1) The study examined how Florida State University students receive and perceive terrorism-related information on social media.
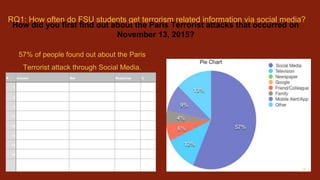
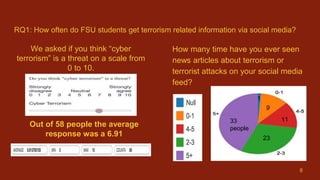
2) Surveys found that 57% of students first learned of the 2015 Paris attacks via social media, and over half see multiple news articles about terrorism on social media daily.
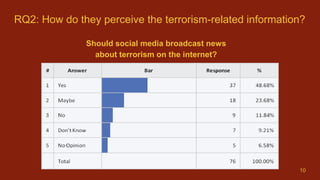
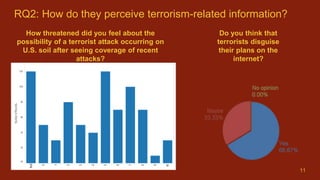
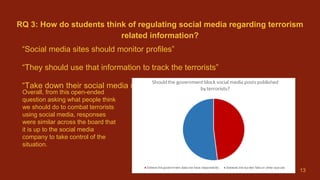
3) While many students feel uneasy about terrorists using social media, nearly half believe social media sites should broadcast terrorism news, but the government should not block related posts or profiles.