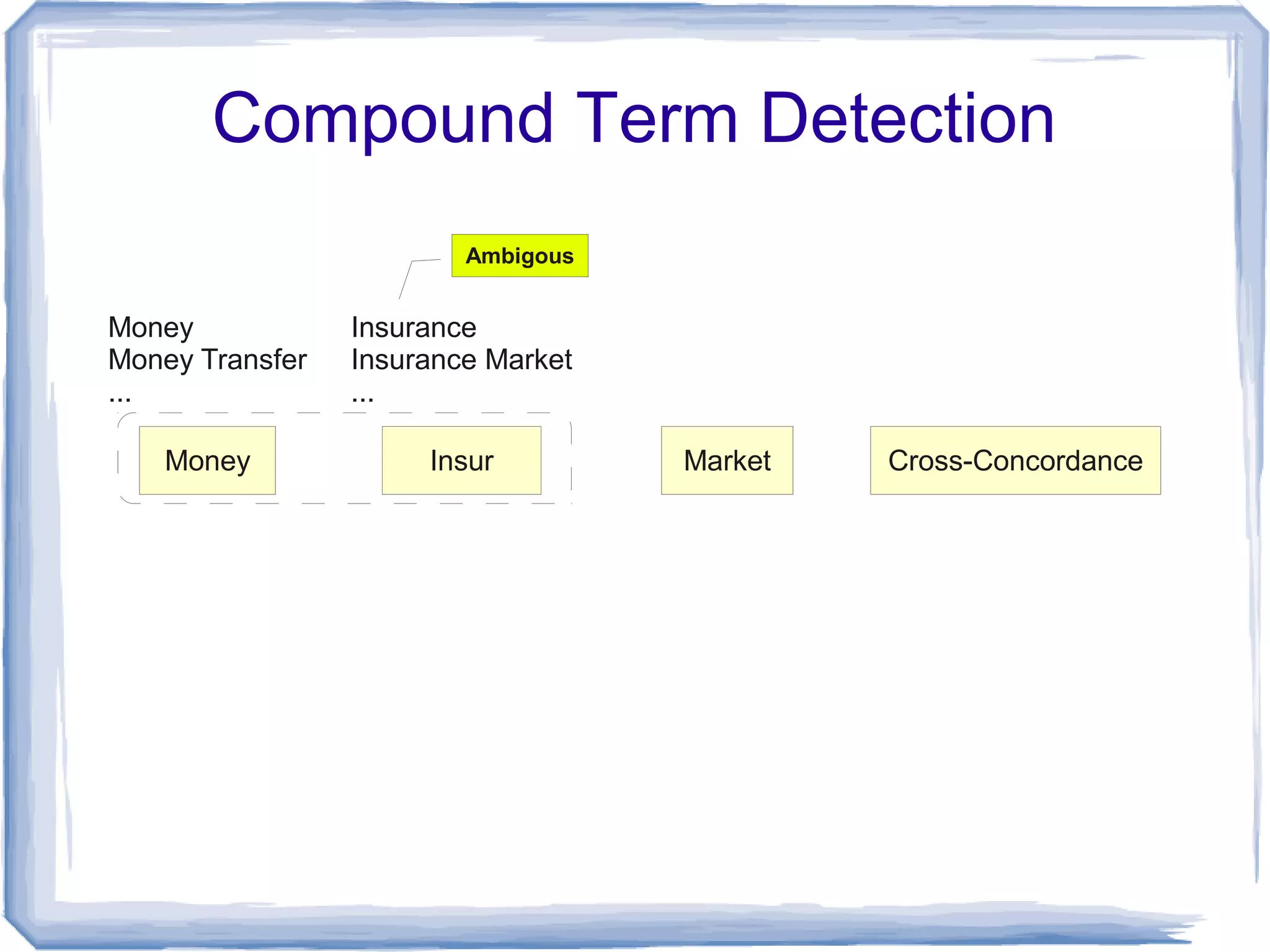
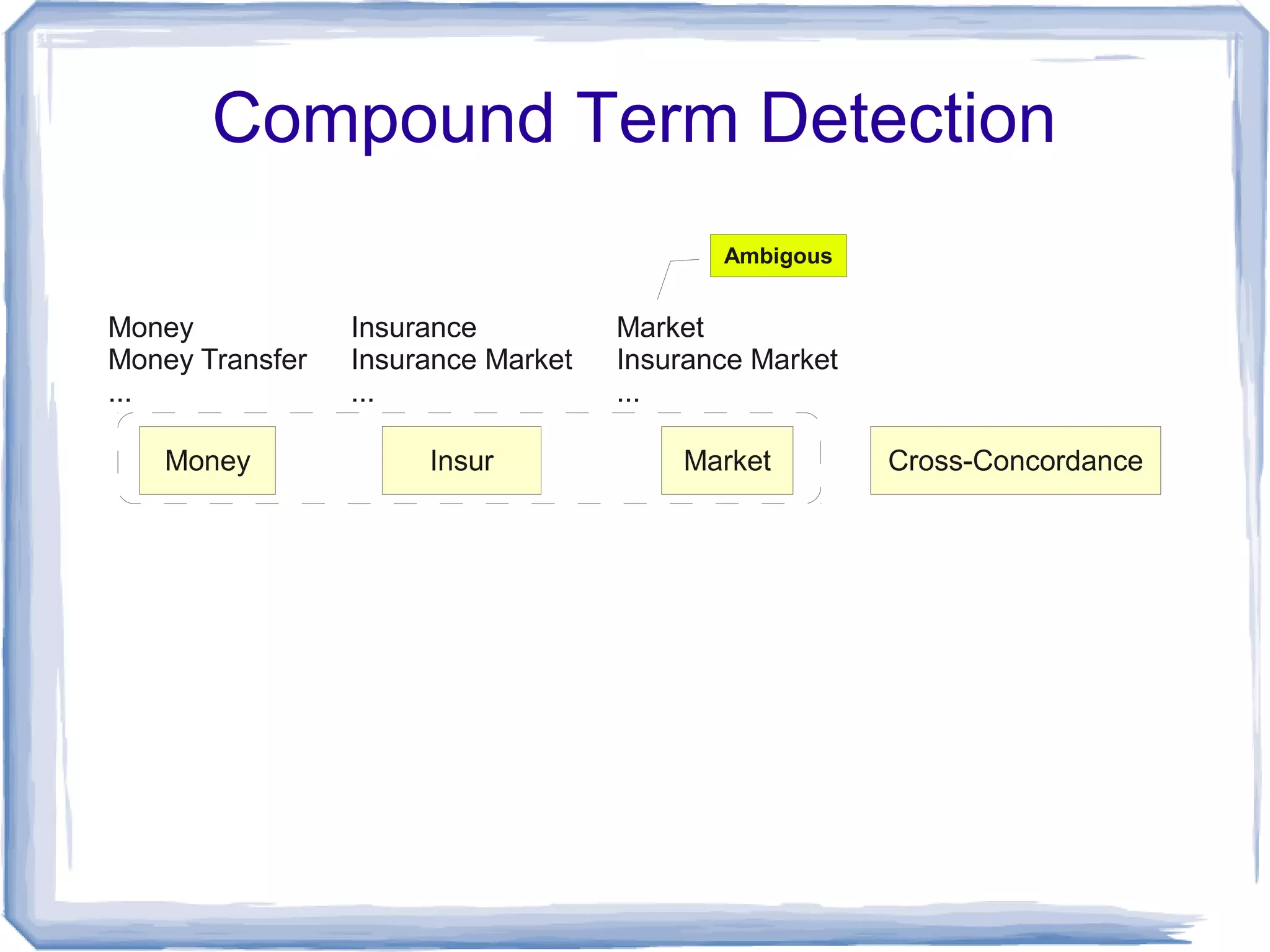
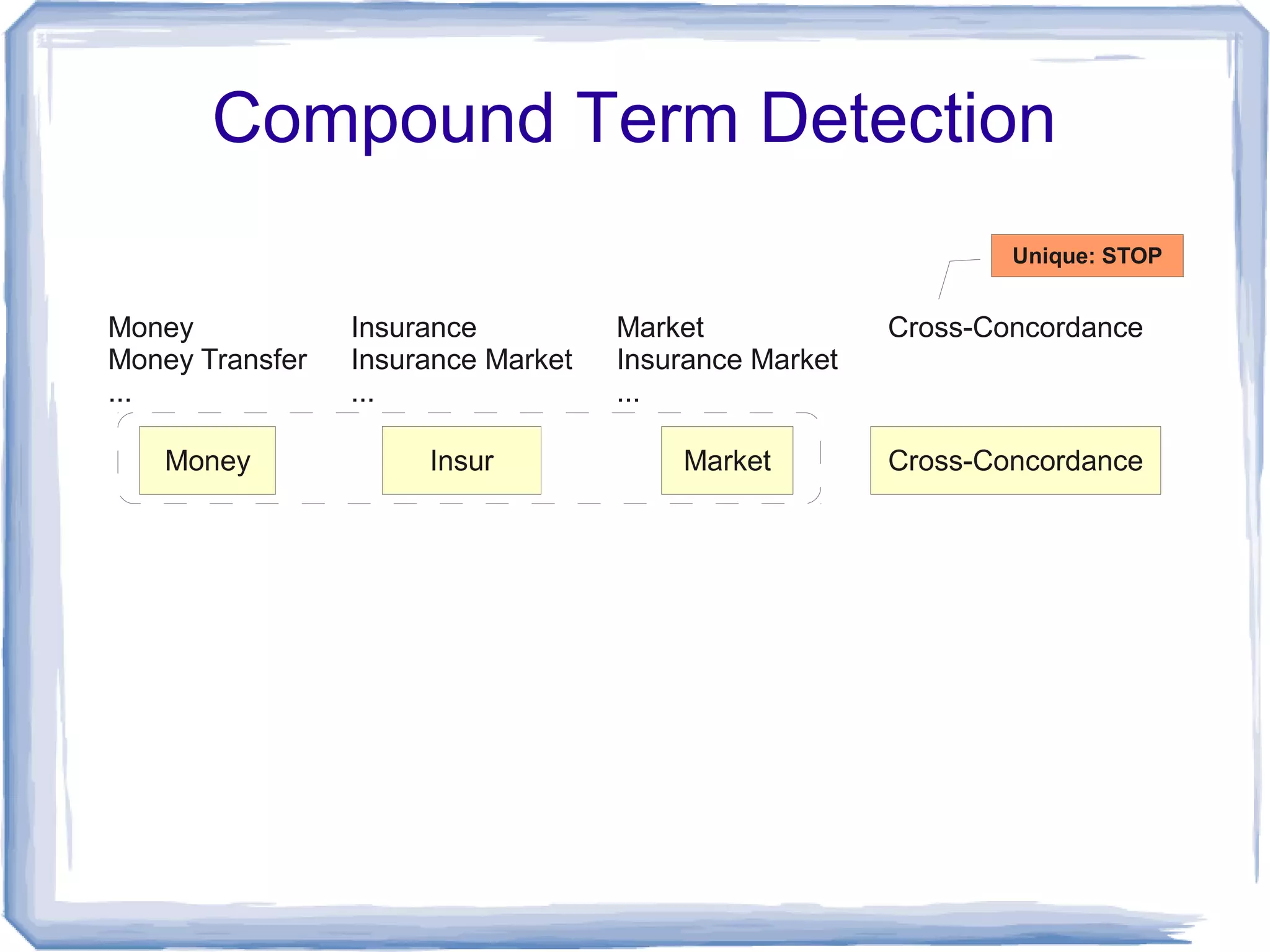
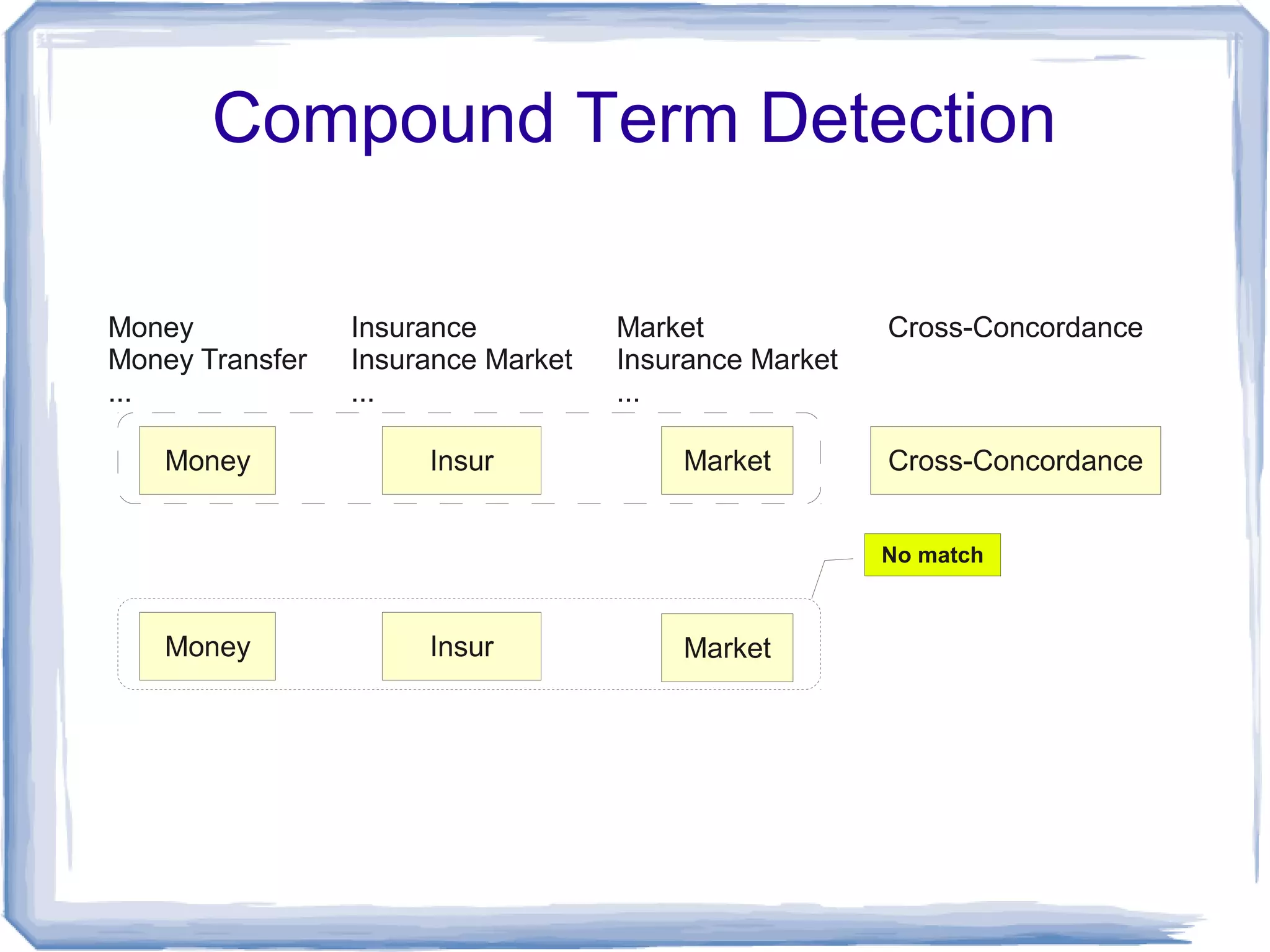
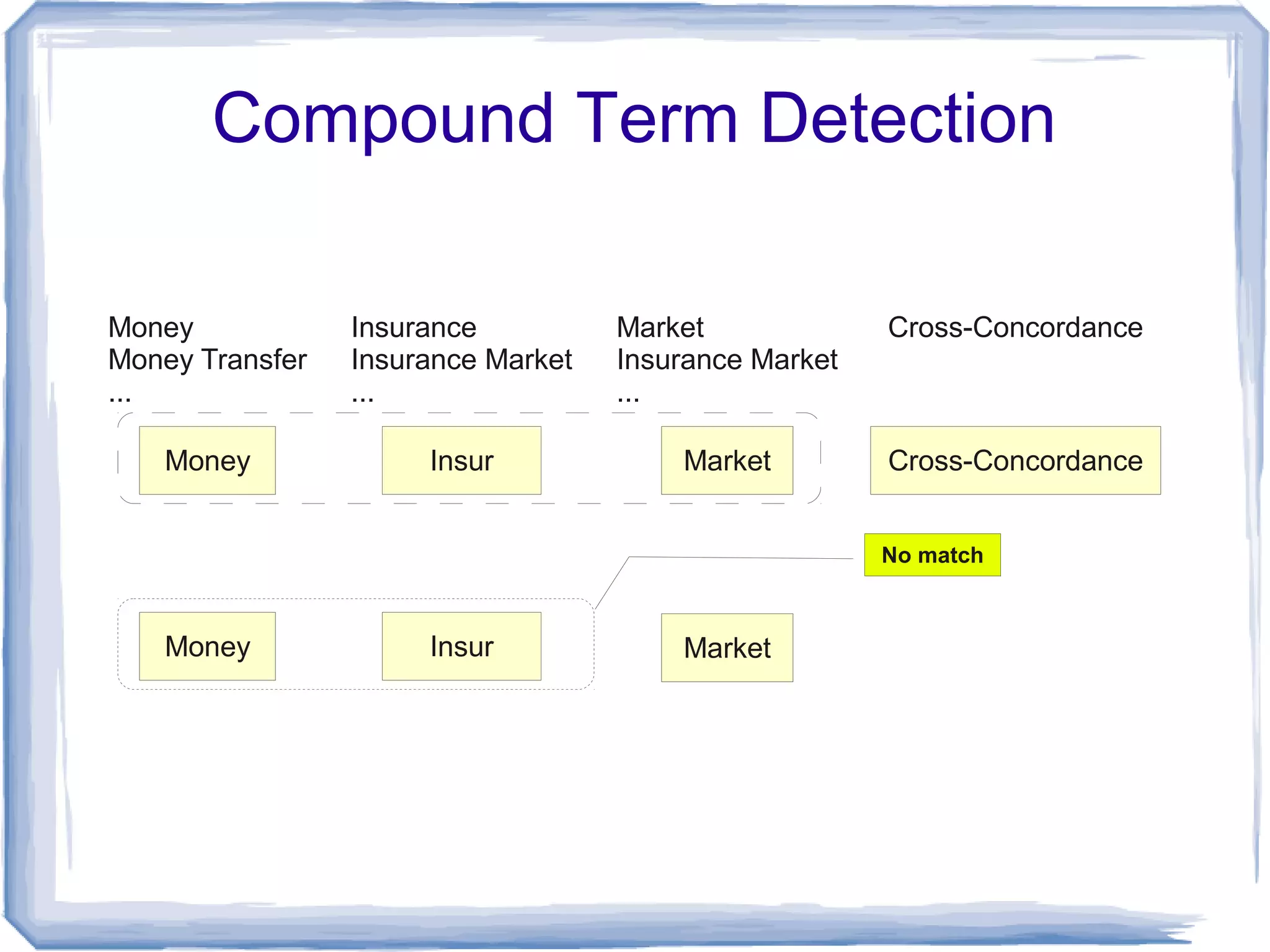
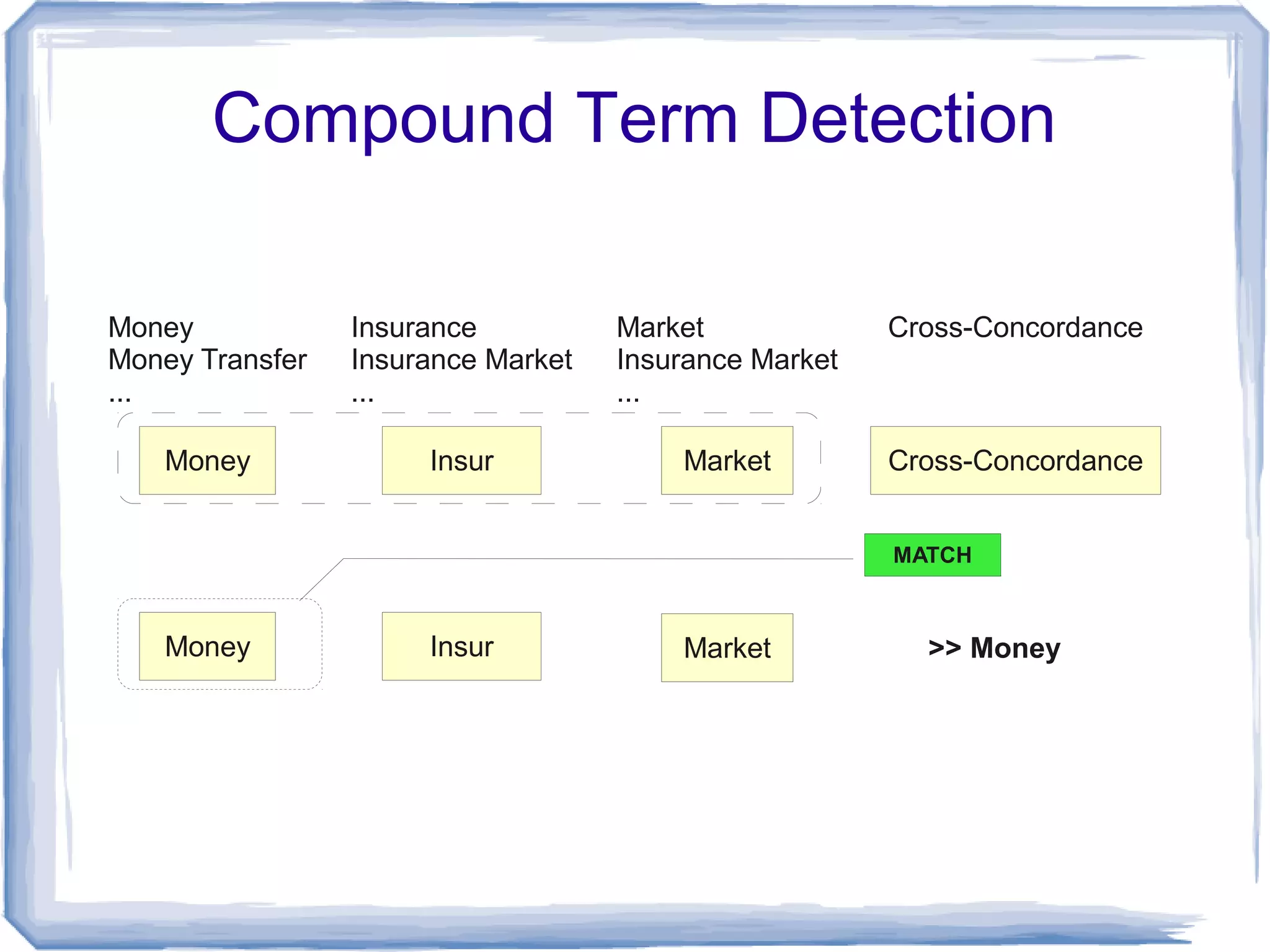
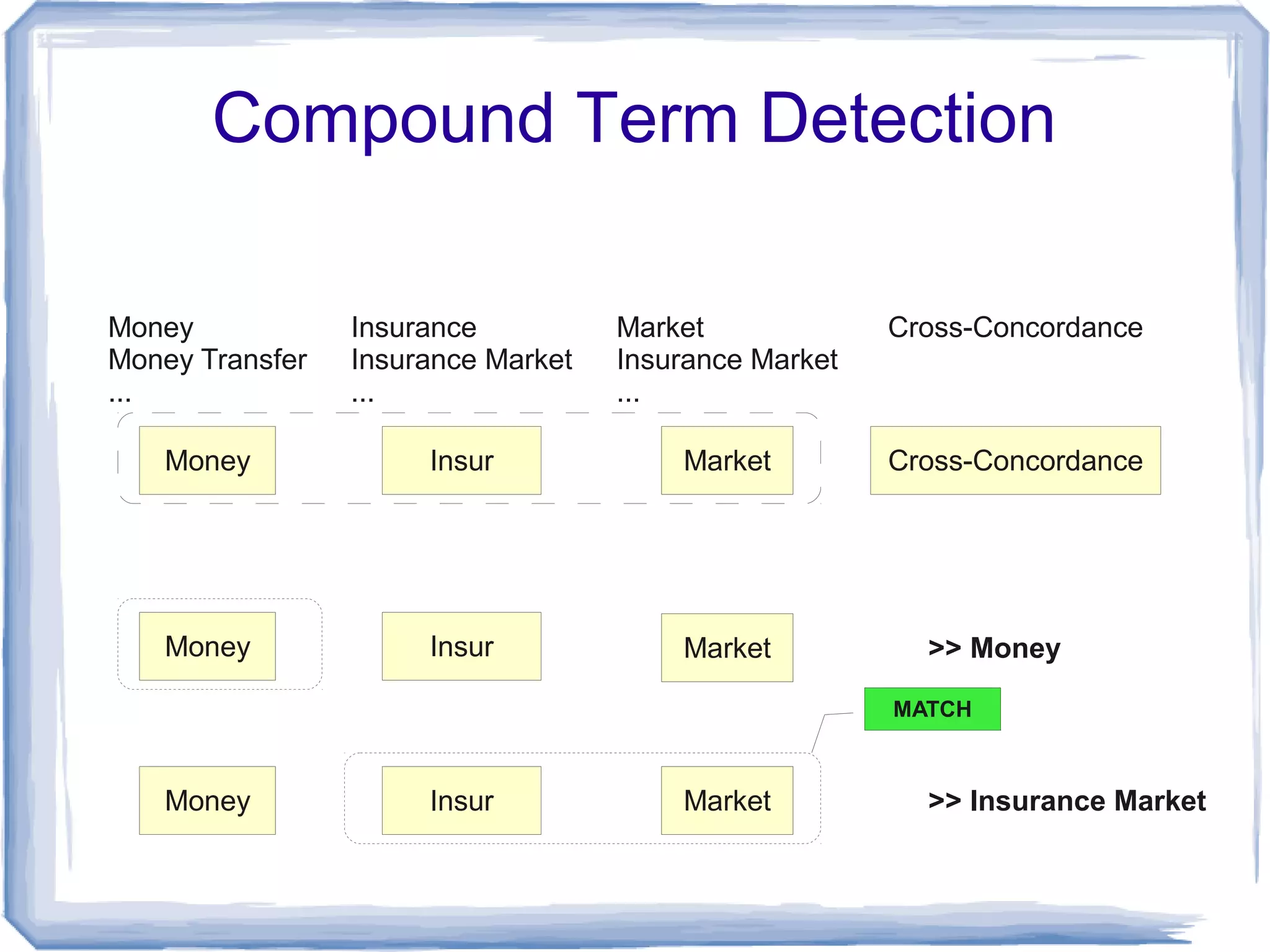
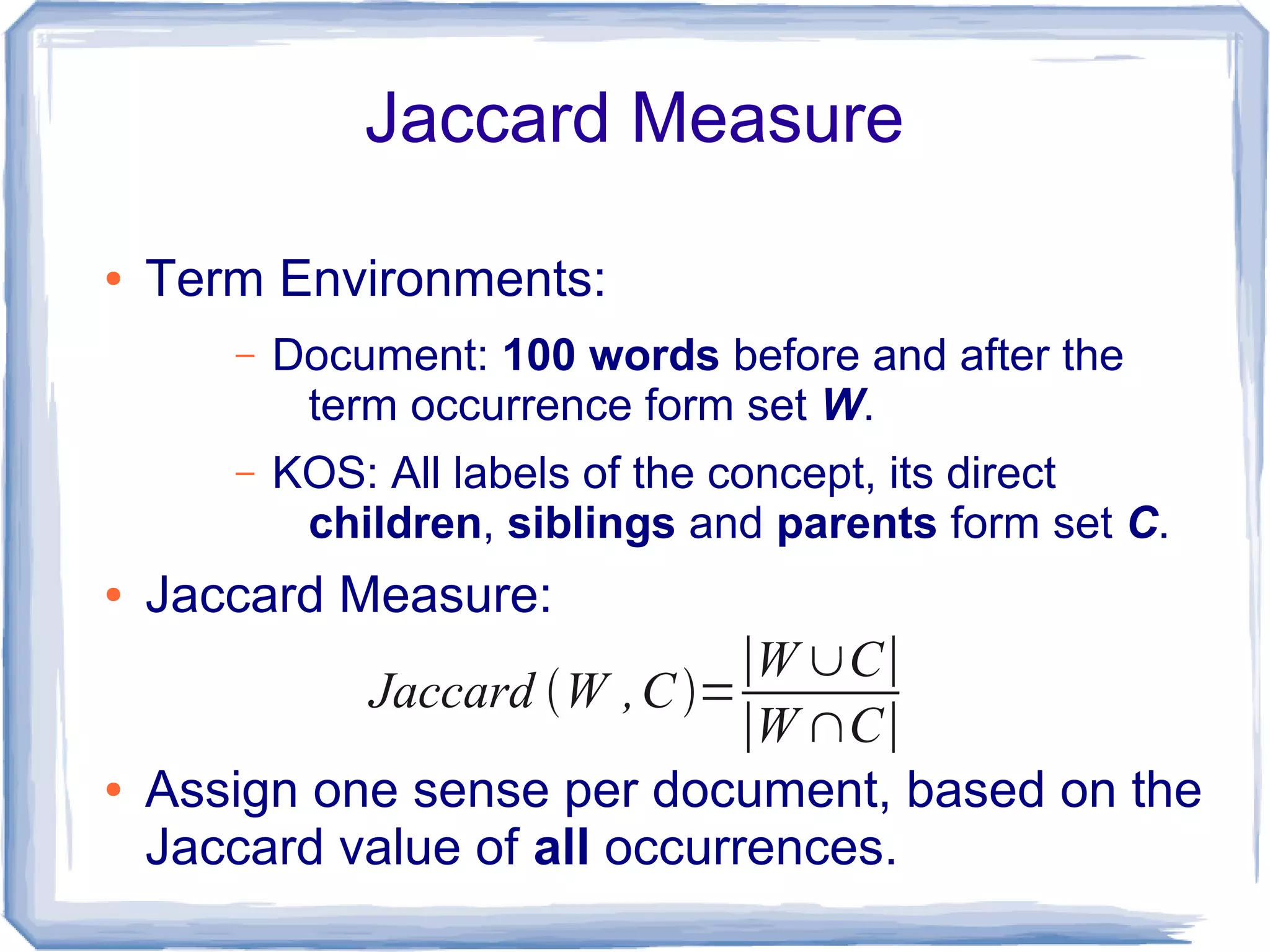
The document discusses the development of Lohai, a free and open-source automatic indexing tool designed for knowledge organization systems (KOS), which emphasizes simplicity and usability without requiring prior training or resources. It details the indexing pipeline, including challenges like disambiguation of terms, unstemming, and word sense disambiguation using Jaccard measures. The tool aims to produce reasonable indexing results while being adaptable and easy to improve, providing a baseline for KOS applications.