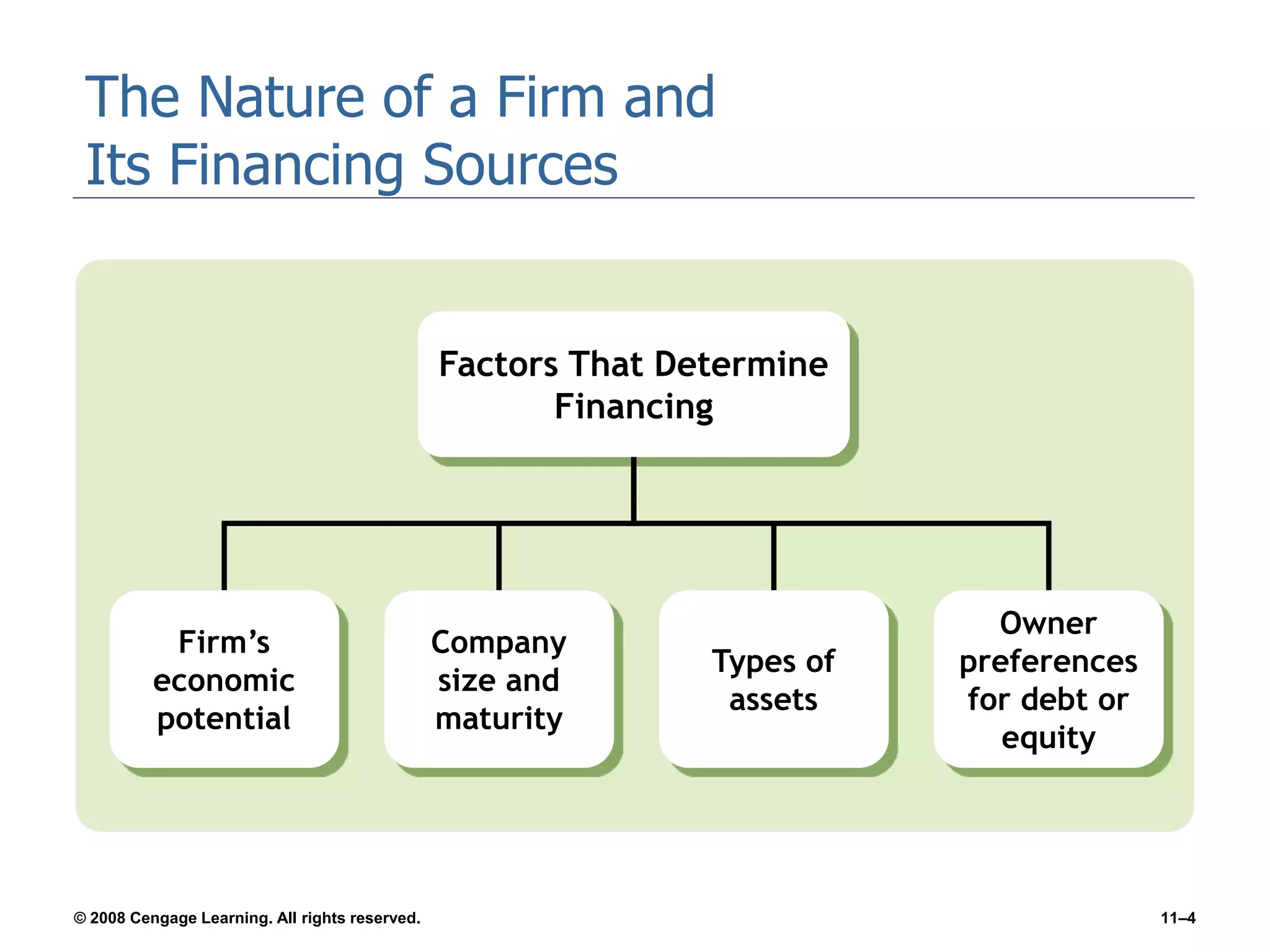
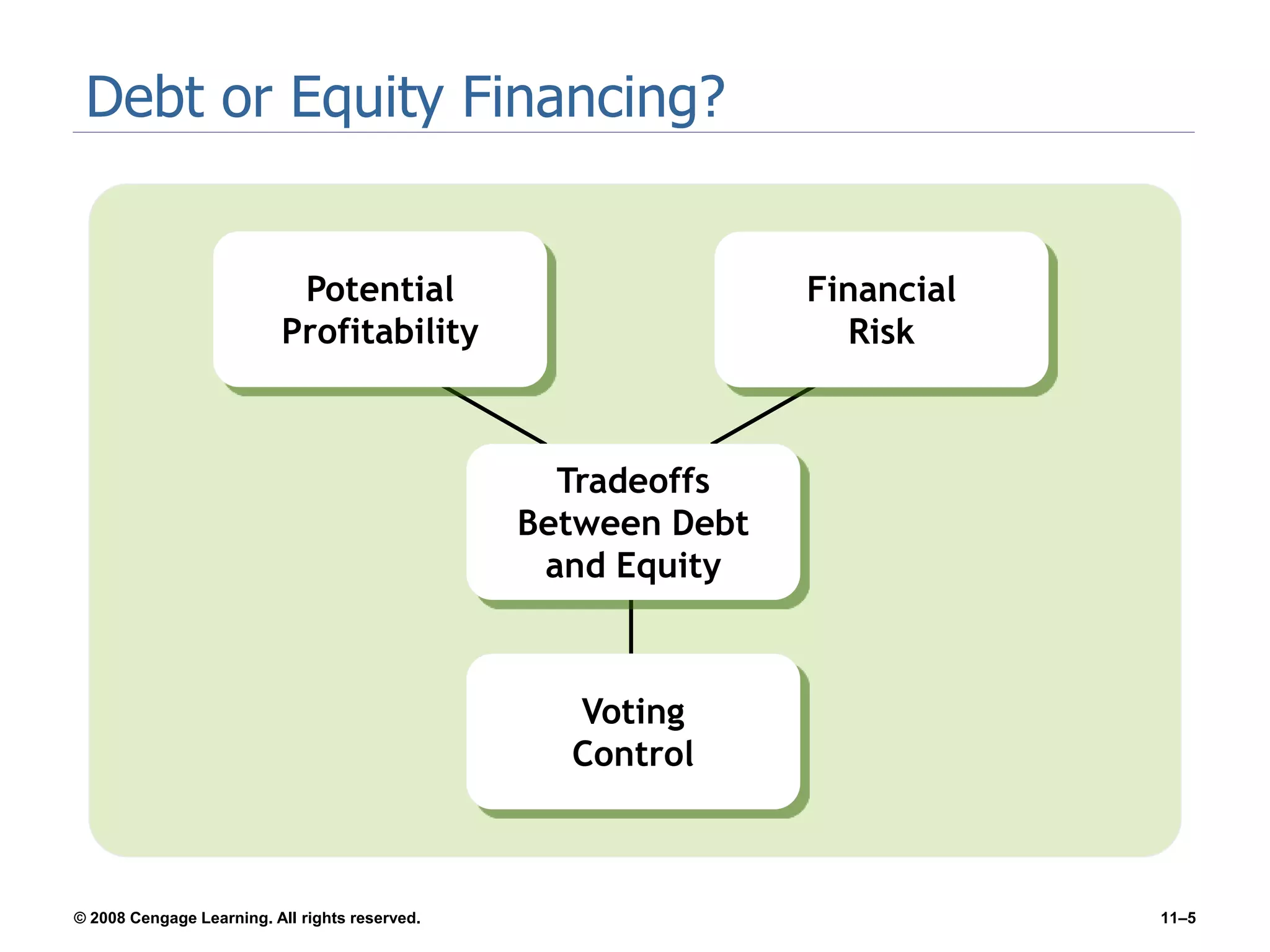
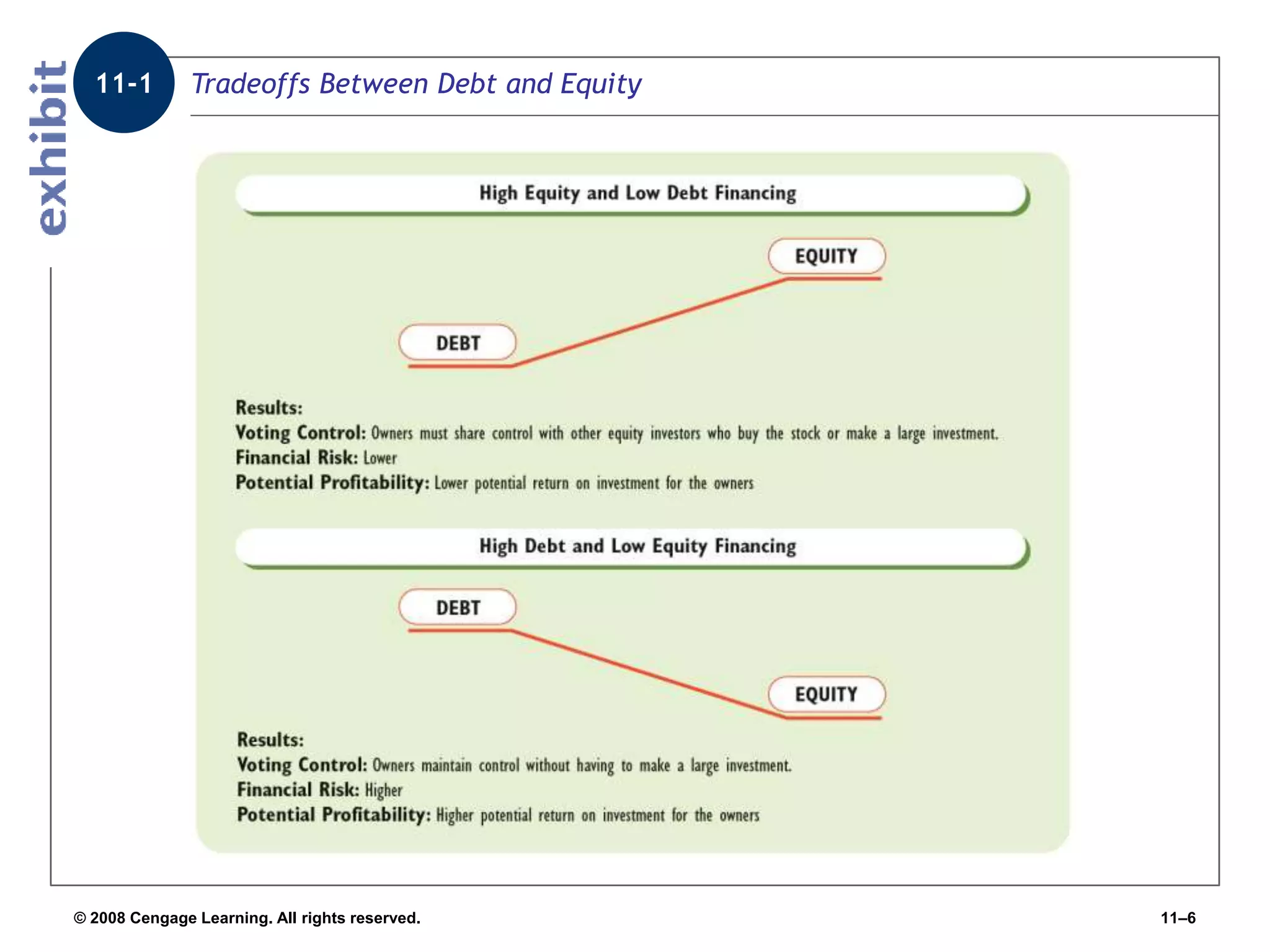
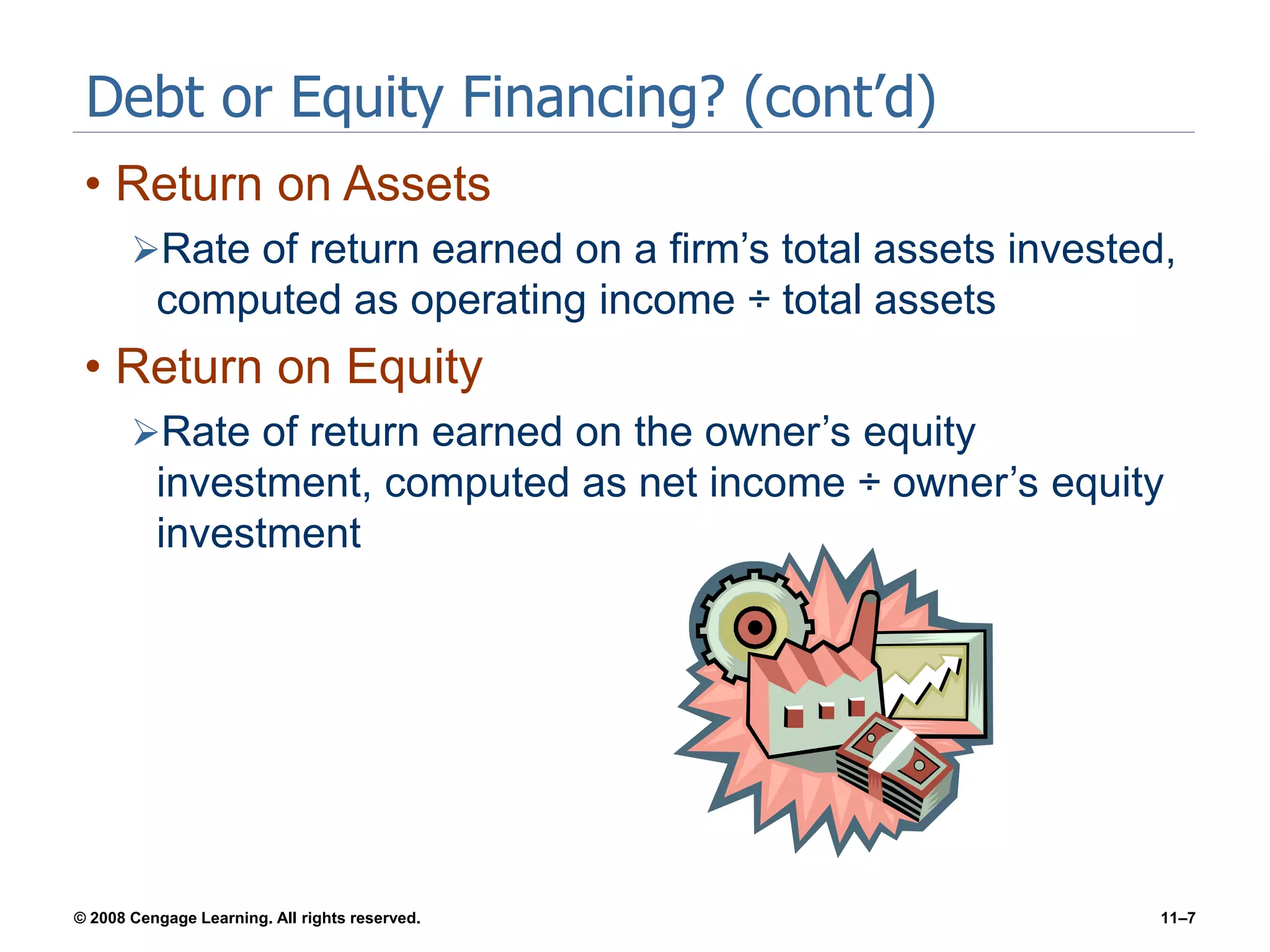
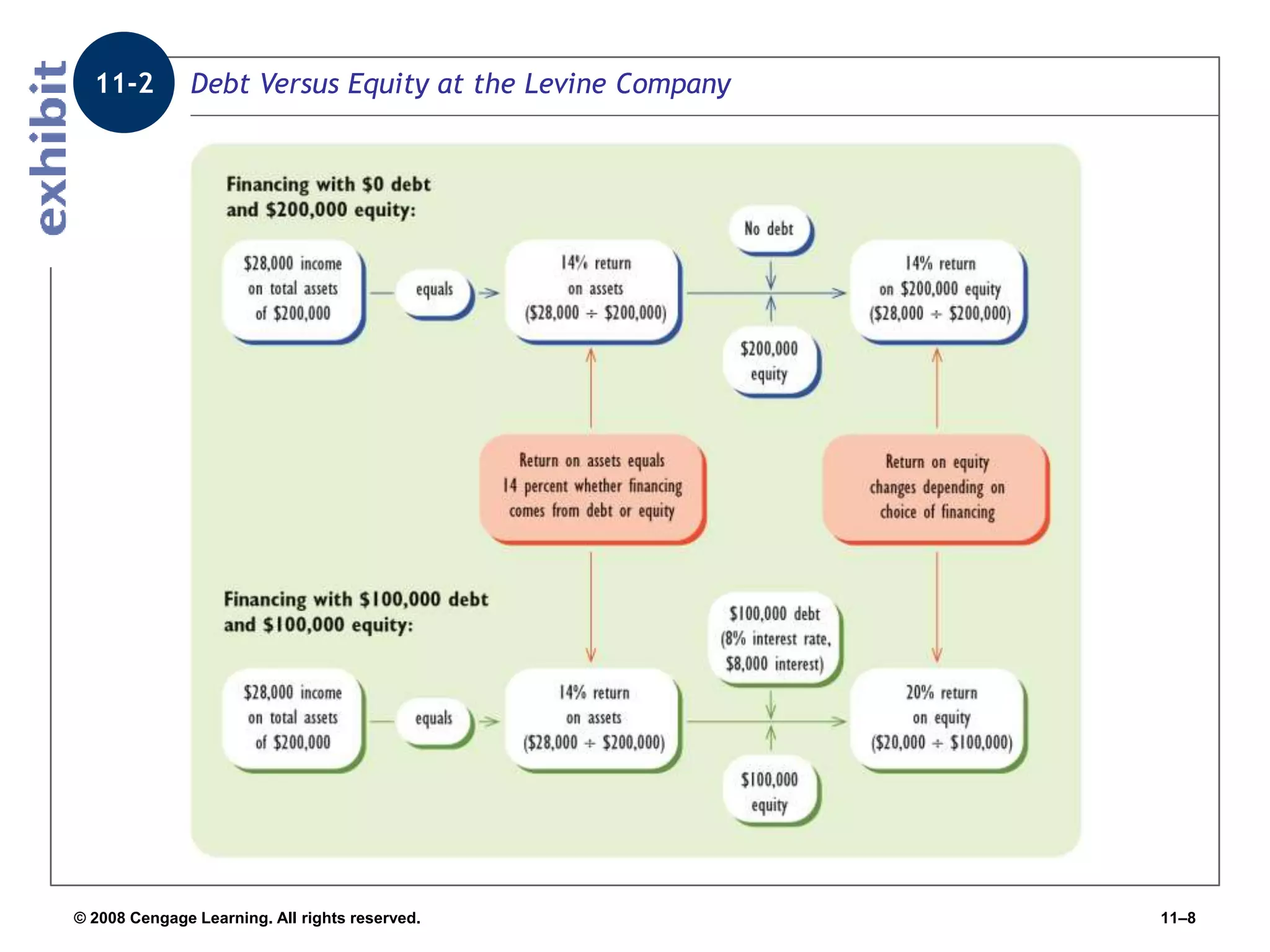
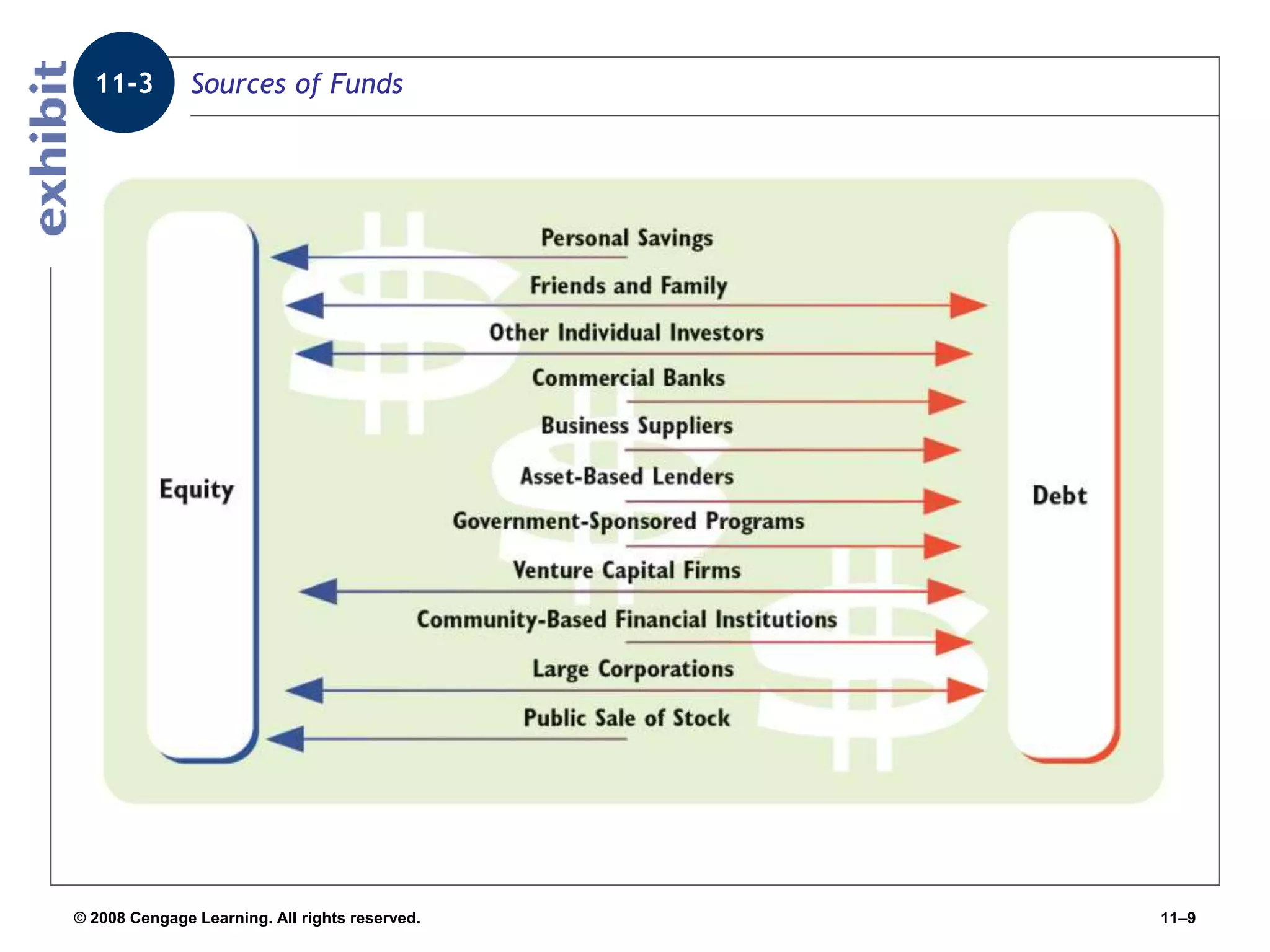
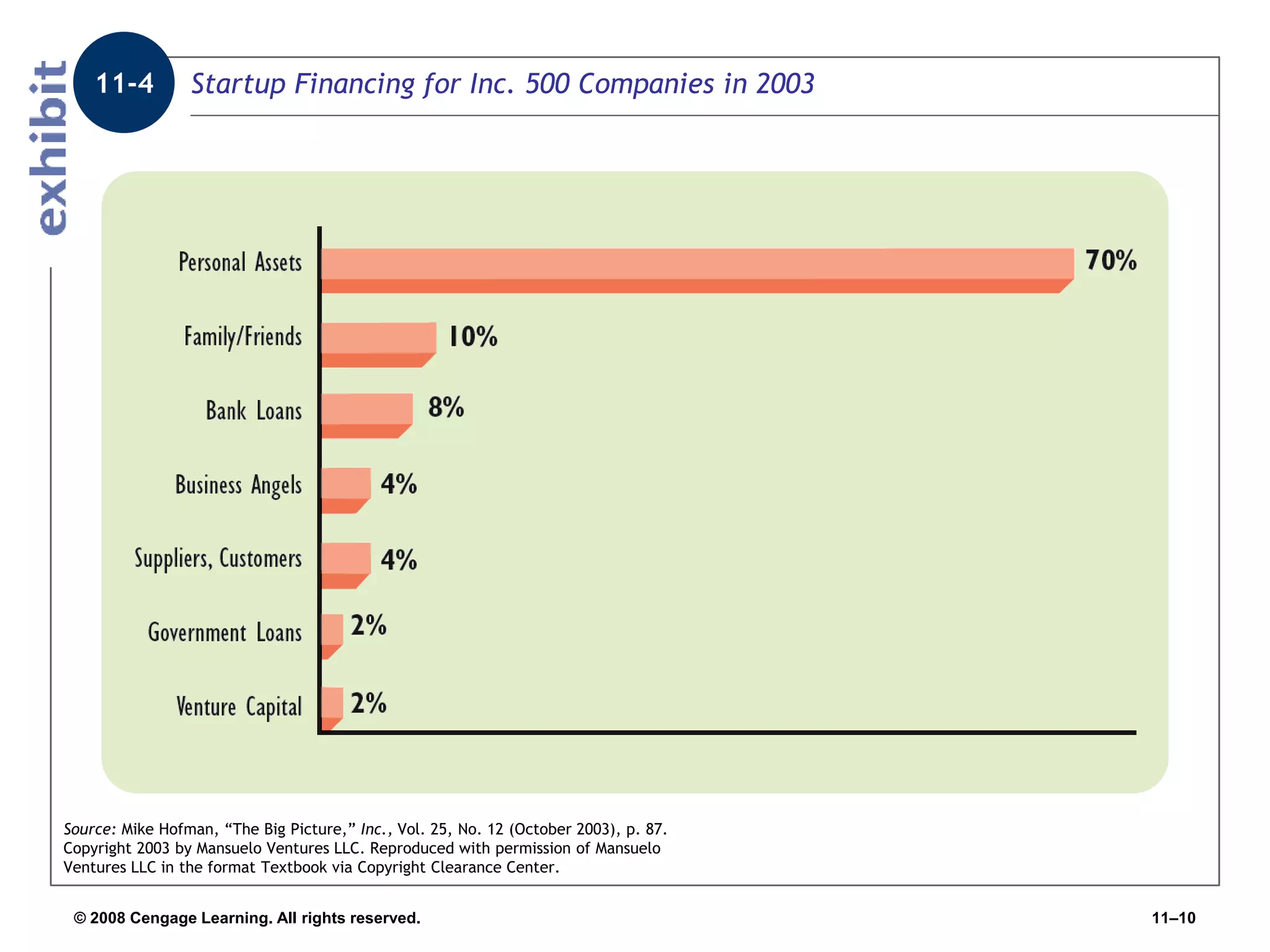
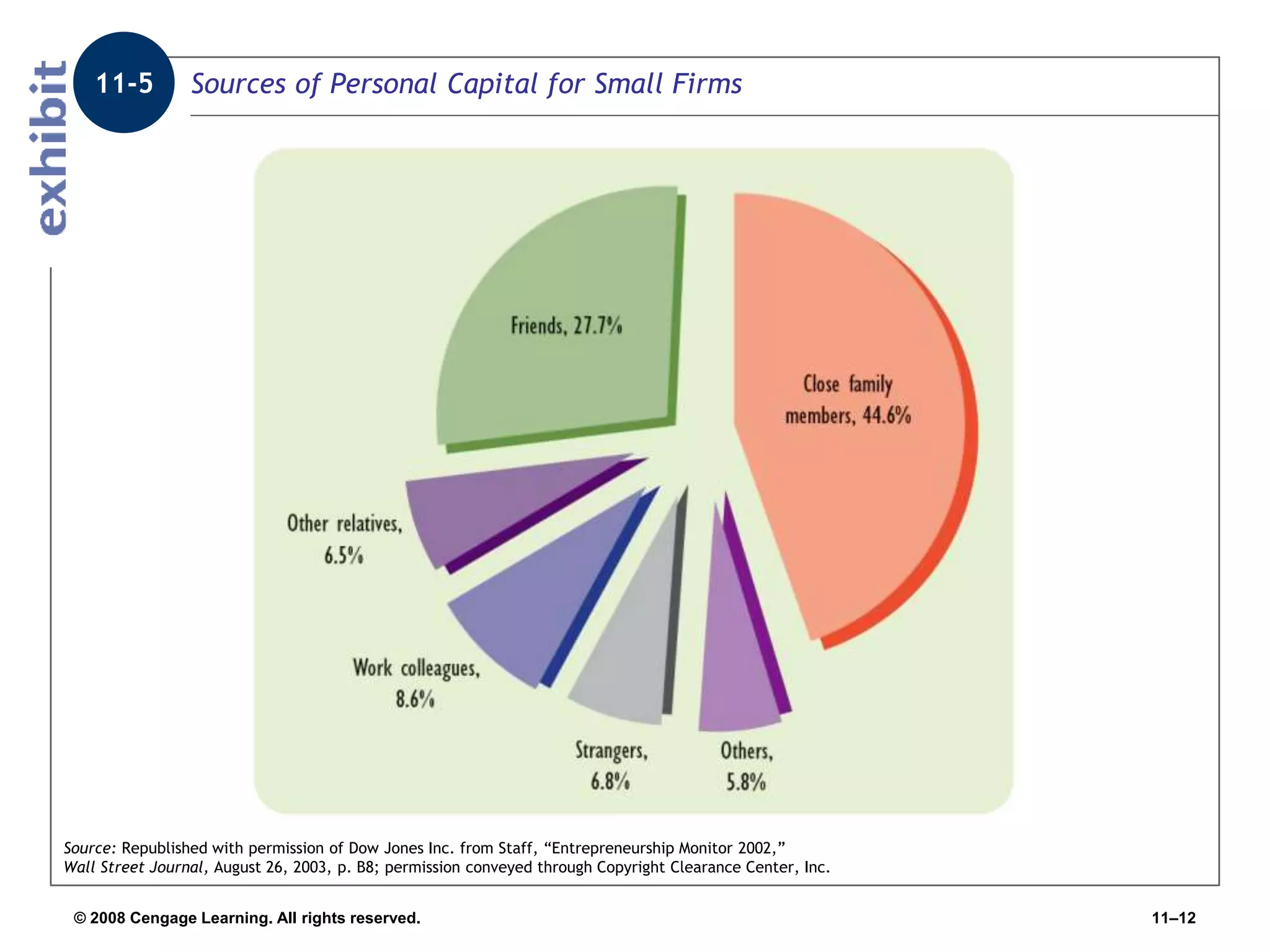
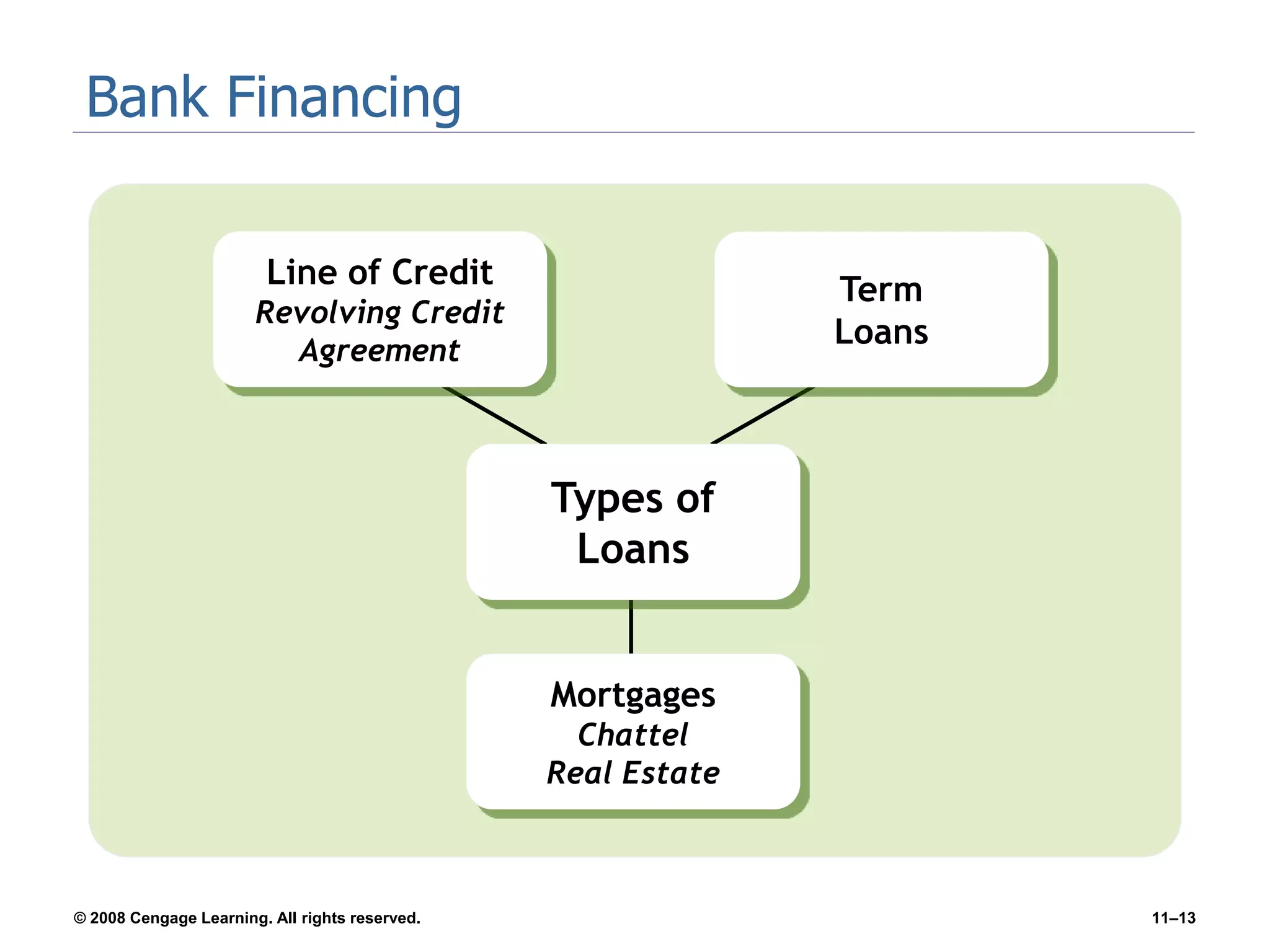
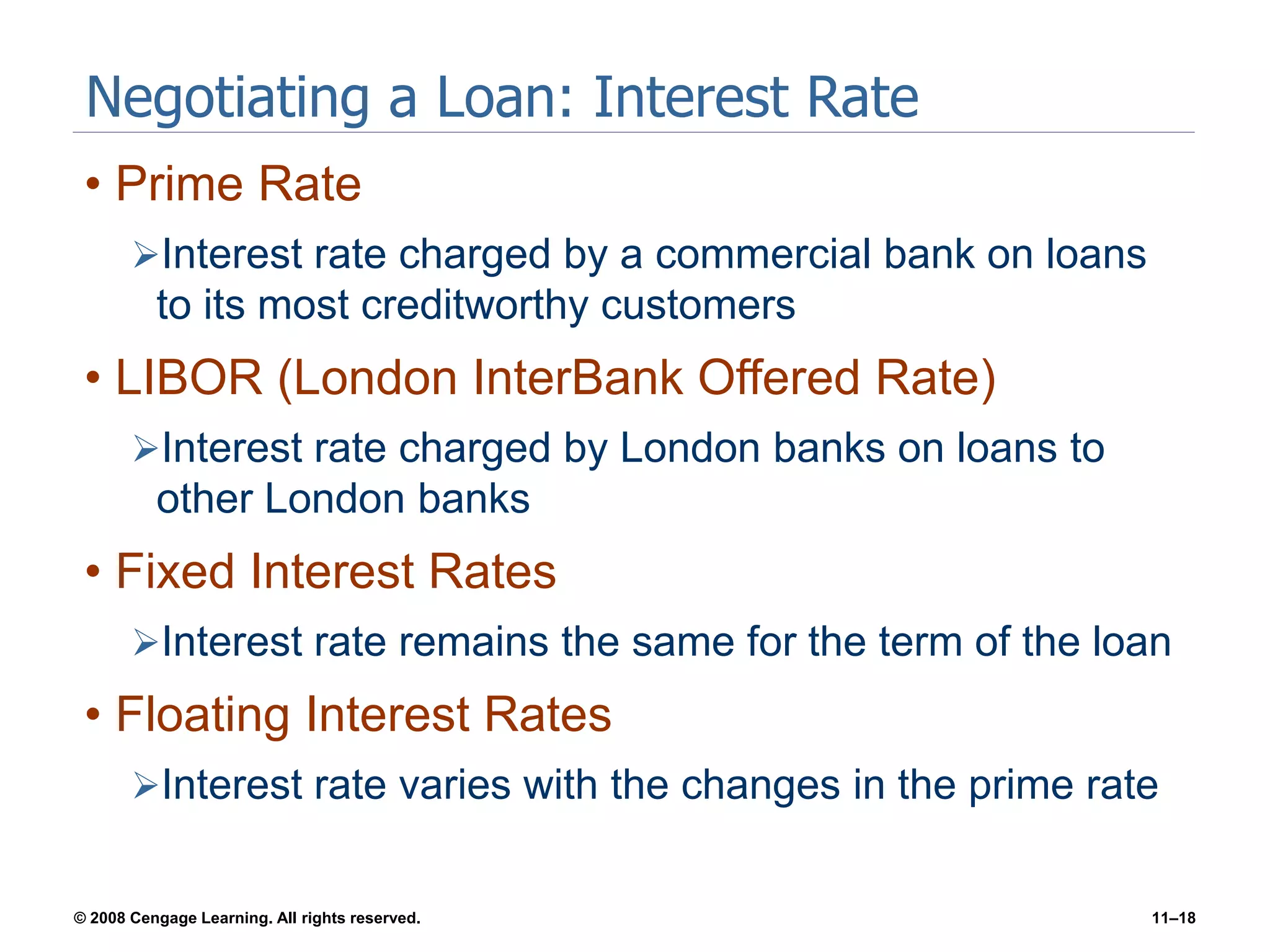
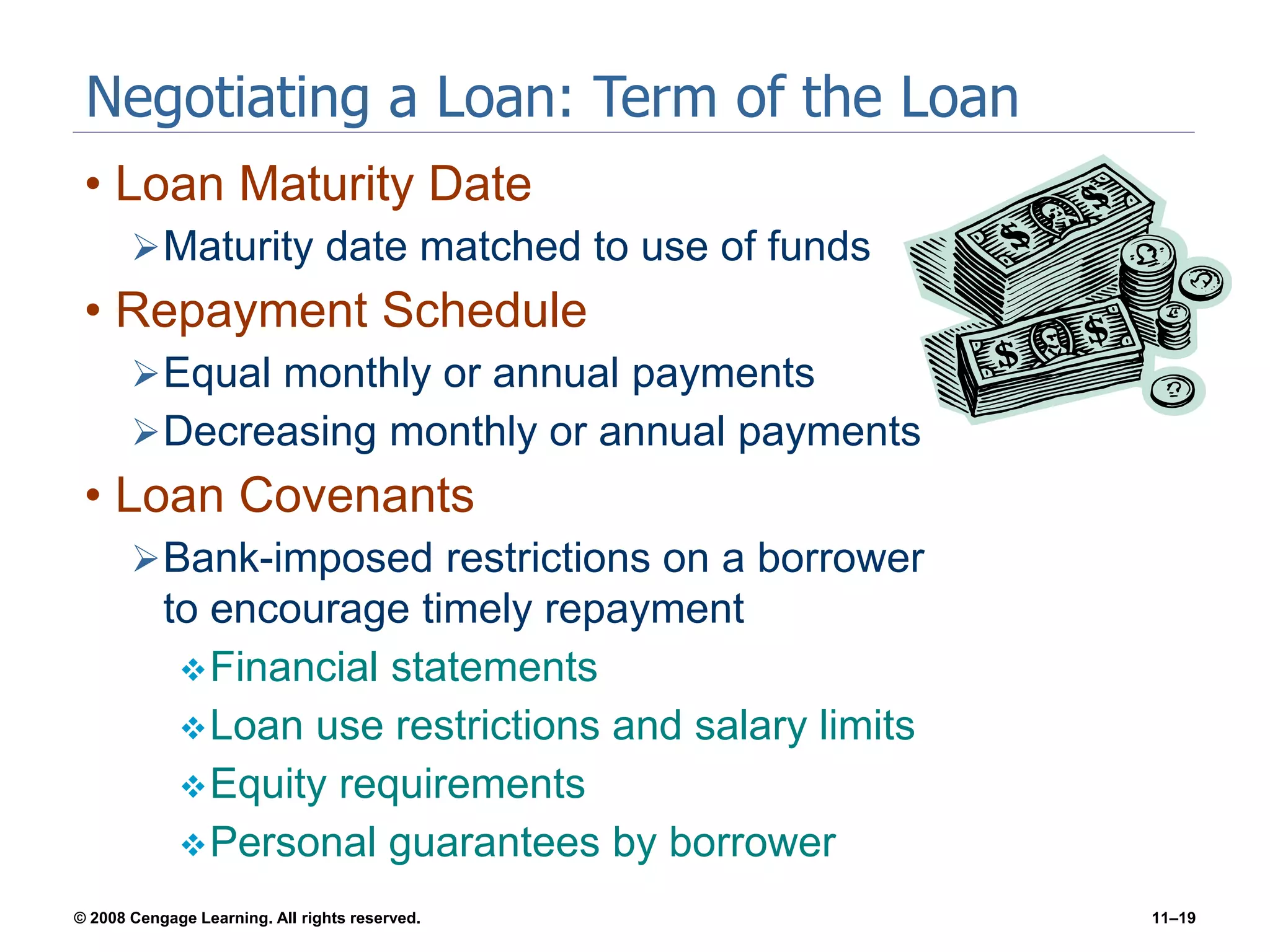
Chapter 11 explores the sources of financing for new ventures, detailing how a firm's nature, size, and maturity influence financing choices between debt and equity. It covers various funding sources, including personal savings, bank loans, private equity investors, and government programs. The chapter also highlights the critical considerations for banks when evaluating loan applications, such as the borrower's character, repayment ability, and the economic conditions affecting the venture.