Lipids ,oils and fats uses, application global trends
•Download as PPT, PDF•
0 likes•6 views
This document discusses lipid absorption, transport, and metabolism in the human body. It covers how different types of lipids are absorbed in the small intestine and transported via lipoproteins such as chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL, and HDL to cells throughout the body. It also addresses health implications like heart disease risk and recommendations to improve LDL/HDL ratios through diet and lifestyle factors.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Lipid Disorders with Cardiac Function Tests.ppt

This document discusses various types of high cholesterol and triglyceride conditions. It describes familial hypercholesterolemia, which is caused by LDL receptor gene mutations and results in very high LDL cholesterol from childhood. It also discusses familial hypertriglyceridemia and conditions involving abnormalities in lipoprotein lipase or apolipoproteins that can cause high triglycerides. Finally, it mentions familial combined hyperlipidemia, which involves elevated levels of both cholesterol and triglycerides.
Lipid profile.pptx and chlestrol hdl vldl

The document discusses lipids and lipoproteins in the bloodstream. It explains that lipids like fatty acids, triglycerides, and cholesterol are carried in the blood by lipoproteins like chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL, and HDL. Chylomicrons carry lipids from the intestines to the liver, VLDL carries lipids from the liver to tissues, LDL carries cholesterol to tissues, and HDL carries cholesterol back to the liver. High levels of LDL and triglycerides and low levels of HDL are risk factors for atherosclerosis and heart disease. The document also provides information on lipid profiles and normal lipid levels.
Impacts of diet on serum lipid profile

This document discusses the impacts of diet on serum lipid profiles. It begins by describing normal cholesterol and triglyceride metabolism in the body. It then discusses how dietary components like saturated fats, trans fats, fiber, and cholesterol affect serum lipids. Lifestyle modifications like following a low-fat, plant-based diet pattern and engaging in regular physical activity are recommended to lower LDL cholesterol and blood pressure. Several clinical trials are summarized that show how replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats from plants lowers cardiovascular disease risk.
Lecture 1 Blood & Dietary lipids -vijayanand.pdf

Blood lipids such as cholesterol and triglycerides are influenced by diet, lifestyle, genetics and health conditions. Cholesterol is transported by lipoproteins and levels should be below 200 mg/dl. Triglyceride levels should be below 150 mg/dl. Dietary lipids come from animal sources like meat and dairy and plant sources like oils. They are broken down into fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, sterols and lipoproteins.
Lecture on oxidation of fatty acids -Vijayanand.pdf

This document discusses lipid metabolism, including the oxidation of fatty acids. It covers the carnitine shuttle that transports long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria for beta-oxidation. Blood lipids like cholesterol and triglycerides are influenced by diet and lifestyle factors. Cholesterol is transported by lipoproteins and circulates in the blood, while triglycerides provide energy between meals. Dietary lipids come from animal sources like meat and dairy, and plant sources like oils.
Fat

This document discusses fatty acid metabolism in humans. It notes that virtually all fatty acids originate from dietary triglycerides, with long-term storage occurring in adipose tissue. Upper body subcutaneous fat accounts for the majority of systemic free fatty acid release, though intra-abdominal fat correlates with higher delivery of free fatty acids to the liver. High levels of free fatty acids can lead to insulin resistance, increased triglycerides, and vascular abnormalities.
Lipids Metabolism.ppt

The document discusses lipids, including their types, functions, disorders related to deficiency or excess, and prevention of lipid disorders. It aims to determine the relationship between lipid intake and human physiology, analyze how individuals react to different lipid intakes, and identify the optimal lipid intake to prevent deficiency or excess. It describes that lipids are fats and oils, classified into fats/waxes and cholesterol/steroids. Saturated, polyunsaturated, and monounsaturated fats are outlined. Lipid functions include energy reserves, cell membrane structures, hormone synthesis, and fat-soluble vitamin absorption. Deficiency and excess can cause disorders, and optimal intake is outlined to prevent related health issues.
LIPOPROTEINS.ppt

This document discusses lipoproteins and their structure and function. It defines lipoproteins as particles made of fat droplets surrounded by a phospholipid layer, allowing fats to be transported through the bloodstream. It describes the different types of lipoproteins (chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL, HDL), their roles in transporting fats and cholesterol, and factors that affect their levels like diet and exercise. Fatty acids are also defined, and classified by saturation, cis/trans configuration, and essential/nonessential status.
Recommended
Lipid Disorders with Cardiac Function Tests.ppt

This document discusses various types of high cholesterol and triglyceride conditions. It describes familial hypercholesterolemia, which is caused by LDL receptor gene mutations and results in very high LDL cholesterol from childhood. It also discusses familial hypertriglyceridemia and conditions involving abnormalities in lipoprotein lipase or apolipoproteins that can cause high triglycerides. Finally, it mentions familial combined hyperlipidemia, which involves elevated levels of both cholesterol and triglycerides.
Lipid profile.pptx and chlestrol hdl vldl

The document discusses lipids and lipoproteins in the bloodstream. It explains that lipids like fatty acids, triglycerides, and cholesterol are carried in the blood by lipoproteins like chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL, and HDL. Chylomicrons carry lipids from the intestines to the liver, VLDL carries lipids from the liver to tissues, LDL carries cholesterol to tissues, and HDL carries cholesterol back to the liver. High levels of LDL and triglycerides and low levels of HDL are risk factors for atherosclerosis and heart disease. The document also provides information on lipid profiles and normal lipid levels.
Impacts of diet on serum lipid profile

This document discusses the impacts of diet on serum lipid profiles. It begins by describing normal cholesterol and triglyceride metabolism in the body. It then discusses how dietary components like saturated fats, trans fats, fiber, and cholesterol affect serum lipids. Lifestyle modifications like following a low-fat, plant-based diet pattern and engaging in regular physical activity are recommended to lower LDL cholesterol and blood pressure. Several clinical trials are summarized that show how replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats from plants lowers cardiovascular disease risk.
Lecture 1 Blood & Dietary lipids -vijayanand.pdf

Blood lipids such as cholesterol and triglycerides are influenced by diet, lifestyle, genetics and health conditions. Cholesterol is transported by lipoproteins and levels should be below 200 mg/dl. Triglyceride levels should be below 150 mg/dl. Dietary lipids come from animal sources like meat and dairy and plant sources like oils. They are broken down into fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, sterols and lipoproteins.
Lecture on oxidation of fatty acids -Vijayanand.pdf

This document discusses lipid metabolism, including the oxidation of fatty acids. It covers the carnitine shuttle that transports long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria for beta-oxidation. Blood lipids like cholesterol and triglycerides are influenced by diet and lifestyle factors. Cholesterol is transported by lipoproteins and circulates in the blood, while triglycerides provide energy between meals. Dietary lipids come from animal sources like meat and dairy, and plant sources like oils.
Fat

This document discusses fatty acid metabolism in humans. It notes that virtually all fatty acids originate from dietary triglycerides, with long-term storage occurring in adipose tissue. Upper body subcutaneous fat accounts for the majority of systemic free fatty acid release, though intra-abdominal fat correlates with higher delivery of free fatty acids to the liver. High levels of free fatty acids can lead to insulin resistance, increased triglycerides, and vascular abnormalities.
Lipids Metabolism.ppt

The document discusses lipids, including their types, functions, disorders related to deficiency or excess, and prevention of lipid disorders. It aims to determine the relationship between lipid intake and human physiology, analyze how individuals react to different lipid intakes, and identify the optimal lipid intake to prevent deficiency or excess. It describes that lipids are fats and oils, classified into fats/waxes and cholesterol/steroids. Saturated, polyunsaturated, and monounsaturated fats are outlined. Lipid functions include energy reserves, cell membrane structures, hormone synthesis, and fat-soluble vitamin absorption. Deficiency and excess can cause disorders, and optimal intake is outlined to prevent related health issues.
LIPOPROTEINS.ppt

This document discusses lipoproteins and their structure and function. It defines lipoproteins as particles made of fat droplets surrounded by a phospholipid layer, allowing fats to be transported through the bloodstream. It describes the different types of lipoproteins (chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL, HDL), their roles in transporting fats and cholesterol, and factors that affect their levels like diet and exercise. Fatty acids are also defined, and classified by saturation, cis/trans configuration, and essential/nonessential status.
Lipopprotein by kk sahu

Lipoproteins are biochemical assemblies of proteins and lipids that transport lipids through the bloodstream. They consist of a hydrophobic core of lipids surrounded by a membrane containing phospholipids, free cholesterol, and apolipoproteins. Lipoproteins are classified based on density into chylomicrons, VLDL, IDL, LDL, and HDL. Chylomicrons and VLDL carry triglycerides from the intestine and liver to tissues, while HDL and LDL transport cholesterol. High LDL and low HDL levels increase the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease. A balanced diet high in fish, nuts, and fiber can lower LDL and raise HDL to reduce disease risk.
Lipids in the blood

This document discusses lipid profile testing and the determination of various lipids in the blood, including total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and others. It provides information on the clinical significance and normal ranges of each lipid, as well as methods for estimating and measuring the different lipids. Key points covered include the importance of cholesterol for various body functions but that too much can lead to health issues; sources of cholesterol from the body and diet; and the relationships between HDL, LDL, and risk for coronary artery disease.
Macronutrients and fuel

The document discusses macronutrients and their role as fuels for exercise. It covers carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and their subtypes. Carbohydrates like glucose, glycogen, and fiber are important fuels for exercise. Lipids provide energy and aid temperature regulation. Protein aids in tissue repair and building. The document outlines the roles, food sources, and intake recommendations for each macronutrient class.
Nutritional importance of fats

Describes different types of fats in human body and their functions. The dietary sources are also discussed.
Update in Dyslipidemias

This document discusses the evaluation and management of dyslipidemias. It begins by defining different types of lipids and their functions. It then evaluates cardiovascular risk scores and current lifestyle modification guidelines. The document reviews the 2013 AHA/ACC guidelines for dyslipidemia management and evaluates pharmacologic treatment options, including statins, ezetimibe, fibrates, niacin, and omega-3 fatty acids. It concludes by outlining recommendations for when to initiate statin therapy or add additional pharmacologic treatment based on a patient's lipid panel and risk factors.
HYPERLIPIDEMIA

The high risks of lipids and its relevance towards the development of different cardiovascular diseases has been known to all where this present slide focuses on that only along with the different treatment procedures,.
Lipid metabolism

Lipoprotein metabolism and disorders
The document discusses lipoprotein metabolism and related disorders. It describes how lipoproteins transport lipids in the bloodstream, including their classification based on density and composition. The metabolism of chylomicrons and very low density lipoproteins is summarized, including the roles of apolipoproteins and lipoprotein lipase. Disorders involving abnormal high or low levels of lipoproteins are described, such as familial hypercholesterolemia and Tangier disease. Fatty liver and impaired lipoprotein synthesis can also disrupt lipid transport.
Sports Nutrition

This document provides information on carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. It begins by explaining the caloric content of carbohydrates and dividing them into simple and complex categories. It then discusses the digestion and metabolism of carbohydrates in the body. For proteins, it describes their structure and function, as well as complete and incomplete protein sources. It outlines protein digestion, synthesis, and recommendations. Finally, it discusses lipids and fatty acids, cholesterol, and fat digestion. It provides an overview of fat metabolism and storage and concludes with general fat recommendations and the relationship between fat and health.
Carbohydrates, Fats and Proteins.ppt

This document provides an overview of macronutrients and their roles in nutrition. It discusses the three main classes of macronutrients that provide energy - carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are broken down into their subcategories and the key roles and functions of each are described. Sources of the different macronutrients and micronutrients like vitamins and minerals are also identified. The document aims to educate on the different food groups and nutrients required for health and their relevance to the human body.
Presentation on lipid

This document summarizes lipids that are important physiologically and their roles in health and disease. It discusses major lipids like fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, sterols, and lipoproteins. Specific fatty acids like saturated, unsaturated, omega-3 and omega-6 are explained. The roles of lipids in brain development, cancer prevention and various lipid-related disorders are highlighted. Atherosclerosis and its pathological progression are also diagrammatically represented.
Hyperlipidaemia.

- There are two essential fatty acids that humans must obtain from their diet: alpha-linolenic acid (ALA, an omega-3 fatty acid) and linoleic acid (LA, an omega-6 fatty acid).
- Good plant-based sources of ALA include chia seeds, flaxseeds, walnuts, canola oil, and walnut oil. While LA is more abundant and found in many plant foods like nuts and seeds.
- These essential fatty acids are polyunsaturated and cannot be made by the body, but they are important for metabolic processes and converting into longer chain omega-3s like EPA and DHA.
Hyperlipidemia 

The seminar covered the management of hyperlipidemia. It discussed the story of lipids in the body and how chylomicrons, LDL, and HDL transport lipids. High LDL and oxidized LDL can lead to atherosclerosis while HDL removes cholesterol from plaque. Causes of hyperlipidemia include diet, medical conditions, and genetic factors. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications, medical nutrition therapy, and pharmacological options like statins. The goals are to lower LDL, total cholesterol, and triglycerides while raising HDL.
HDL 

This document discusses lipoproteins and lipid profiles. It describes the different types of lipoproteins including HDL, LDL, VLDL, and chylomicrons. HDL is described as "good cholesterol" that removes cholesterol from the body, while LDL is described as "bad cholesterol" that deposits cholesterol in tissues and increases disease risk. Normal ranges for HDL and LDL are provided. Factors that influence lipid profiles like smoking, alcohol, medications, and medical conditions are also summarized.
02 nutrition

The document discusses various topics related to nutrition including macromolecules that provide energy like proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. It describes the roles of the liver, vitamins, minerals, and enzymes in breaking down nutrients. Specific carbohydrates like monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides are defined. The document also covers protein structure, fat types, cholesterol, blood sugar regulation, energy requirements, metabolic rate, and eating disorders like anorexia and bulimia.
NUTRITION-2.ppt

DR VISHNU KUMAR
PROFESSOR AND HOD BIOCHEMISTRY, MADHAV PRASAD TRIPATHI GOVERNMENT MEDICAL COLLEGE, SIDDHARTH NAGAR, UTTAR PRADESH.
Lipoprotiens

Understand the structures of various lipoproteins. Understand the role of lipoproteins in cholesterol metabolism
Omega 3 juice for hyperlipidemia & essential elements for pregnancy

Kapidex Juice provides a concise summary of lipids, lipoproteins, and dyslipidemia. It discusses the medical background of lipids and their functions. The document outlines the four principal types of lipoproteins, their compositions, and contributions to total plasma cholesterol. It also defines dyslipidemia and discusses primary and secondary causes. Finally, the document provides details about Kapidex Juice, including its active ingredients and their benefits for lowering triglycerides and reducing cardiovascular risk.
Sheq foundation health promotion 

This document provides a summary of topics covered in a health improvement program, including diabetes, hypertension, cholesterol, eating habits, and sexually transmitted diseases. It focuses on defining and describing diabetes, including the different types of diabetes, causes and treatments. It also discusses cholesterol levels and factors that affect cholesterol. Hypertension is defined as high blood pressure and risks of untreated hypertension are outlined. The goal of the program is to improve health through addressing these key health topics.
快速办理(Adelaide毕业证书)阿德莱德大学毕业证文凭证书一模一样

学校原件一模一样【微信:741003700 】《(Adelaide毕业证书)阿德莱德大学毕业证文凭证书》【微信:741003700 】学位证,留信认证(真实可查,永久存档)原件一模一样纸张工艺/offer、雅思、外壳等材料/诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本,帮您解决无法毕业带来的各种难题!外壳,原版制作,诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本。行业标杆!精益求精,诚心合作,真诚制作!多年品质 ,按需精细制作,24小时接单,全套进口原装设备。十五年致力于帮助留学生解决难题,包您满意。
本公司拥有海外各大学样板无数,能完美还原。
1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。材料咨询办理、认证咨询办理请加学历顾问Q/微741003700
【主营项目】
一.毕业证【q微741003700】成绩单、使馆认证、教育部认证、雅思托福成绩单、学生卡等!
二.真实使馆公证(即留学回国人员证明,不成功不收费)
三.真实教育部学历学位认证(教育部存档!教育部留服网站永久可查)
四.办理各国各大学文凭(一对一专业服务,可全程监控跟踪进度)
如果您处于以下几种情况:
◇在校期间,因各种原因未能顺利毕业……拿不到官方毕业证【q/微741003700】
◇面对父母的压力,希望尽快拿到;
◇不清楚认证流程以及材料该如何准备;
◇回国时间很长,忘记办理;
◇回国马上就要找工作,办给用人单位看;
◇企事业单位必须要求办理的
◇需要报考公务员、购买免税车、落转户口
◇申请留学生创业基金
留信网认证的作用:
1:该专业认证可证明留学生真实身份
2:同时对留学生所学专业登记给予评定
3:国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书
4:这个认证书并且可以归档倒地方
5:凡事获得留信网入网的信息将会逐步更新到个人身份内,将在公安局网内查询个人身份证信息后,同步读取人才网入库信息
6:个人职称评审加20分
7:个人信誉贷款加10分
8:在国家人才网主办的国家网络招聘大会中纳入资料,供国家高端企业选择人才
Heritage Conservation.Strategies and Options for Preserving India Heritage

Presentation looks at the role , relevance and importance of built and natural heritage, issues faced by heritage in the Indian context and options which can be leveraged to preserve and conserve the heritage.It also lists the challenges faced by the heritage due to rapid urbanisation, land speculation and commercialisation in the urban areas. In addition, ppt lays down the roadmap for the preservation, conservation and making value addition to the available heritage by making it integral part of the planning , designing and management of the human settlements.
More Related Content
Similar to Lipids ,oils and fats uses, application global trends
Lipopprotein by kk sahu

Lipoproteins are biochemical assemblies of proteins and lipids that transport lipids through the bloodstream. They consist of a hydrophobic core of lipids surrounded by a membrane containing phospholipids, free cholesterol, and apolipoproteins. Lipoproteins are classified based on density into chylomicrons, VLDL, IDL, LDL, and HDL. Chylomicrons and VLDL carry triglycerides from the intestine and liver to tissues, while HDL and LDL transport cholesterol. High LDL and low HDL levels increase the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease. A balanced diet high in fish, nuts, and fiber can lower LDL and raise HDL to reduce disease risk.
Lipids in the blood

This document discusses lipid profile testing and the determination of various lipids in the blood, including total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and others. It provides information on the clinical significance and normal ranges of each lipid, as well as methods for estimating and measuring the different lipids. Key points covered include the importance of cholesterol for various body functions but that too much can lead to health issues; sources of cholesterol from the body and diet; and the relationships between HDL, LDL, and risk for coronary artery disease.
Macronutrients and fuel

The document discusses macronutrients and their role as fuels for exercise. It covers carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and their subtypes. Carbohydrates like glucose, glycogen, and fiber are important fuels for exercise. Lipids provide energy and aid temperature regulation. Protein aids in tissue repair and building. The document outlines the roles, food sources, and intake recommendations for each macronutrient class.
Nutritional importance of fats

Describes different types of fats in human body and their functions. The dietary sources are also discussed.
Update in Dyslipidemias

This document discusses the evaluation and management of dyslipidemias. It begins by defining different types of lipids and their functions. It then evaluates cardiovascular risk scores and current lifestyle modification guidelines. The document reviews the 2013 AHA/ACC guidelines for dyslipidemia management and evaluates pharmacologic treatment options, including statins, ezetimibe, fibrates, niacin, and omega-3 fatty acids. It concludes by outlining recommendations for when to initiate statin therapy or add additional pharmacologic treatment based on a patient's lipid panel and risk factors.
HYPERLIPIDEMIA

The high risks of lipids and its relevance towards the development of different cardiovascular diseases has been known to all where this present slide focuses on that only along with the different treatment procedures,.
Lipid metabolism

Lipoprotein metabolism and disorders
The document discusses lipoprotein metabolism and related disorders. It describes how lipoproteins transport lipids in the bloodstream, including their classification based on density and composition. The metabolism of chylomicrons and very low density lipoproteins is summarized, including the roles of apolipoproteins and lipoprotein lipase. Disorders involving abnormal high or low levels of lipoproteins are described, such as familial hypercholesterolemia and Tangier disease. Fatty liver and impaired lipoprotein synthesis can also disrupt lipid transport.
Sports Nutrition

This document provides information on carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. It begins by explaining the caloric content of carbohydrates and dividing them into simple and complex categories. It then discusses the digestion and metabolism of carbohydrates in the body. For proteins, it describes their structure and function, as well as complete and incomplete protein sources. It outlines protein digestion, synthesis, and recommendations. Finally, it discusses lipids and fatty acids, cholesterol, and fat digestion. It provides an overview of fat metabolism and storage and concludes with general fat recommendations and the relationship between fat and health.
Carbohydrates, Fats and Proteins.ppt

This document provides an overview of macronutrients and their roles in nutrition. It discusses the three main classes of macronutrients that provide energy - carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are broken down into their subcategories and the key roles and functions of each are described. Sources of the different macronutrients and micronutrients like vitamins and minerals are also identified. The document aims to educate on the different food groups and nutrients required for health and their relevance to the human body.
Presentation on lipid

This document summarizes lipids that are important physiologically and their roles in health and disease. It discusses major lipids like fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, sterols, and lipoproteins. Specific fatty acids like saturated, unsaturated, omega-3 and omega-6 are explained. The roles of lipids in brain development, cancer prevention and various lipid-related disorders are highlighted. Atherosclerosis and its pathological progression are also diagrammatically represented.
Hyperlipidaemia.

- There are two essential fatty acids that humans must obtain from their diet: alpha-linolenic acid (ALA, an omega-3 fatty acid) and linoleic acid (LA, an omega-6 fatty acid).
- Good plant-based sources of ALA include chia seeds, flaxseeds, walnuts, canola oil, and walnut oil. While LA is more abundant and found in many plant foods like nuts and seeds.
- These essential fatty acids are polyunsaturated and cannot be made by the body, but they are important for metabolic processes and converting into longer chain omega-3s like EPA and DHA.
Hyperlipidemia 

The seminar covered the management of hyperlipidemia. It discussed the story of lipids in the body and how chylomicrons, LDL, and HDL transport lipids. High LDL and oxidized LDL can lead to atherosclerosis while HDL removes cholesterol from plaque. Causes of hyperlipidemia include diet, medical conditions, and genetic factors. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications, medical nutrition therapy, and pharmacological options like statins. The goals are to lower LDL, total cholesterol, and triglycerides while raising HDL.
HDL 

This document discusses lipoproteins and lipid profiles. It describes the different types of lipoproteins including HDL, LDL, VLDL, and chylomicrons. HDL is described as "good cholesterol" that removes cholesterol from the body, while LDL is described as "bad cholesterol" that deposits cholesterol in tissues and increases disease risk. Normal ranges for HDL and LDL are provided. Factors that influence lipid profiles like smoking, alcohol, medications, and medical conditions are also summarized.
02 nutrition

The document discusses various topics related to nutrition including macromolecules that provide energy like proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. It describes the roles of the liver, vitamins, minerals, and enzymes in breaking down nutrients. Specific carbohydrates like monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides are defined. The document also covers protein structure, fat types, cholesterol, blood sugar regulation, energy requirements, metabolic rate, and eating disorders like anorexia and bulimia.
NUTRITION-2.ppt

DR VISHNU KUMAR
PROFESSOR AND HOD BIOCHEMISTRY, MADHAV PRASAD TRIPATHI GOVERNMENT MEDICAL COLLEGE, SIDDHARTH NAGAR, UTTAR PRADESH.
Lipoprotiens

Understand the structures of various lipoproteins. Understand the role of lipoproteins in cholesterol metabolism
Omega 3 juice for hyperlipidemia & essential elements for pregnancy

Kapidex Juice provides a concise summary of lipids, lipoproteins, and dyslipidemia. It discusses the medical background of lipids and their functions. The document outlines the four principal types of lipoproteins, their compositions, and contributions to total plasma cholesterol. It also defines dyslipidemia and discusses primary and secondary causes. Finally, the document provides details about Kapidex Juice, including its active ingredients and their benefits for lowering triglycerides and reducing cardiovascular risk.
Sheq foundation health promotion 

This document provides a summary of topics covered in a health improvement program, including diabetes, hypertension, cholesterol, eating habits, and sexually transmitted diseases. It focuses on defining and describing diabetes, including the different types of diabetes, causes and treatments. It also discusses cholesterol levels and factors that affect cholesterol. Hypertension is defined as high blood pressure and risks of untreated hypertension are outlined. The goal of the program is to improve health through addressing these key health topics.
Similar to Lipids ,oils and fats uses, application global trends (20)
Omega 3 juice for hyperlipidemia & essential elements for pregnancy

Omega 3 juice for hyperlipidemia & essential elements for pregnancy
Recently uploaded
快速办理(Adelaide毕业证书)阿德莱德大学毕业证文凭证书一模一样

学校原件一模一样【微信:741003700 】《(Adelaide毕业证书)阿德莱德大学毕业证文凭证书》【微信:741003700 】学位证,留信认证(真实可查,永久存档)原件一模一样纸张工艺/offer、雅思、外壳等材料/诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本,帮您解决无法毕业带来的各种难题!外壳,原版制作,诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本。行业标杆!精益求精,诚心合作,真诚制作!多年品质 ,按需精细制作,24小时接单,全套进口原装设备。十五年致力于帮助留学生解决难题,包您满意。
本公司拥有海外各大学样板无数,能完美还原。
1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。材料咨询办理、认证咨询办理请加学历顾问Q/微741003700
【主营项目】
一.毕业证【q微741003700】成绩单、使馆认证、教育部认证、雅思托福成绩单、学生卡等!
二.真实使馆公证(即留学回国人员证明,不成功不收费)
三.真实教育部学历学位认证(教育部存档!教育部留服网站永久可查)
四.办理各国各大学文凭(一对一专业服务,可全程监控跟踪进度)
如果您处于以下几种情况:
◇在校期间,因各种原因未能顺利毕业……拿不到官方毕业证【q/微741003700】
◇面对父母的压力,希望尽快拿到;
◇不清楚认证流程以及材料该如何准备;
◇回国时间很长,忘记办理;
◇回国马上就要找工作,办给用人单位看;
◇企事业单位必须要求办理的
◇需要报考公务员、购买免税车、落转户口
◇申请留学生创业基金
留信网认证的作用:
1:该专业认证可证明留学生真实身份
2:同时对留学生所学专业登记给予评定
3:国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书
4:这个认证书并且可以归档倒地方
5:凡事获得留信网入网的信息将会逐步更新到个人身份内,将在公安局网内查询个人身份证信息后,同步读取人才网入库信息
6:个人职称评审加20分
7:个人信誉贷款加10分
8:在国家人才网主办的国家网络招聘大会中纳入资料,供国家高端企业选择人才
Heritage Conservation.Strategies and Options for Preserving India Heritage

Presentation looks at the role , relevance and importance of built and natural heritage, issues faced by heritage in the Indian context and options which can be leveraged to preserve and conserve the heritage.It also lists the challenges faced by the heritage due to rapid urbanisation, land speculation and commercialisation in the urban areas. In addition, ppt lays down the roadmap for the preservation, conservation and making value addition to the available heritage by making it integral part of the planning , designing and management of the human settlements.
在线办理(UCM毕业证书)加州大学美熹德分校毕业证文凭证书一模一样

学校原件一模一样【微信:741003700 】《(UCM毕业证书)加州大学美熹德分校毕业证文凭证书》【微信:741003700 】学位证,留信认证(真实可查,永久存档)原件一模一样纸张工艺/offer、雅思、外壳等材料/诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本,帮您解决无法毕业带来的各种难题!外壳,原版制作,诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本。行业标杆!精益求精,诚心合作,真诚制作!多年品质 ,按需精细制作,24小时接单,全套进口原装设备。十五年致力于帮助留学生解决难题,包您满意。
本公司拥有海外各大学样板无数,能完美还原。
1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。材料咨询办理、认证咨询办理请加学历顾问Q/微741003700
【主营项目】
一.毕业证【q微741003700】成绩单、使馆认证、教育部认证、雅思托福成绩单、学生卡等!
二.真实使馆公证(即留学回国人员证明,不成功不收费)
三.真实教育部学历学位认证(教育部存档!教育部留服网站永久可查)
四.办理各国各大学文凭(一对一专业服务,可全程监控跟踪进度)
如果您处于以下几种情况:
◇在校期间,因各种原因未能顺利毕业……拿不到官方毕业证【q/微741003700】
◇面对父母的压力,希望尽快拿到;
◇不清楚认证流程以及材料该如何准备;
◇回国时间很长,忘记办理;
◇回国马上就要找工作,办给用人单位看;
◇企事业单位必须要求办理的
◇需要报考公务员、购买免税车、落转户口
◇申请留学生创业基金
留信网认证的作用:
1:该专业认证可证明留学生真实身份
2:同时对留学生所学专业登记给予评定
3:国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书
4:这个认证书并且可以归档倒地方
5:凡事获得留信网入网的信息将会逐步更新到个人身份内,将在公安局网内查询个人身份证信息后,同步读取人才网入库信息
6:个人职称评审加20分
7:个人信誉贷款加10分
8:在国家人才网主办的国家网络招聘大会中纳入资料,供国家高端企业选择人才
一比一原版(Sheffield毕业证书)谢菲尔德大学毕业证如何办理

学校原件一模一样【微信:6496090 】【(Sheffield毕业证书)谢菲尔德大学毕业证成绩单】【微信:6496090 】学位证,留信认证(真实可查,永久存档)原件一模一样纸张工艺/offer、雅思、外壳等材料/诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本,帮您解决无法毕业带来的各种难题!外壳,原版制作,诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本。行业标杆!精益求精,诚心合作,真诚制作!多年品质 ,按需精细制作,24小时接单,全套进口原装设备。十五年致力于帮助留学生解决难题,包您满意。
本公司拥有海外各大学样板无数,能完美还原。
1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。材料咨询办理、认证咨询办理请加学历顾问Q/微6496090
【主营项目】
一.毕业证【q微6496090】成绩单、使馆认证、教育部认证、雅思托福成绩单、学生卡等!
二.真实使馆公证(即留学回国人员证明,不成功不收费)
三.真实教育部学历学位认证(教育部存档!教育部留服网站永久可查)
四.办理各国各大学文凭(一对一专业服务,可全程监控跟踪进度)
如果您处于以下几种情况:
◇在校期间,因各种原因未能顺利毕业……拿不到官方毕业证【q/微6496090】
◇面对父母的压力,希望尽快拿到;
◇不清楚认证流程以及材料该如何准备;
◇回国时间很长,忘记办理;
◇回国马上就要找工作,办给用人单位看;
◇企事业单位必须要求办理的
◇需要报考公务员、购买免税车、落转户口
◇申请留学生创业基金
留信网认证的作用:
1:该专业认证可证明留学生真实身份
2:同时对留学生所学专业登记给予评定
3:国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书
4:这个认证书并且可以归档倒地方
5:凡事获得留信网入网的信息将会逐步更新到个人身份内,将在公安局网内查询个人身份证信息后,同步读取人才网入库信息
6:个人职称评审加20分
7:个人信誉贷款加10分
8:在国家人才网主办的国家网络招聘大会中纳入资料,供国家高端企业选择人才
办理(Sheffield毕业证书)谢菲尔德大学毕业证【微信:6496090 】外观非常简单,由纸质材料制成,上面印有校徽、校名、毕业生姓名、专业等信息。
办理(Sheffield毕业证书)谢菲尔德大学毕业证【微信:6496090 】格式相对统一,各专业都有相应的模板。通常包括以下部分:
校徽:象征着学校的荣誉和传承。
校名:学校英文全称
授予学位:本部分将注明获得的具体学位名称。
毕业生姓名:这是最重要的信息之一,标志着该证书是由特定人员获得的。
颁发日期:这是毕业正式生效的时间,也代表着毕业生学业的结束。
其他信息:根据不同的专业和学位,可能会有一些特定的信息或章节。
办理(Sheffield毕业证书)谢菲尔德大学毕业证【微信:6496090 】价值很高,需要妥善保管。一般来说,应放置在安全、干燥、防潮的地方,避免长时间暴露在阳光下。如需使用,最好使用复印件而不是原件,以免丢失。
综上所述,办理(Sheffield毕业证书)谢菲尔德大学毕业证【微信:6496090 】是证明身份和学历的高价值文件。外观简单庄重,格式统一,包括重要的个人信息和发布日期。对持有人来说,妥善保管是非常重要的。
FOOD OBESITY IN NORTH AMERICA ( NEW).pptx

FOOD OBESITY IN AMERICA AND MARKETING CAMPAIGNS ESTABLISHED TO DEFEAT IT
Recently uploaded (7)
Heritage Conservation.Strategies and Options for Preserving India Heritage

Heritage Conservation.Strategies and Options for Preserving India Heritage
NANOTECHNOLOGY IN FOOD PACKAGING (FOOD TECHNOLOGY)

NANOTECHNOLOGY IN FOOD PACKAGING (FOOD TECHNOLOGY)
Lipids ,oils and fats uses, application global trends
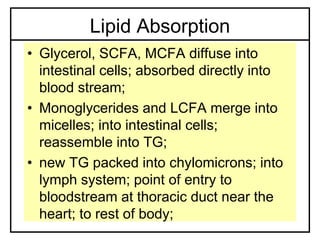
- 1. Lipid Absorption • Glycerol, SCFA, MCFA diffuse into intestinal cells; absorbed directly into blood stream; • Monoglycerides and LCFA merge into micelles; into intestinal cells; reassemble into TG; • new TG packed into chylomicrons; into lymph system; point of entry to bloodstream at thoracic duct near the heart; to rest of body;
- 3. Lipid Transport • Lipoproteins: clusters of lipids associated with proteins that serve as transport vehicles for lipids in the lymph and blood; • 4 main types of lipoproteins – 1. Chylomicrons – 2. VLDL – 3. LDL – 4. HDL
- 4. Lipoproteins • 1. Chylomicrons – transport diet-derived lipids (mostly TG) from intestine to rest of the body; – cells from all over the body remove lipids as the chylomicrons pass by; get smaller; protein remnants left; go to liver; • 2. VLDL (Very Low Density Lipoprotein) – liver site of lipid synthesis; lipid packaged with proteins shipped to other parts of the body; cells remove TG; become more dense;
- 5. Lipoproteins • 3. LDL (Low Density Lipoproteins) – derived from VLDL; circulate throughout body; content available to cells to build new membranes, make hormones, or store; – LDL receptors on liver cells remove LDL from circulation; • 4. HDL (High Density Lipoproteins) – carries cholesterol and other lipids from the cells back to the liver for recycling or disposal – mostly protein;
- 7. Lipid Metabolism • Storing Fat as Fat – Fat cells of adipose tissue take up and store fat; – LPL on adipose cell surface captures circulating TG after meals; • Making Fat from Carb or Protein – FA can be made from carb or pro components; – requires energy • Making Fat from Fat – little energy to do this;
- 8. Health Implications • LDL (lousy):linked to heart disease • HDL (happy): protective from heart disease • Factors that improve LDL-HDL ratio: – weight control – MUFA/PUFA vs. SFA – Soluble fiber – Antioxidants – Physical activity – Moderate alcohol consumption
- 9. Heart Disease • Blood Lipid Profile: – Total Cholesterol: Desirable: < 200 mg/dl – (borderline:200-239 and high: >240) – LDL Cholesterol: Optimal: < 100 mg/dl – (near optimal: 100-129; borderline high:130- 159 – High: 160-189; Very High: >190) – HDL Cholesterol: Risk factor: <40 mg/dl – 40-59: better; >60: protective – Triglyceride: Desirable: < 150 mg/dl; – (B: 150-199; high: 200-499; very high: >500)
- 10. Health Effects of Lipids • Risks from Saturated Fats – saturated fats raise LDL cholesterol – LDL raises the risk of heart disease • Risks from trans-Fats – raise LDL cholesterol and lower HDL chol. • Cardiovascular disease (CVD) – all diseases of the heart and blood vessels • Coronary heart disease (CHD) – arteries around heart are blocked, cause damage
- 15. Fat • Benefits from Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fats/Cancer/Obesity/Fat restriction • Recommended Intakes of Fat: – Total Fat 30% of total kcals – Saturated fat less than 10% of total kcals – Cholesterol less than 300 mg • Reduce Total Fat, Saturated Fat, trans- fat intake from foods • Reduce Cholesterol Intake
- 16. Healthy Food Choices • Balance Omega-3 and Omega-6 Intakes • Select Lean Meats and Nonfat milks • Eat Plenty of Vegetables, Fruits, Grains • Use Fats and Oils Sparingly • Look for Invisible Fat • Choose Wisely • Read Food Labels
- 17. • J.M. went to see her medical provider to discuss results of recent lab work: Chol: 250 mg/dl; LDL: 150 mg/dl; HDL: 65 mg/dl; Trig. 120 mg/dl. Her food recall is: bkf: 3 eggs, 3 sl. white toast with butter, 16 oz OJ lun: bologna & cheddar swich, hoho, coke din: fried chicken thigh, mashed potato, gravy, corn snack: bowl of ice cream • 1. Evaluate J.M. lab results--high?low? What are the recommended levels? • 2. How is her essential fatty acid intake? What foods would you recommend she consume? • 3. Is J.M. consuming any sat. fat? MUF? PUF? Trans? • 4. List suggested dietary changes for J.M. • 5. What disease should J.M. be concerned about? • 6. J.M. is told to increase her fiber intake. Why? How?
- 18. • 7. Describe 4 types of lipoproteins. • 8. Look at your food label: – What type of fat does it contain? – Is there any cholesterol? – What fat is listed in the ingredient list?