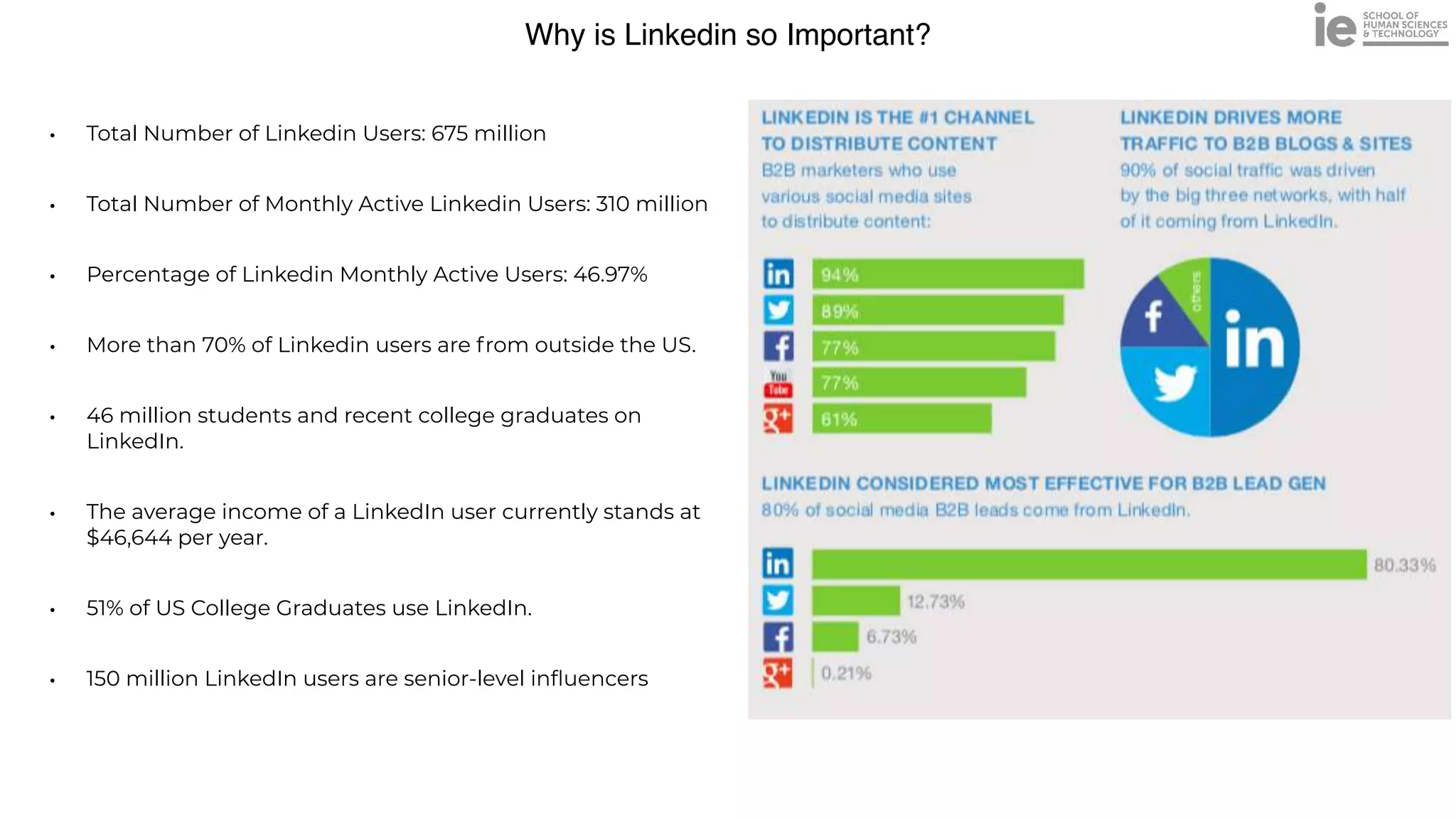
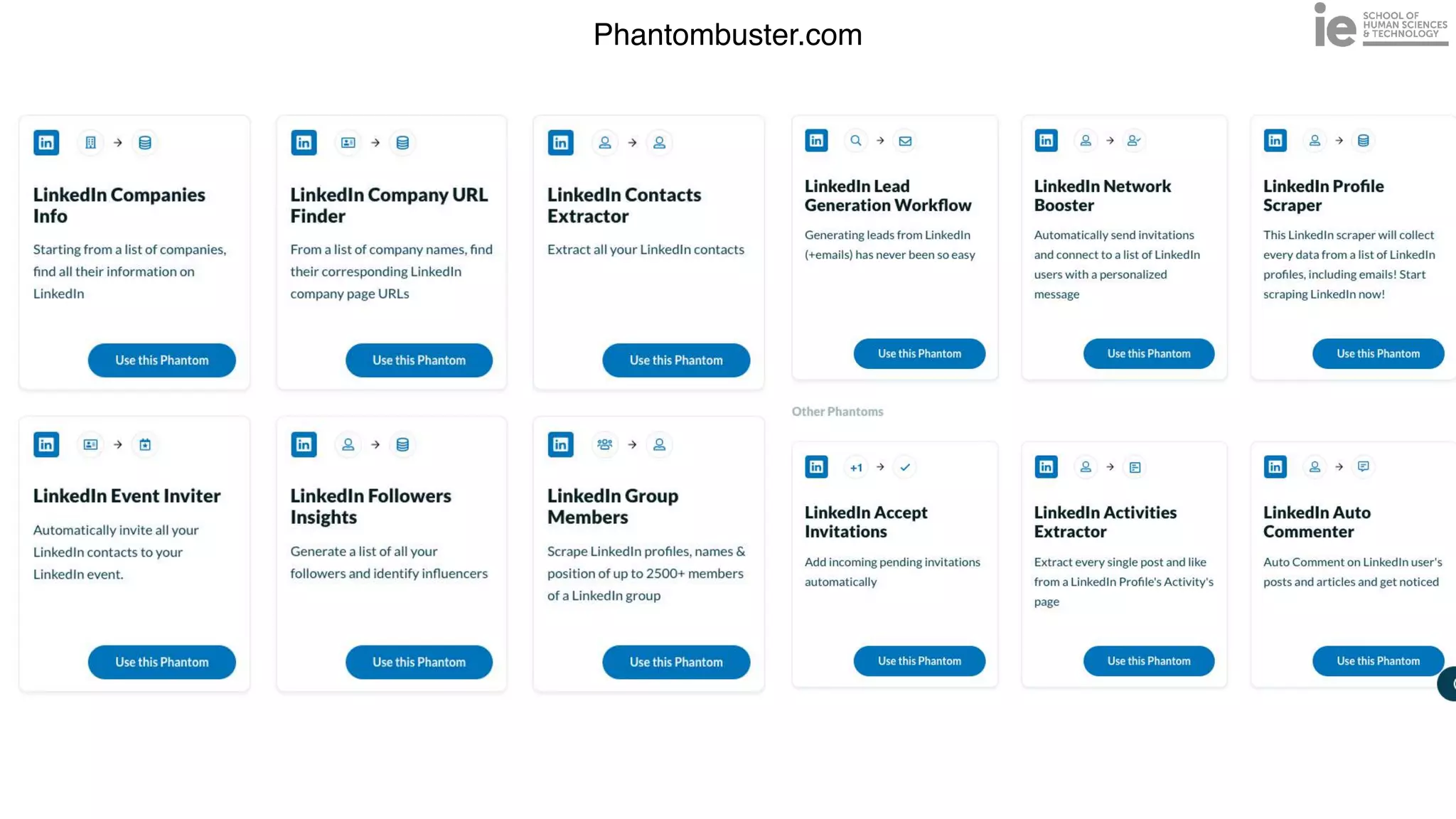
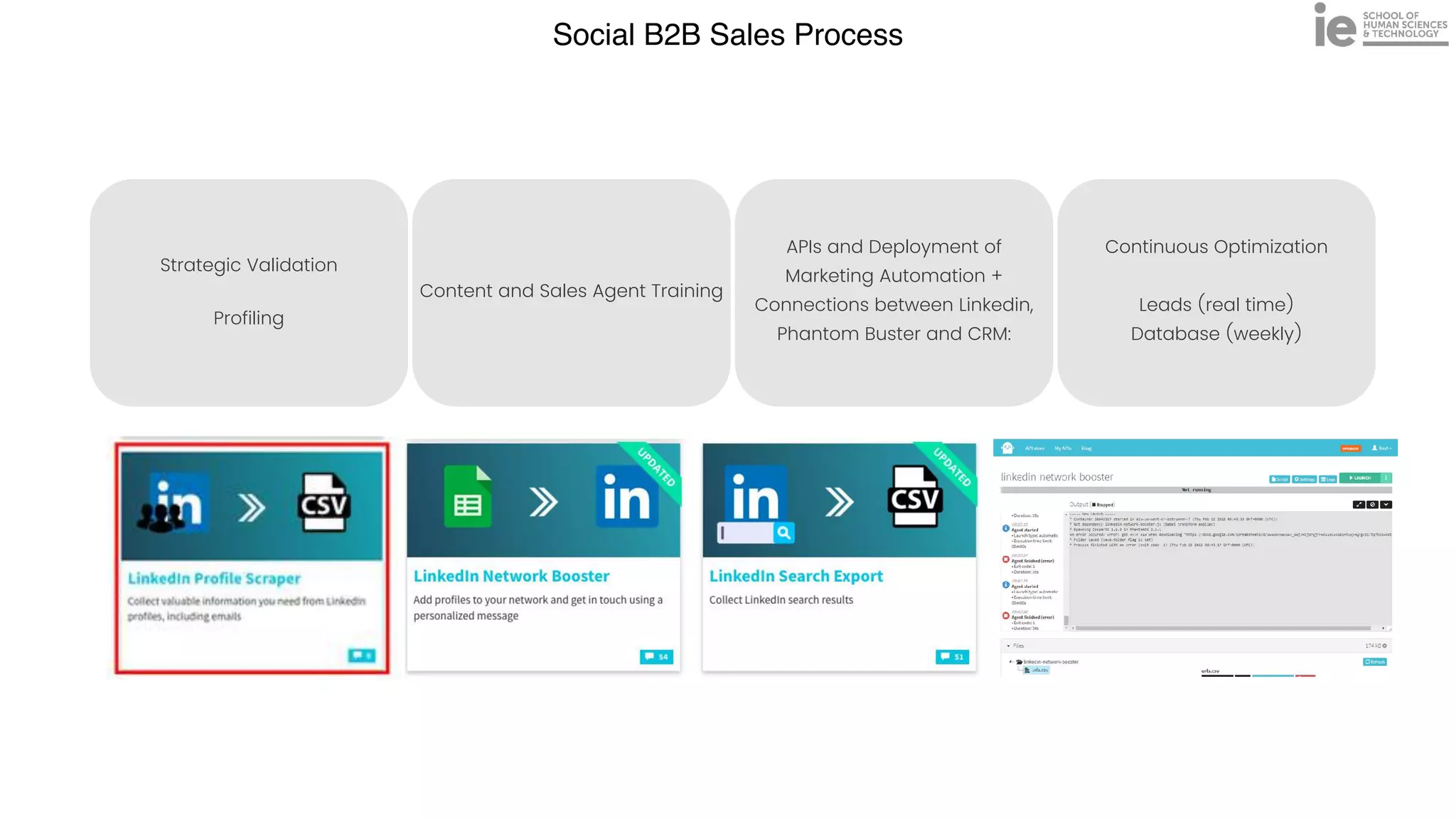
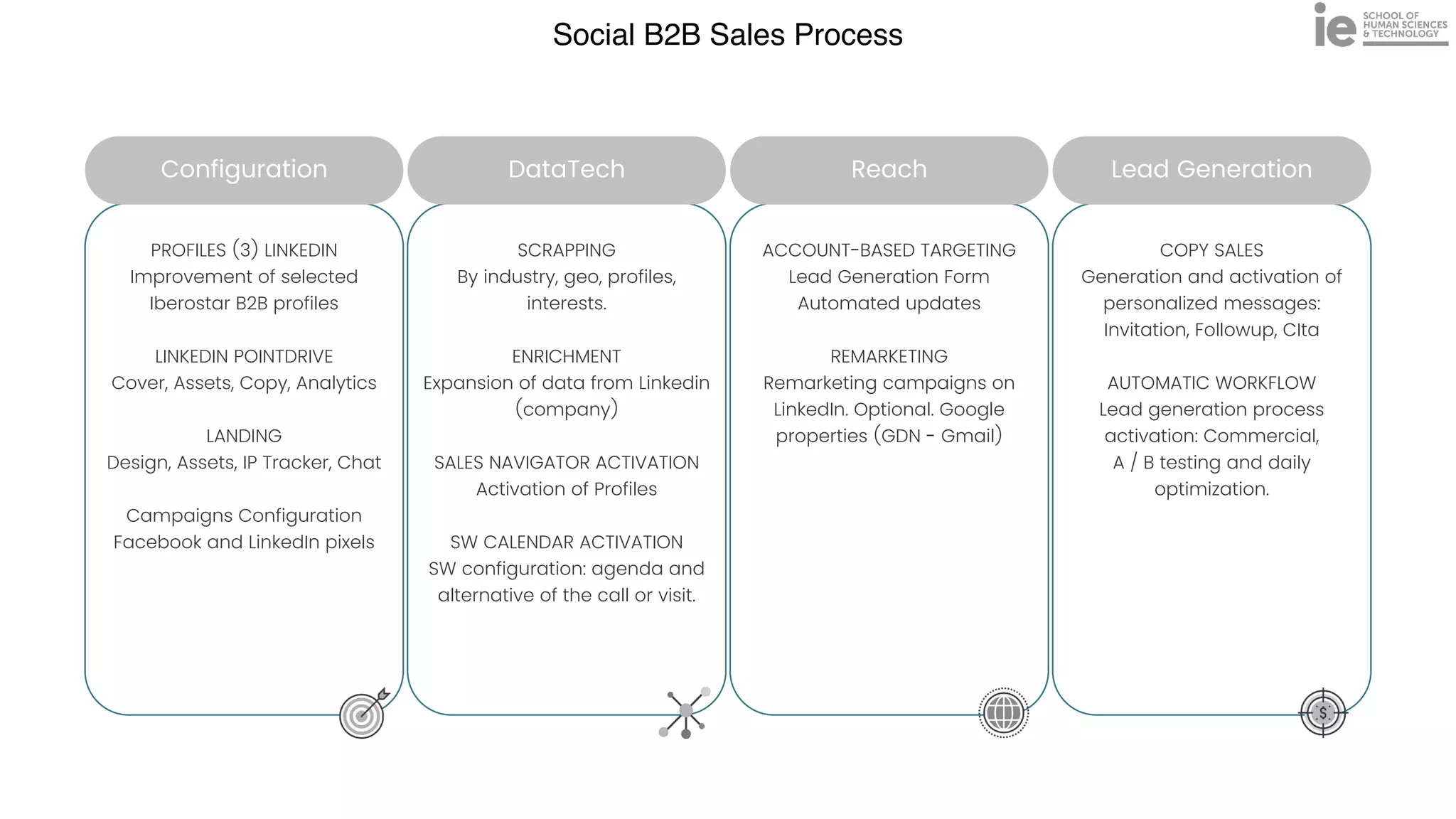
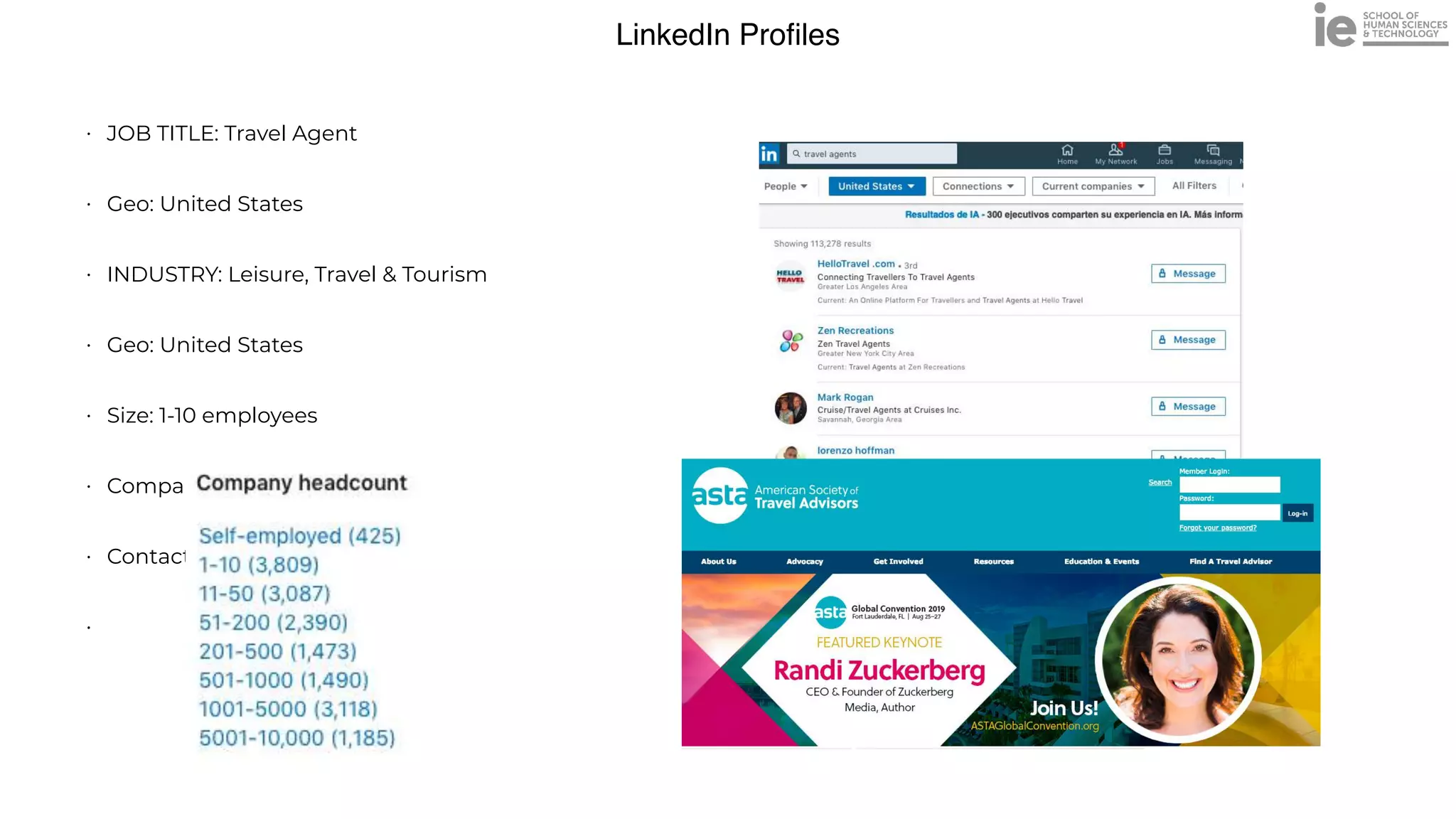
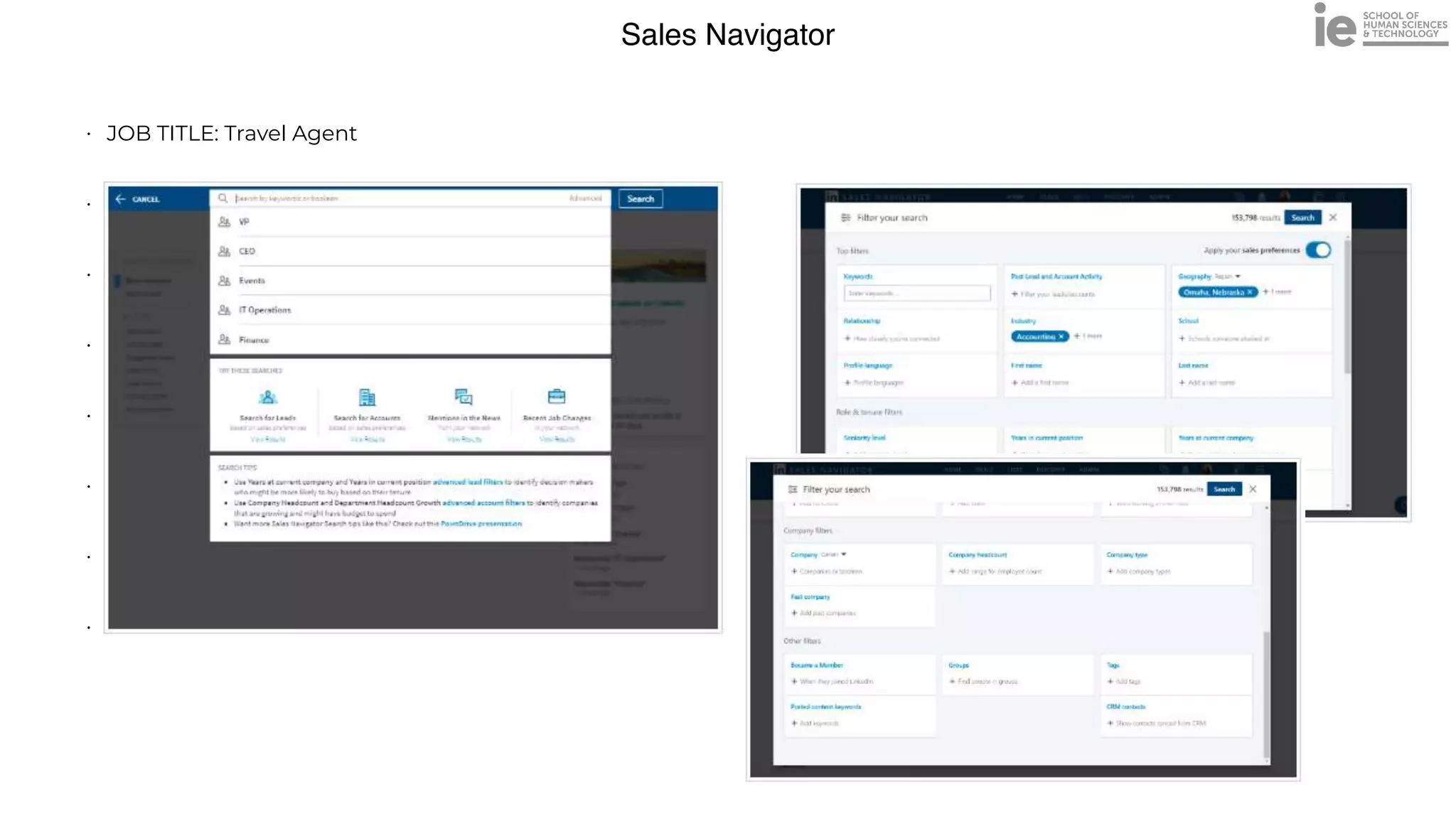
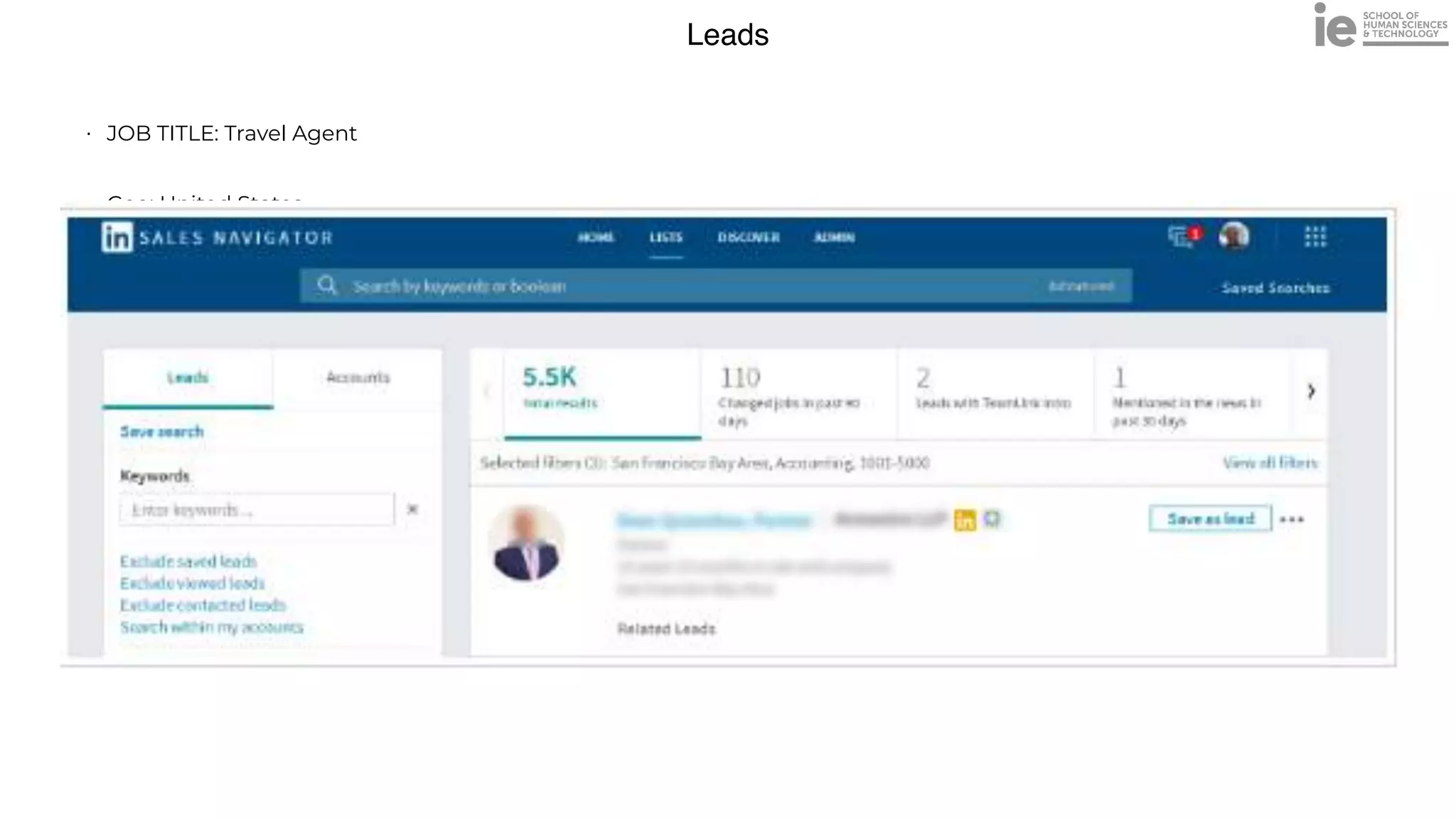
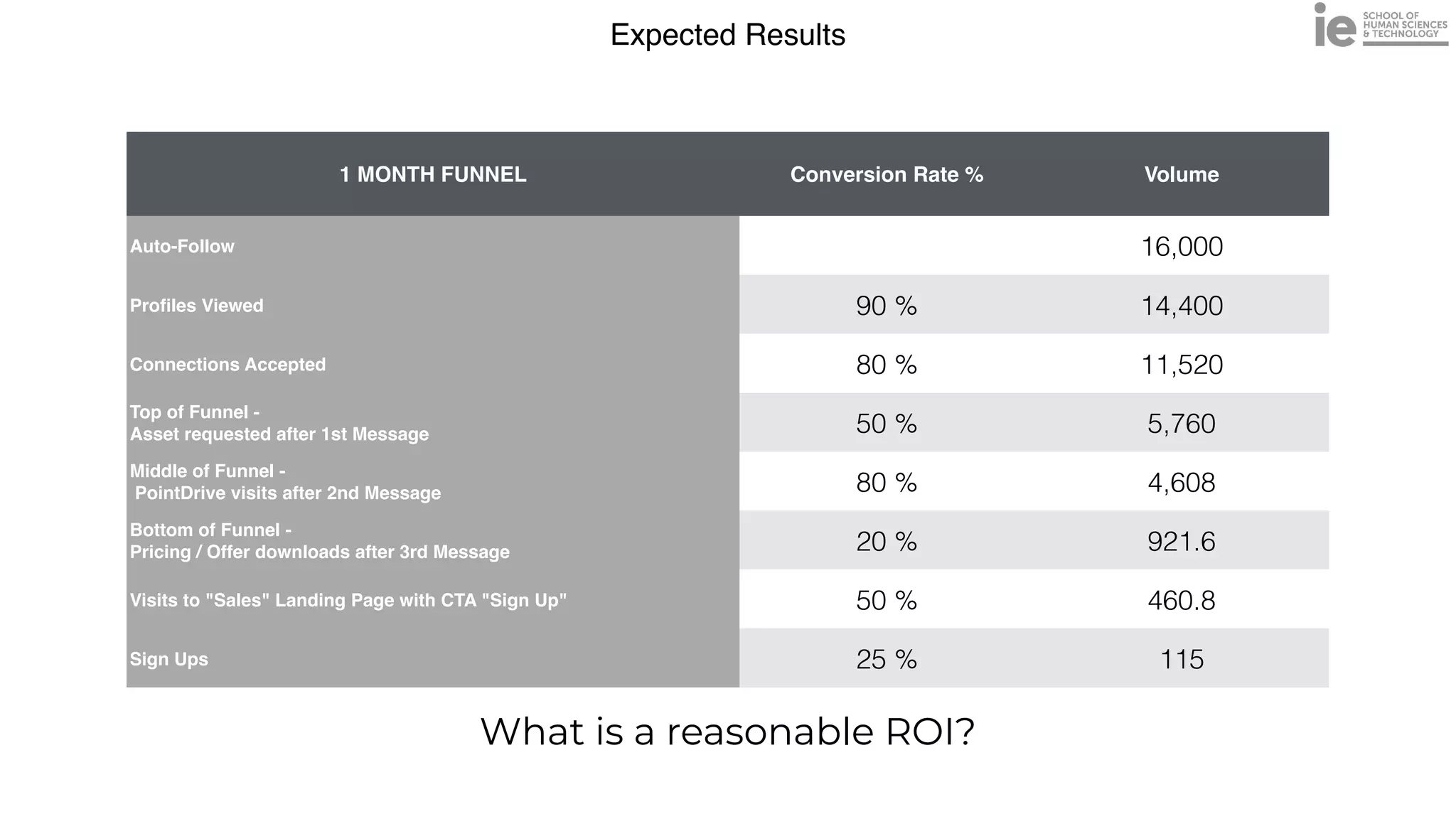
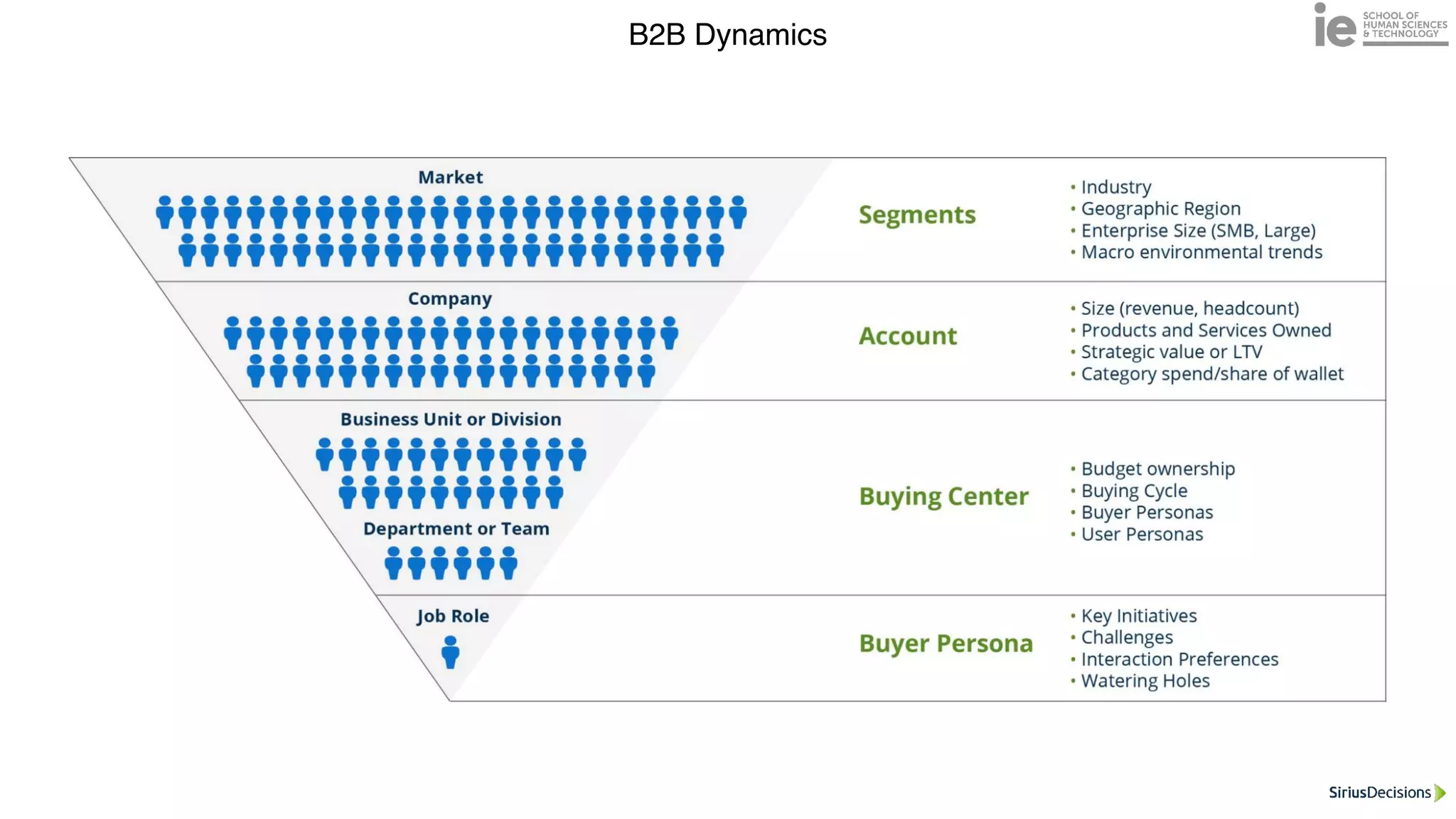
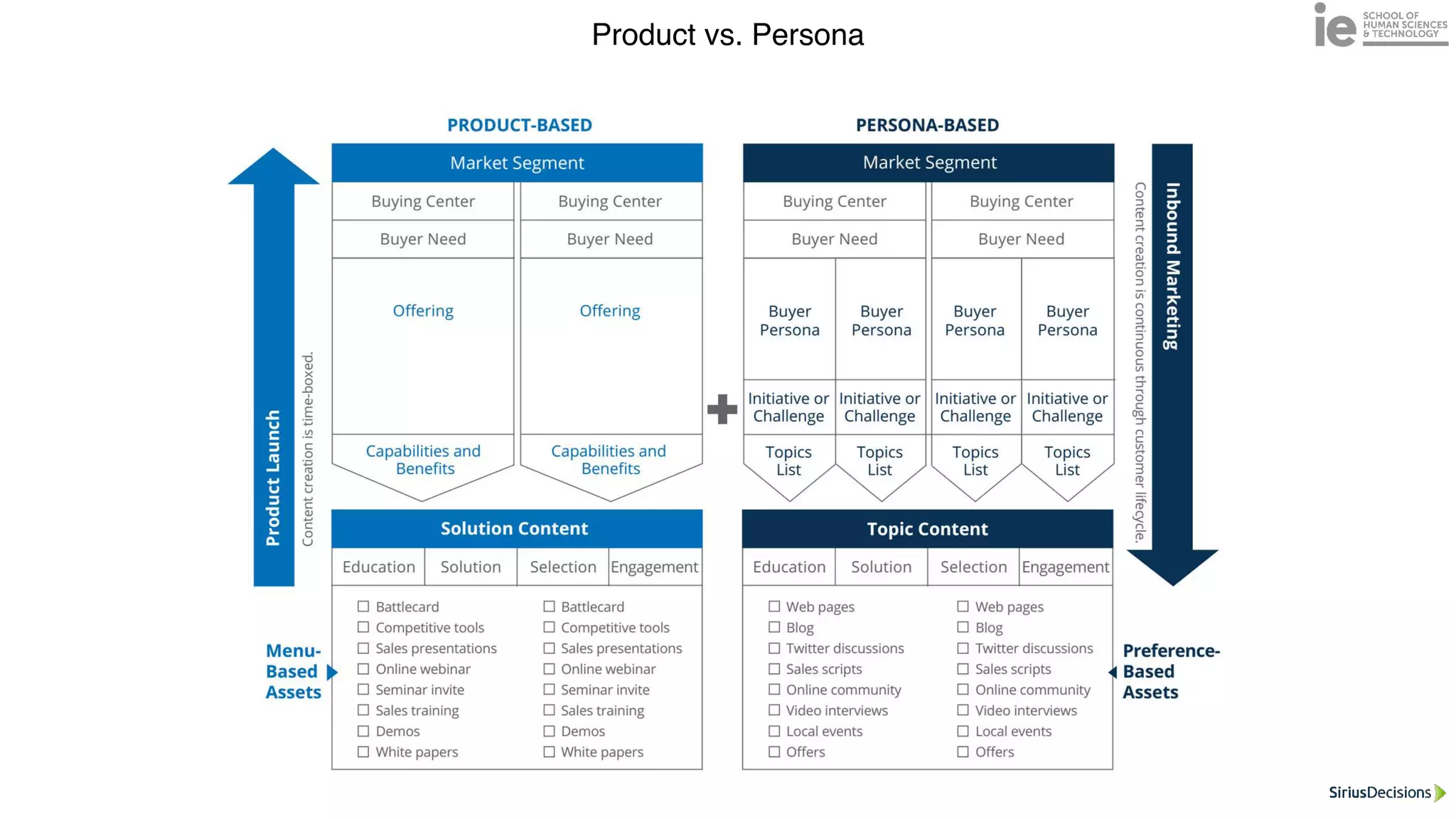
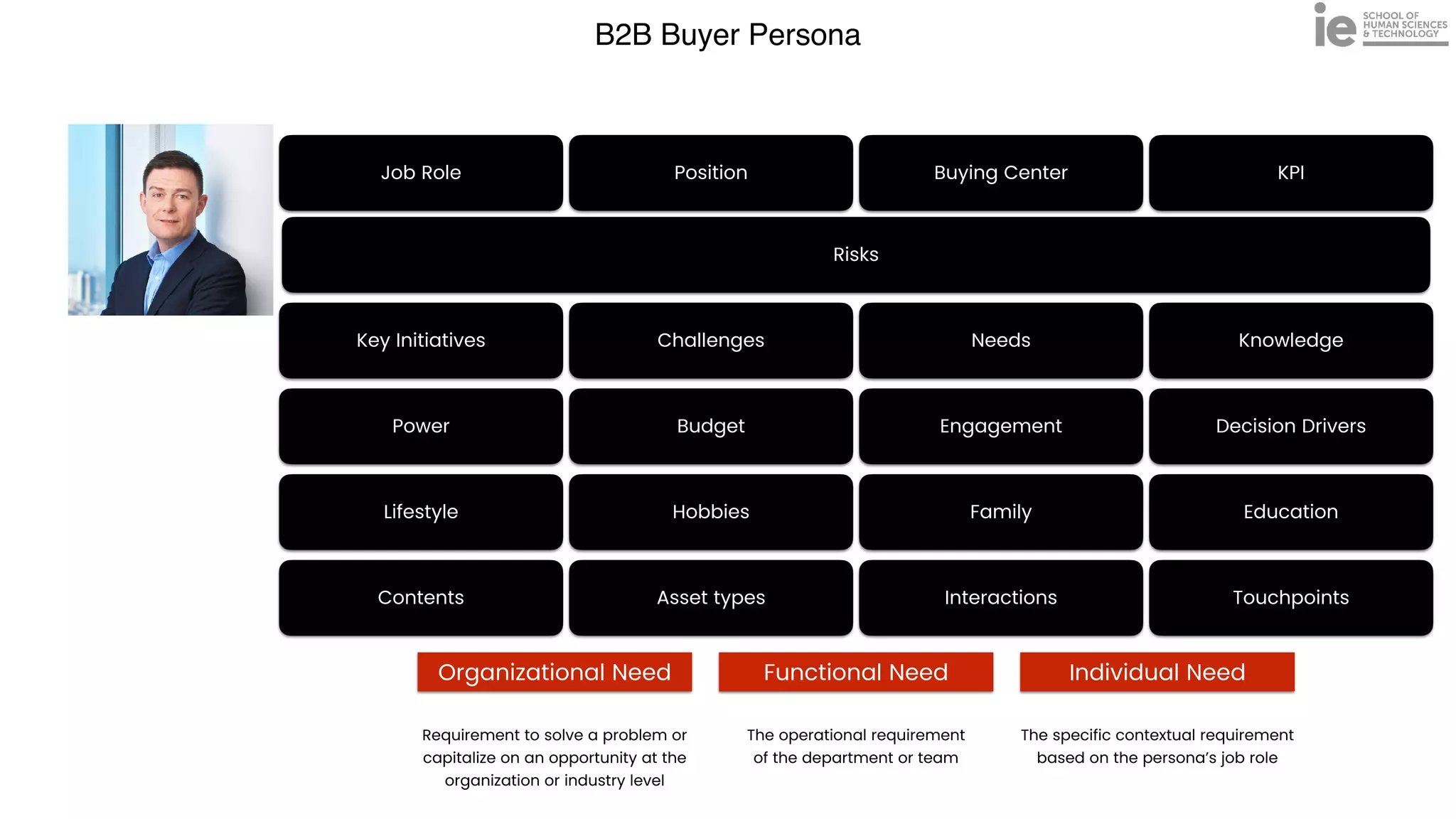
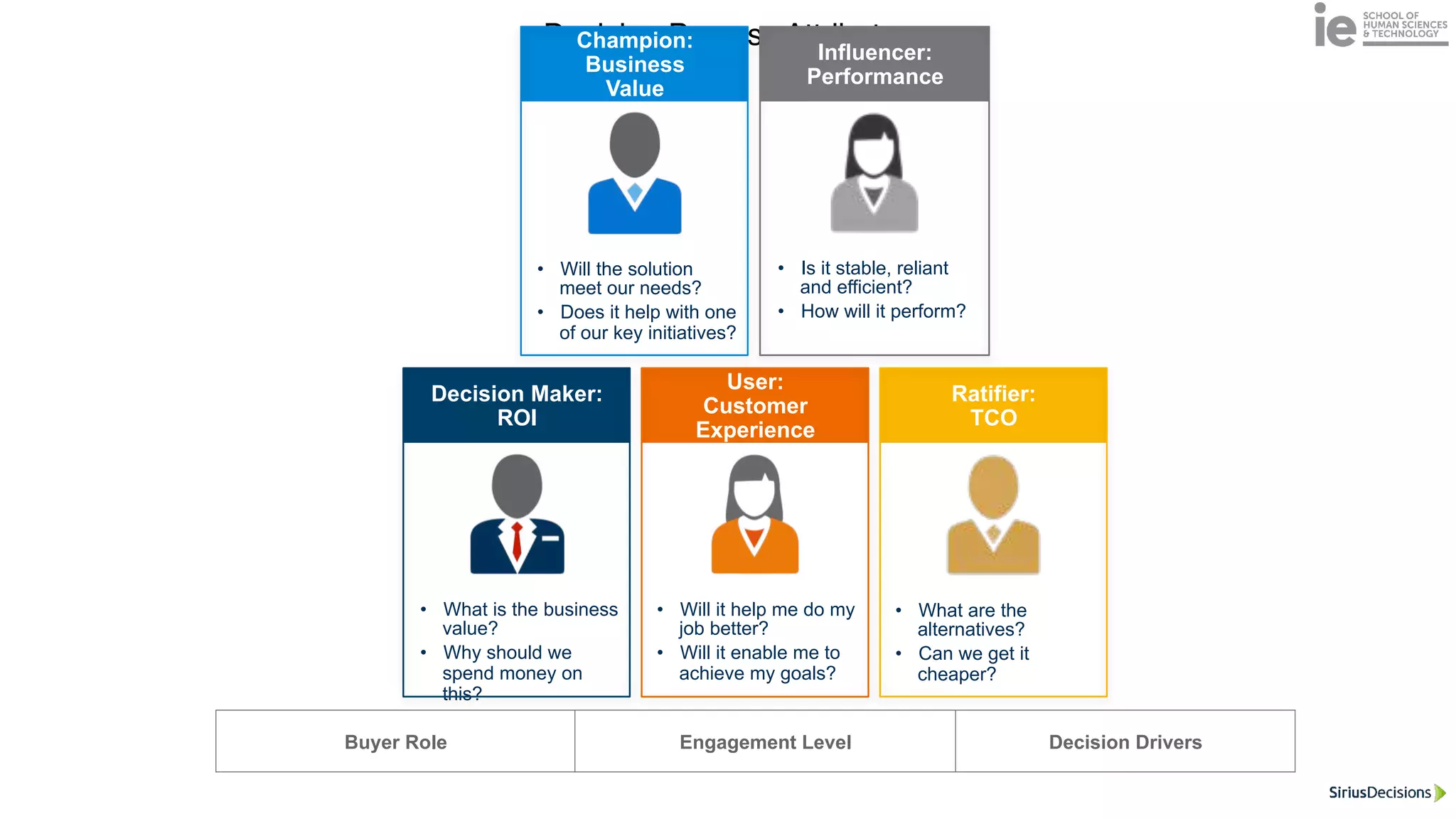
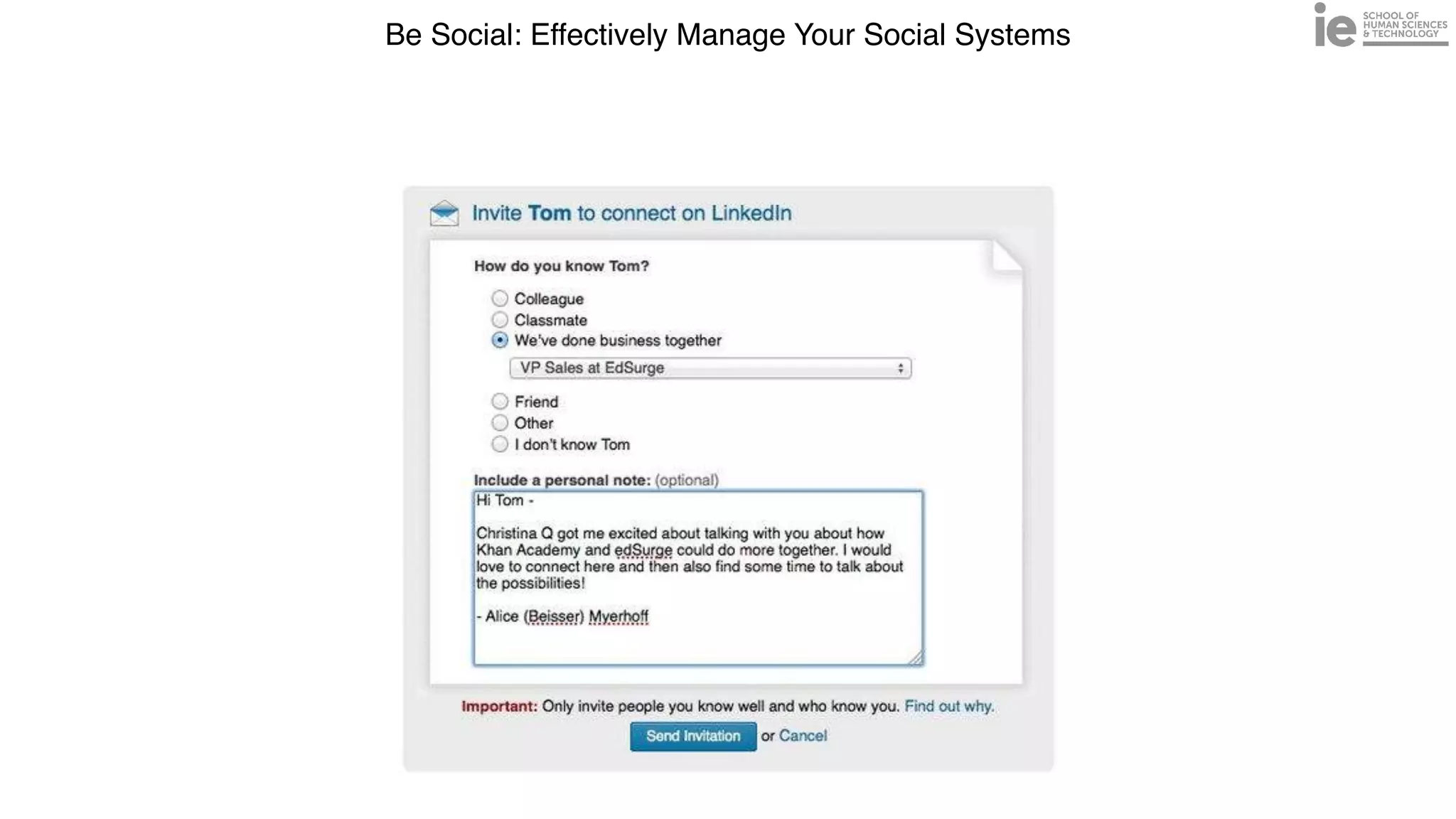
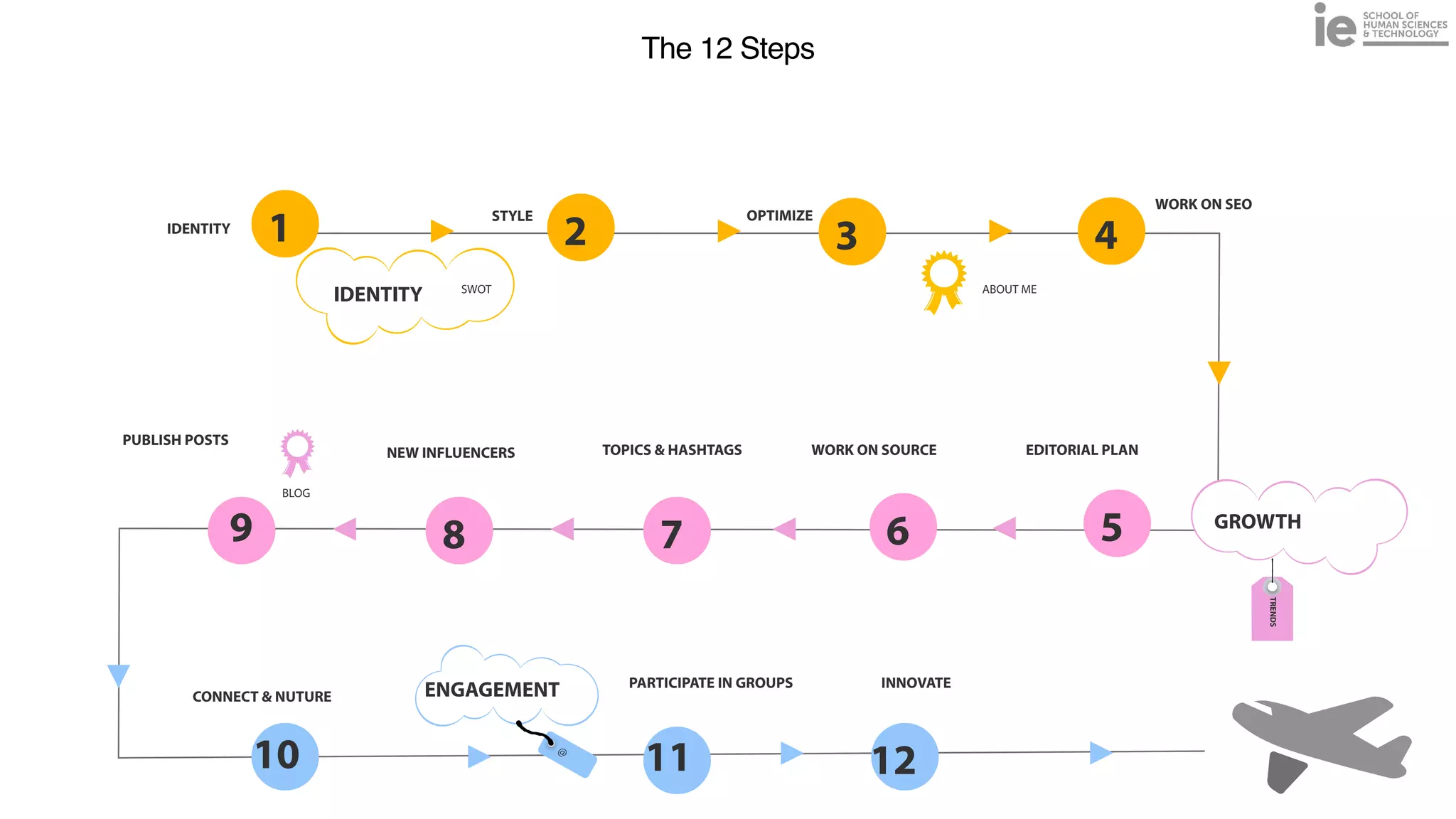
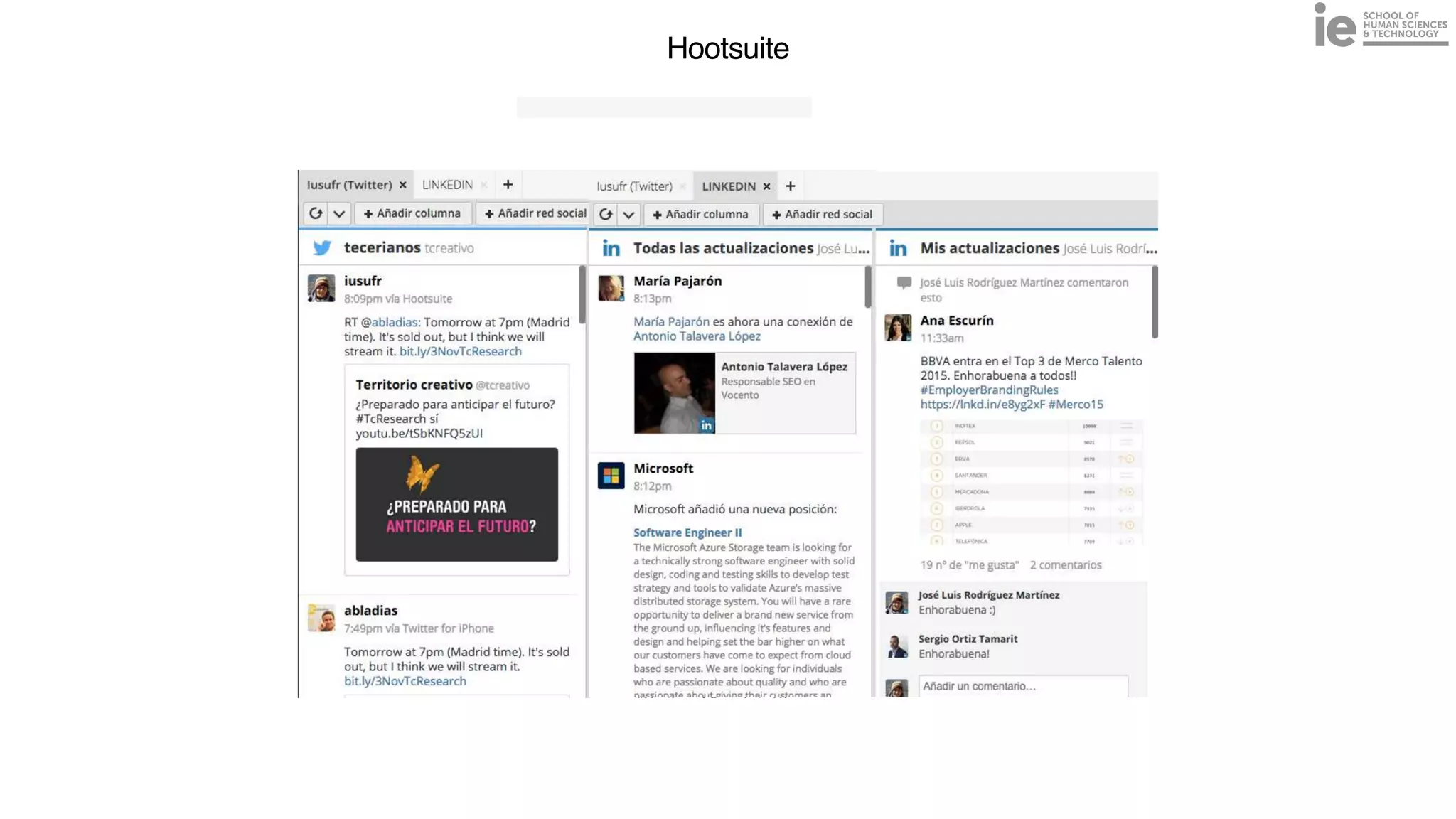
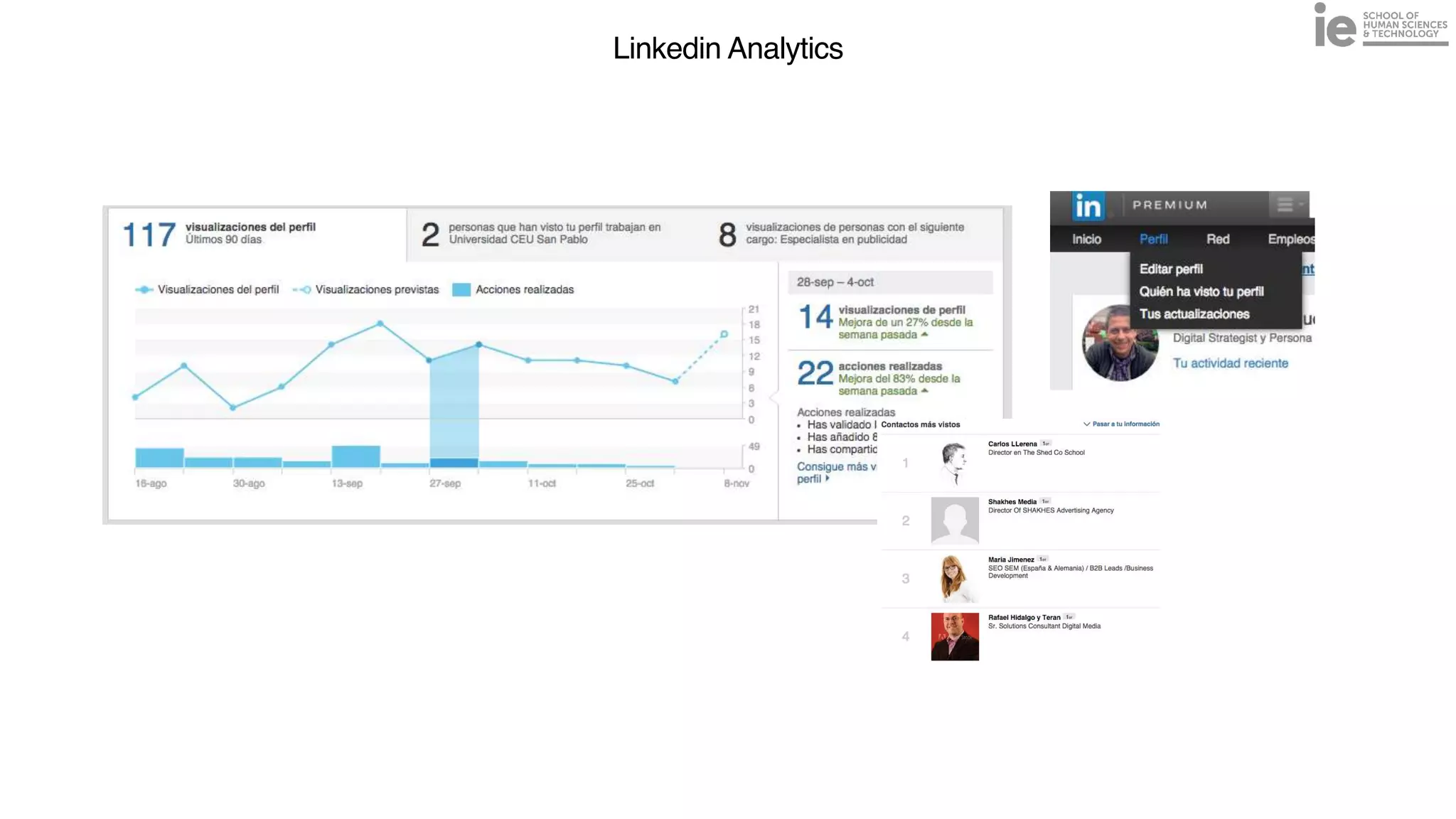
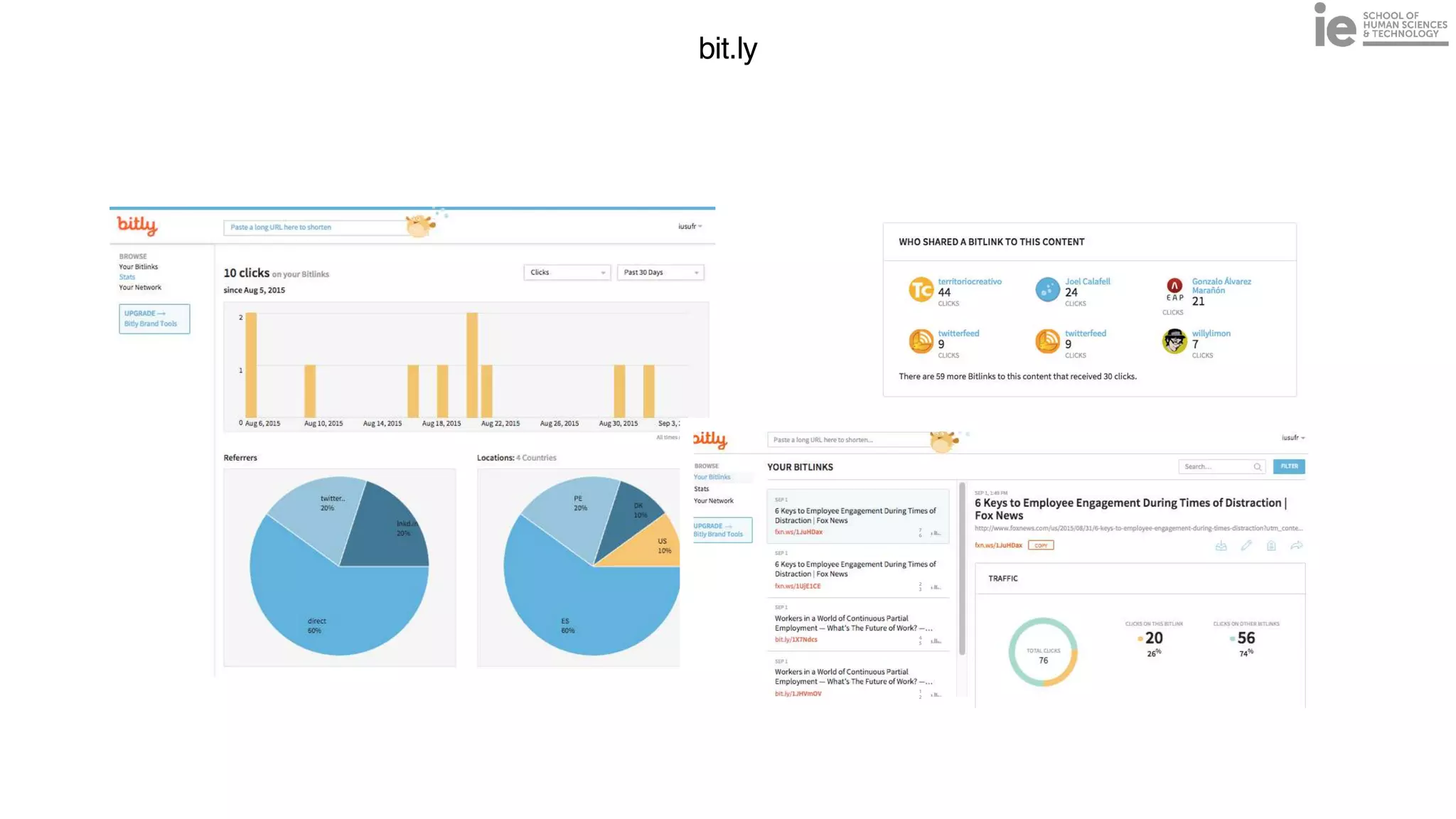
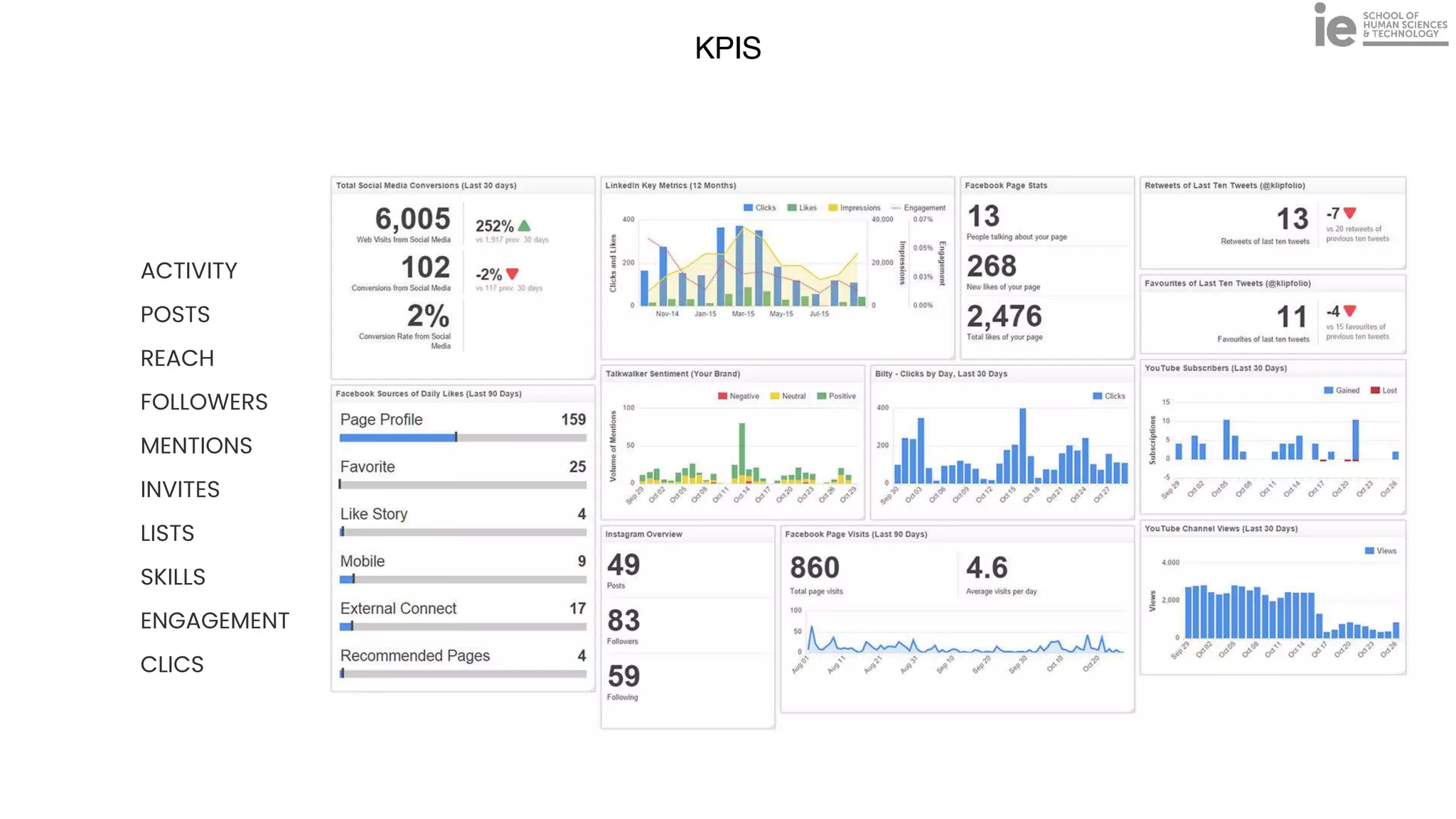
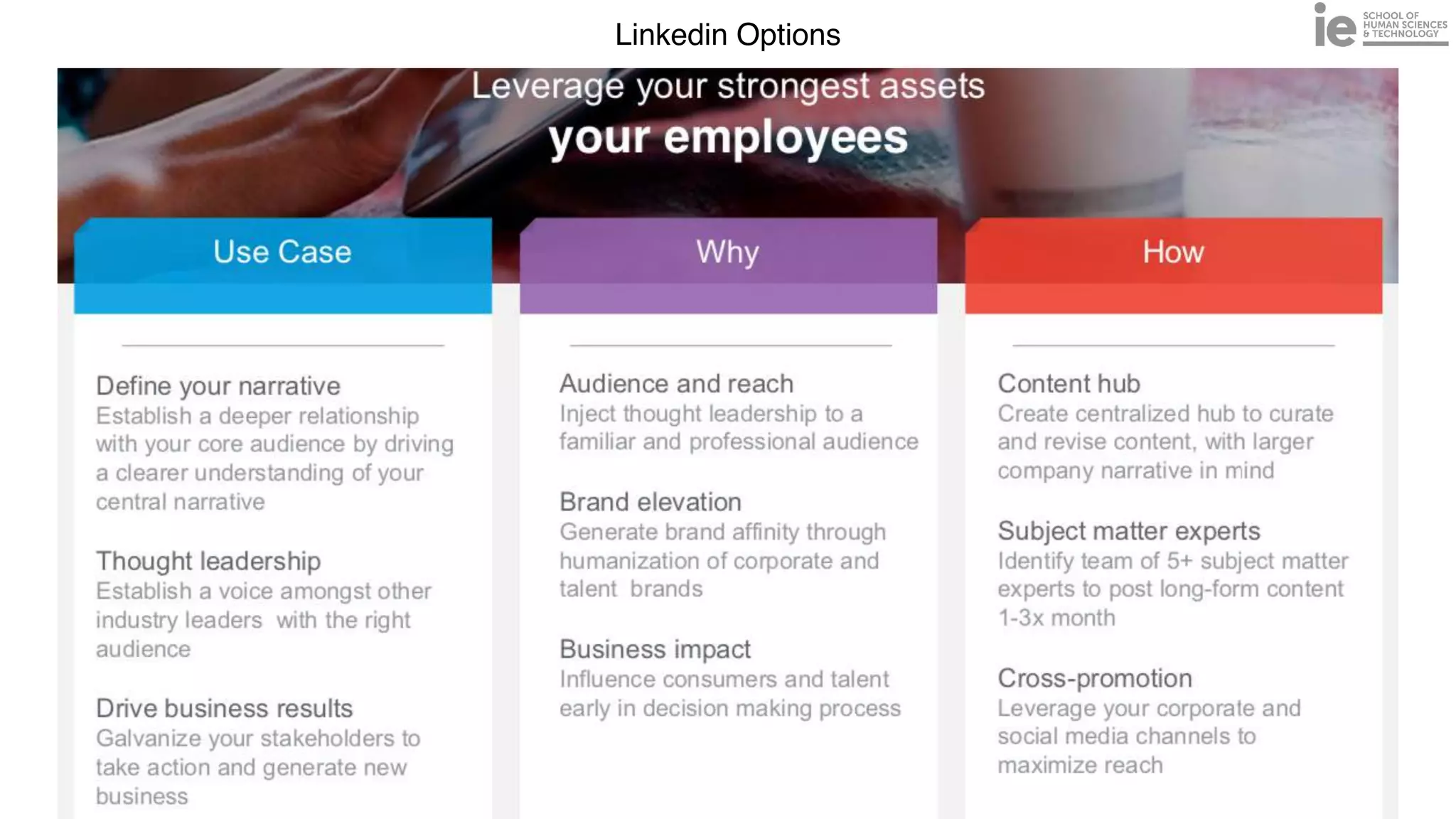
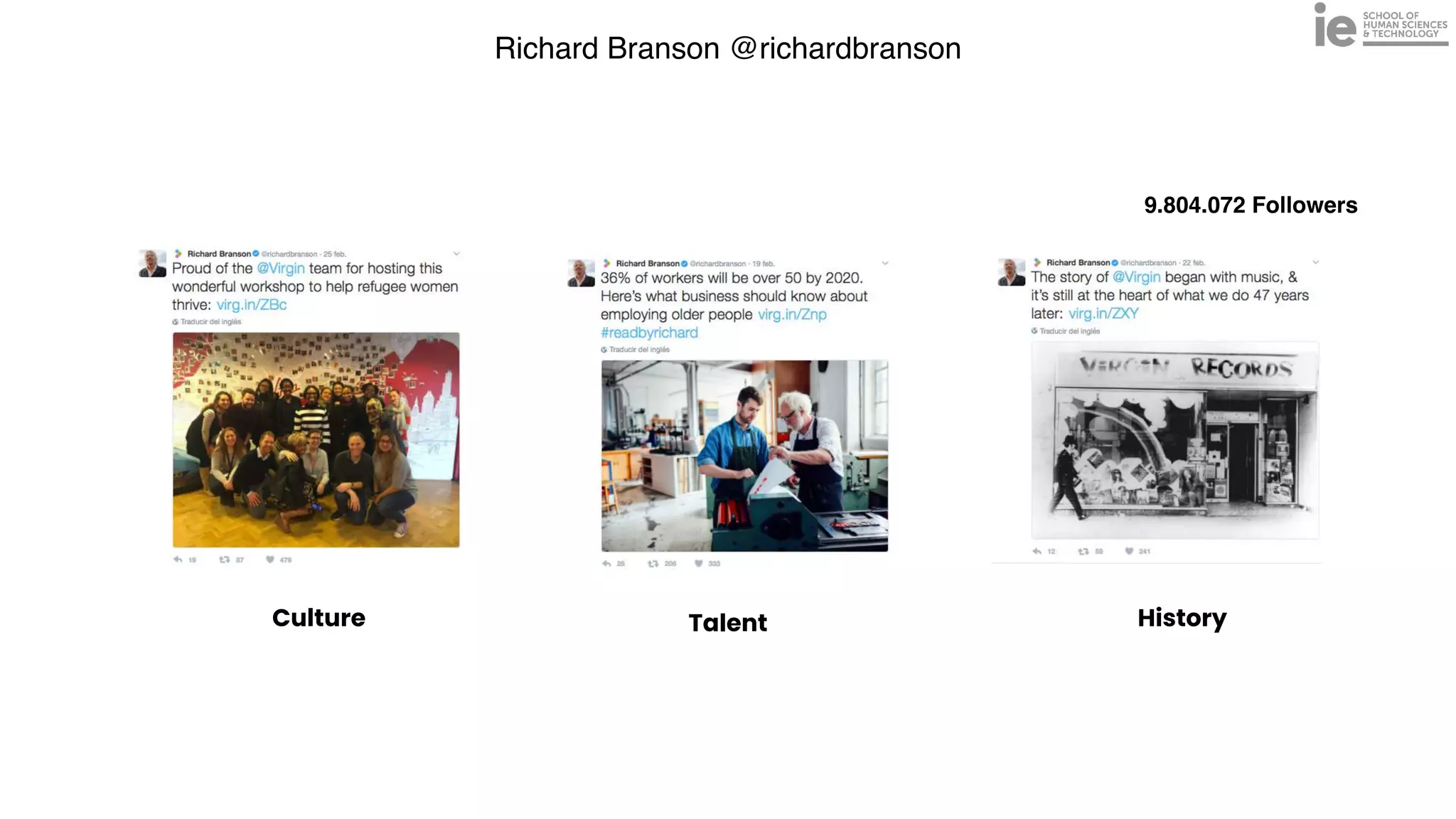
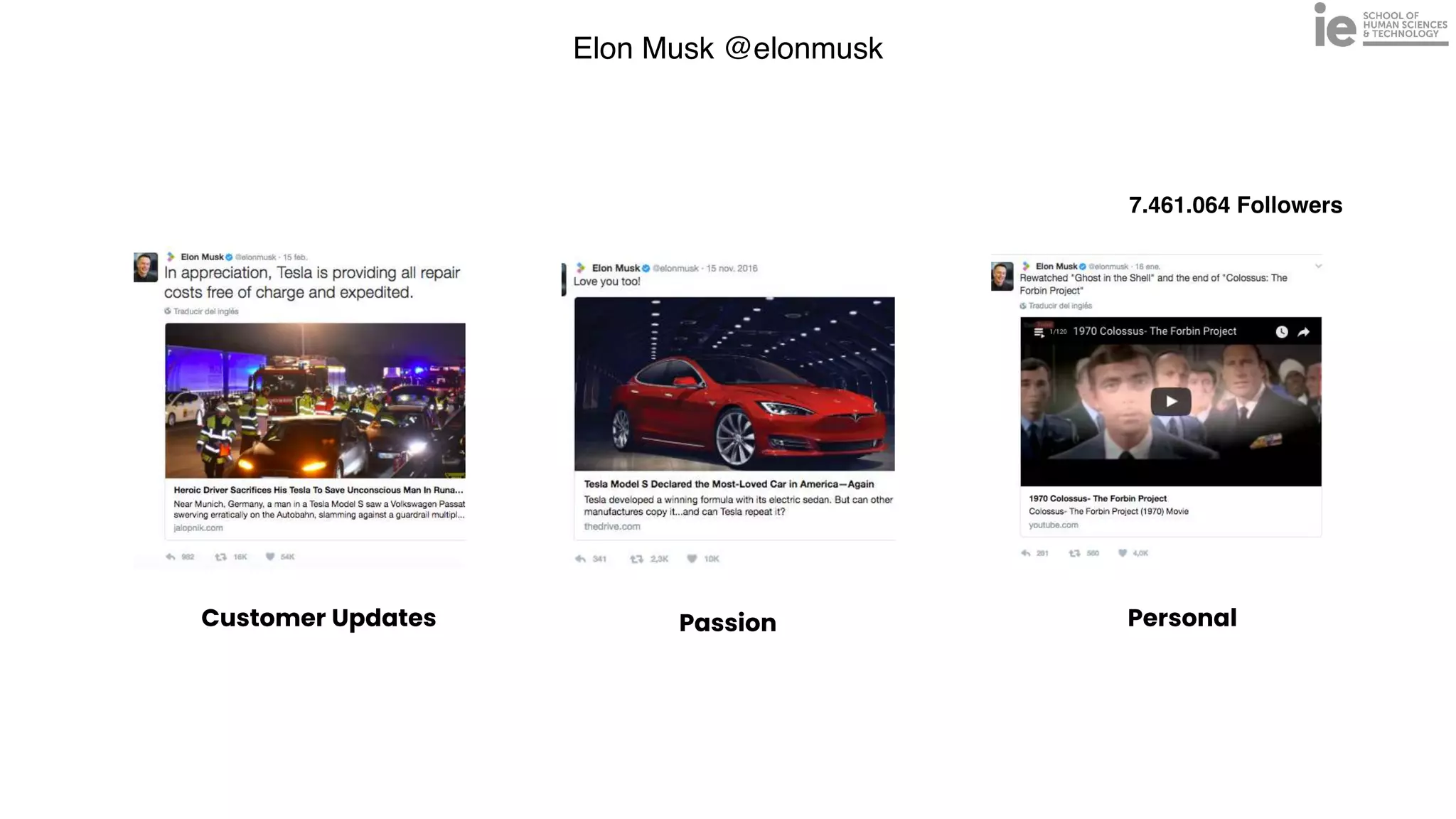
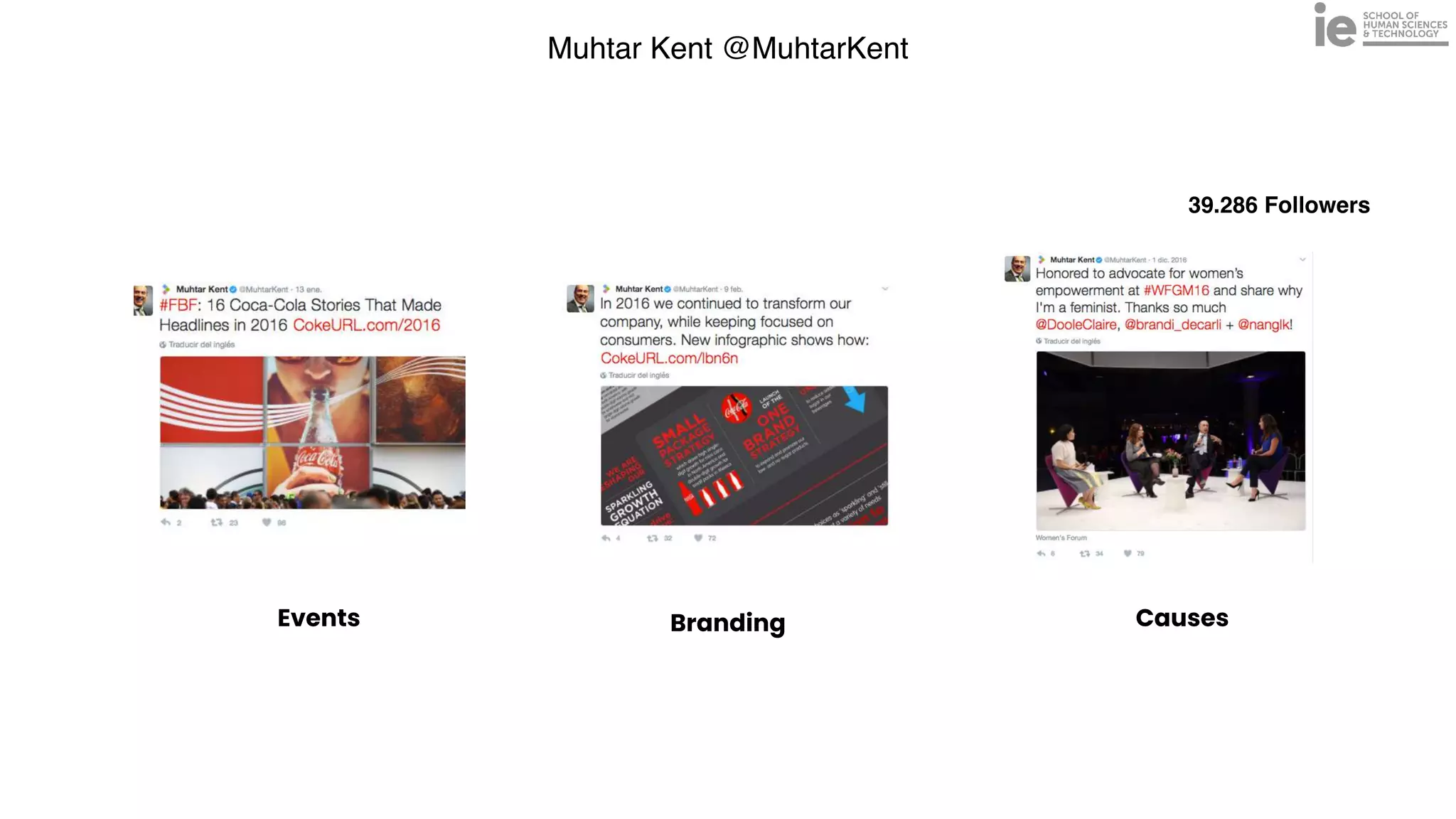
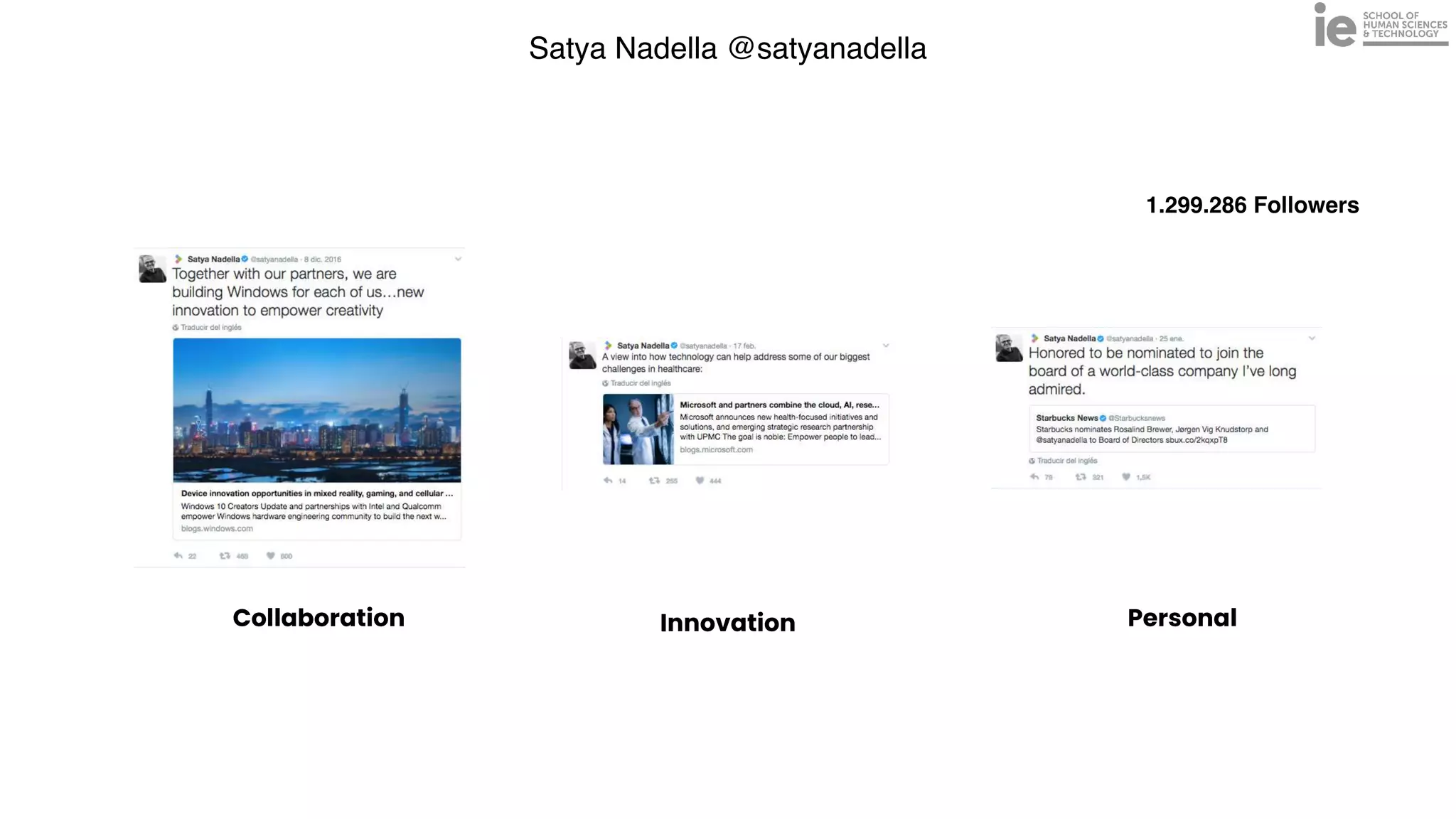
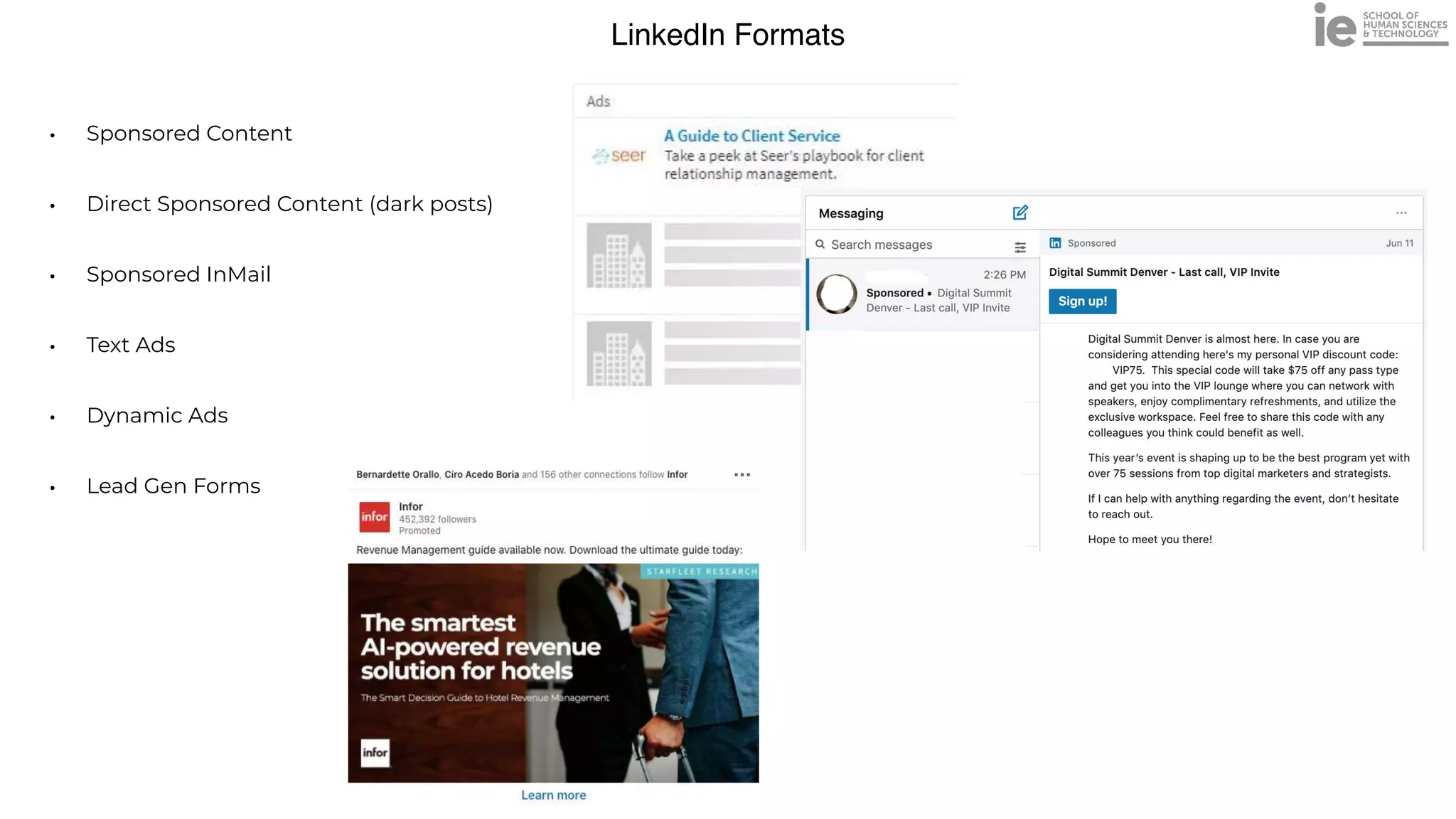
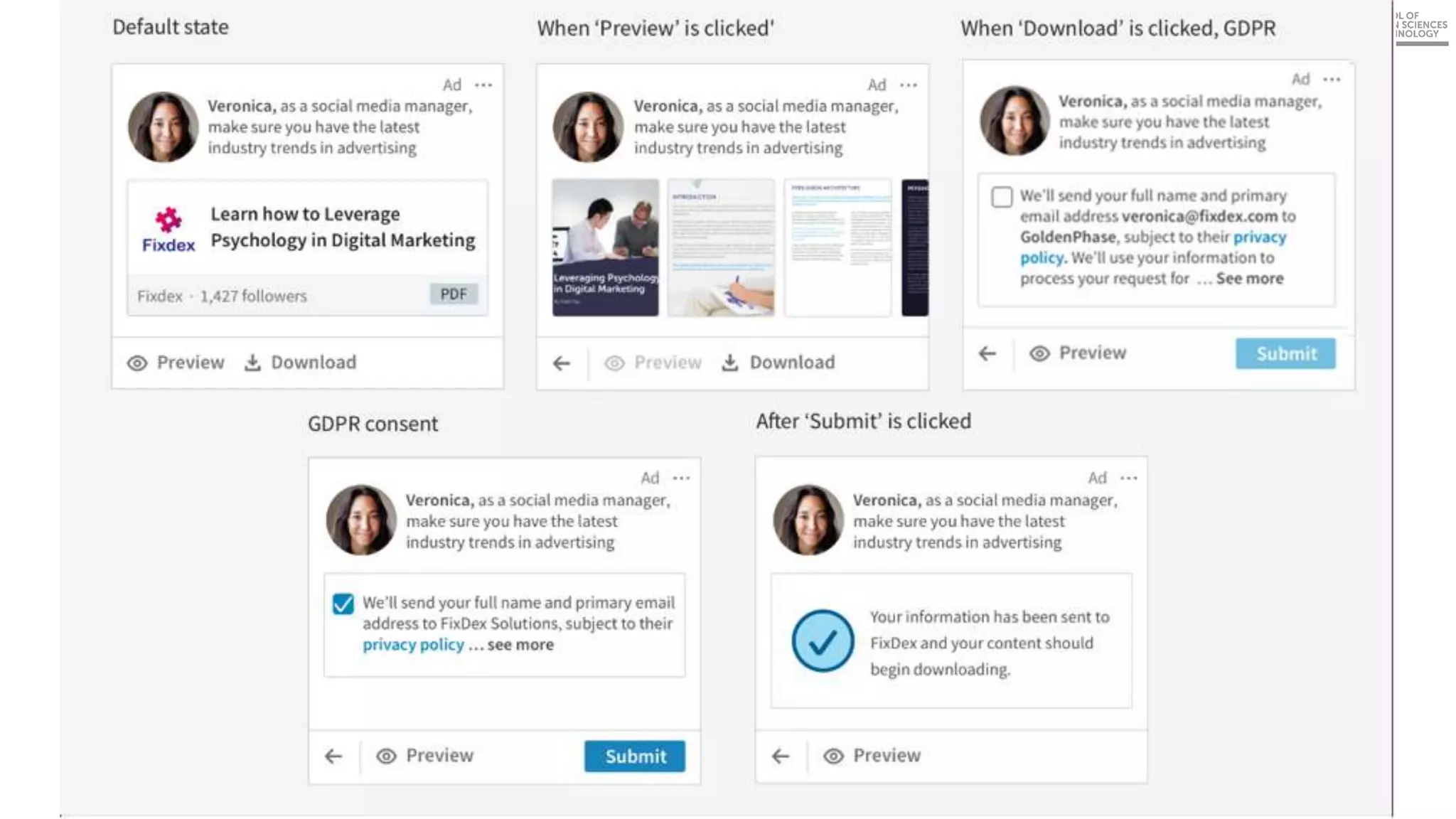
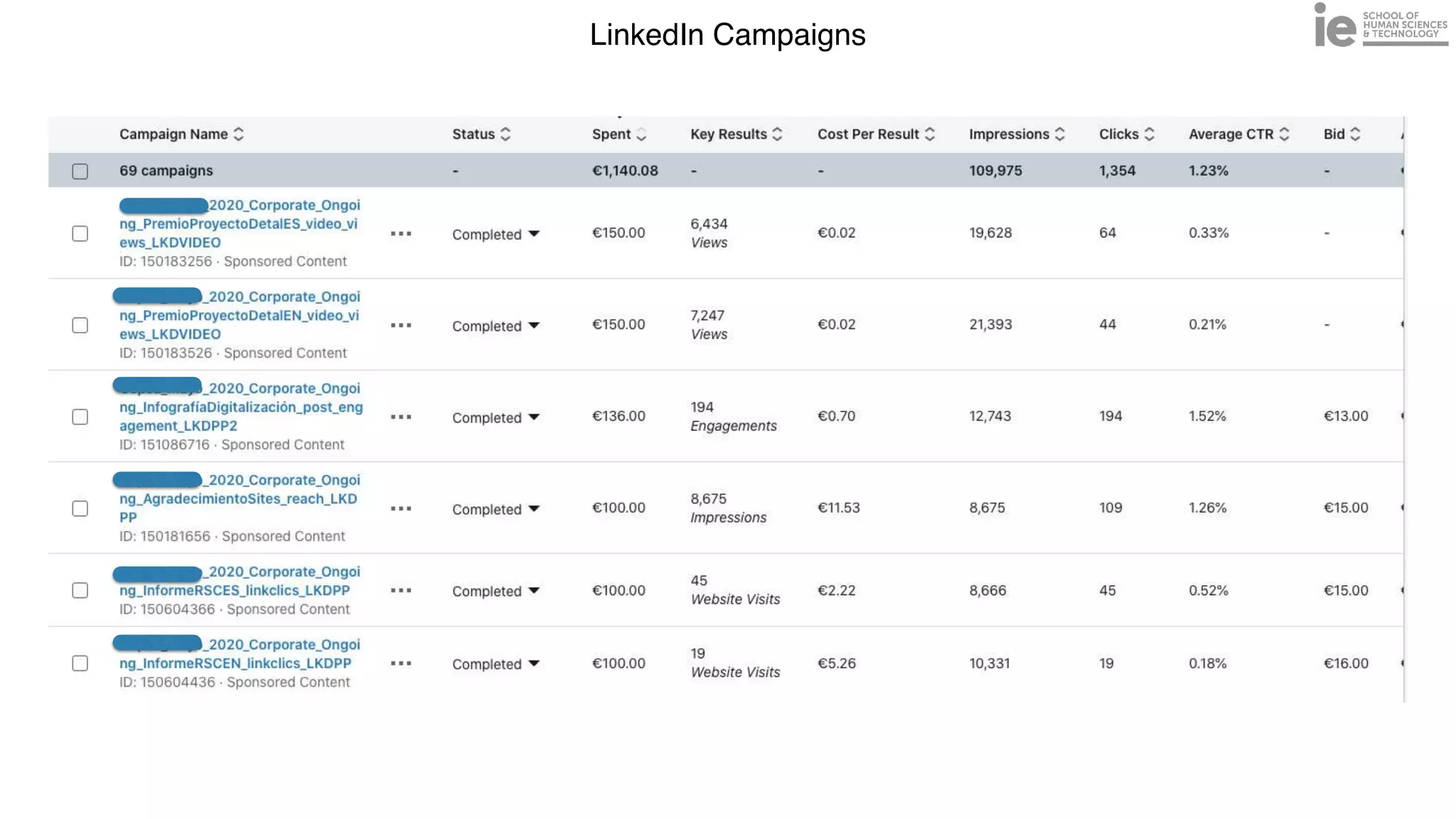
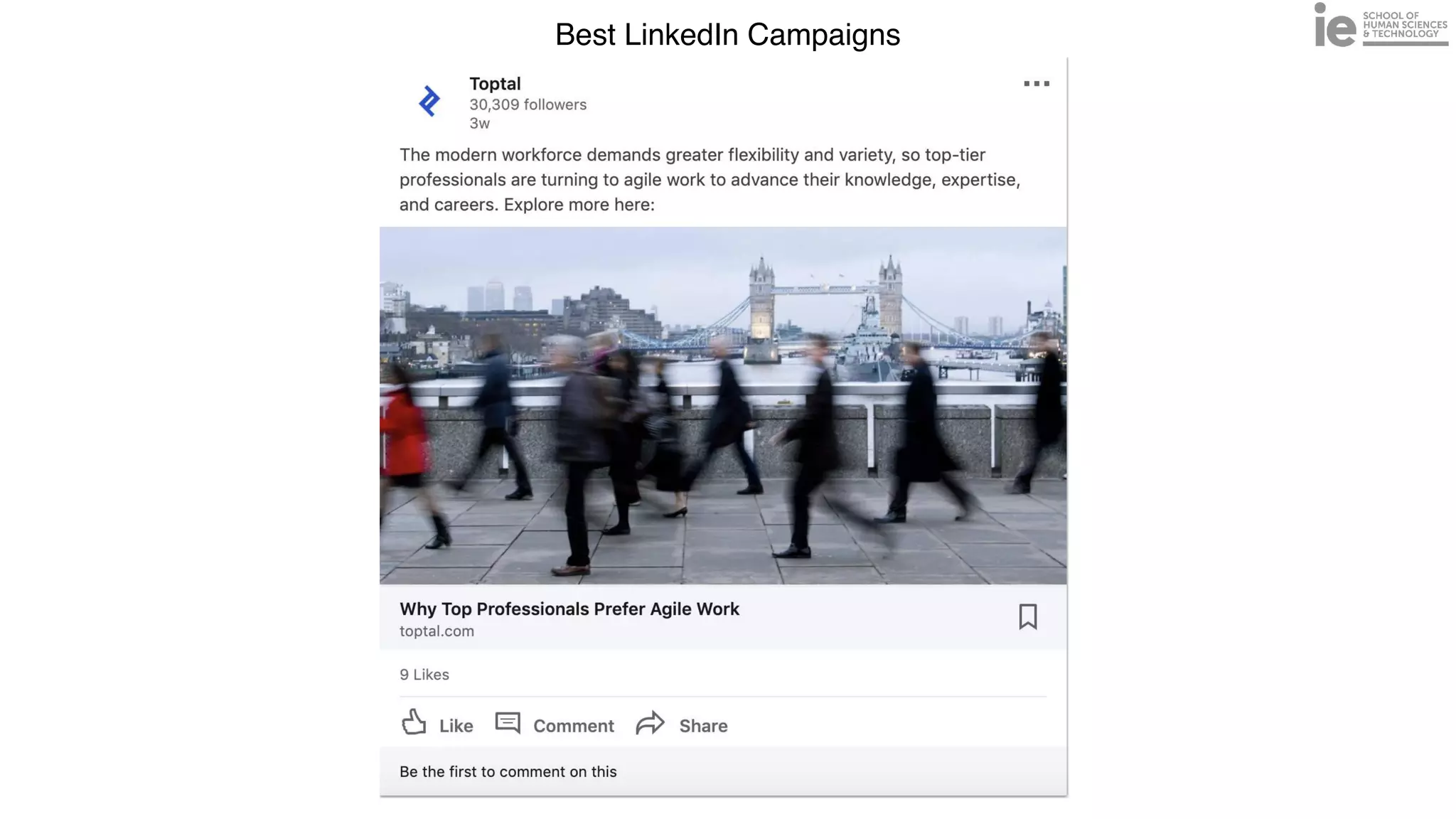
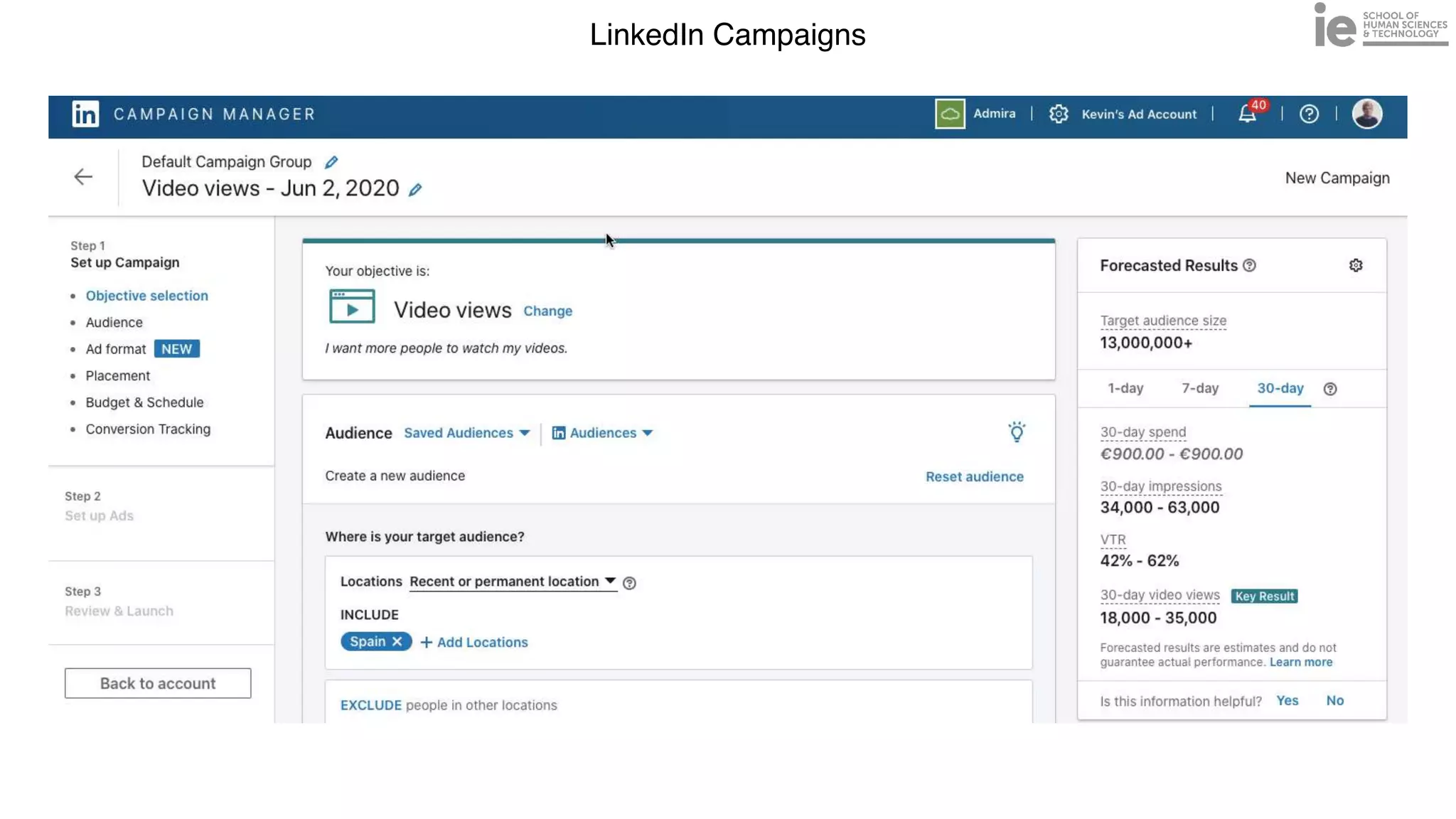
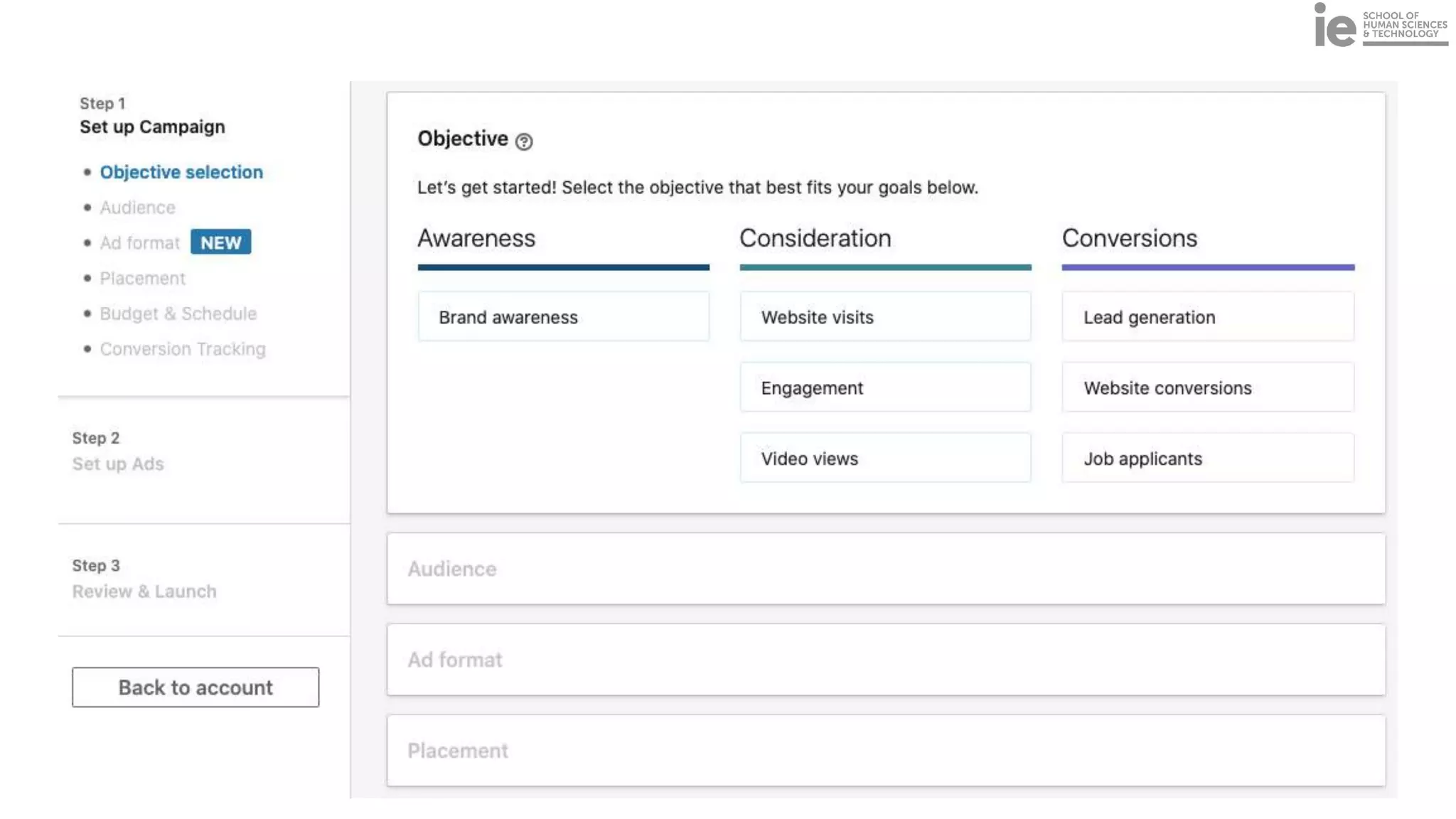
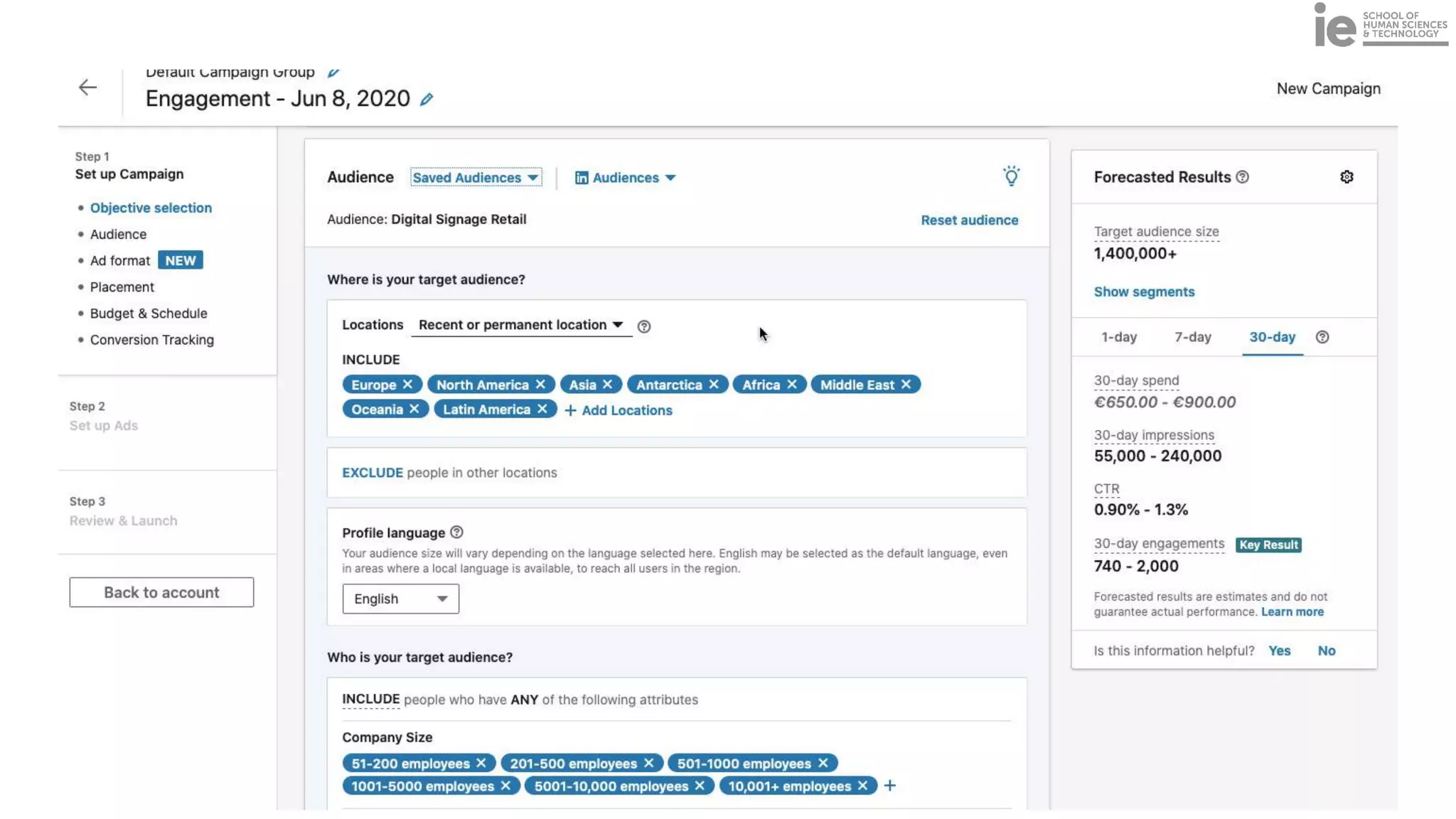
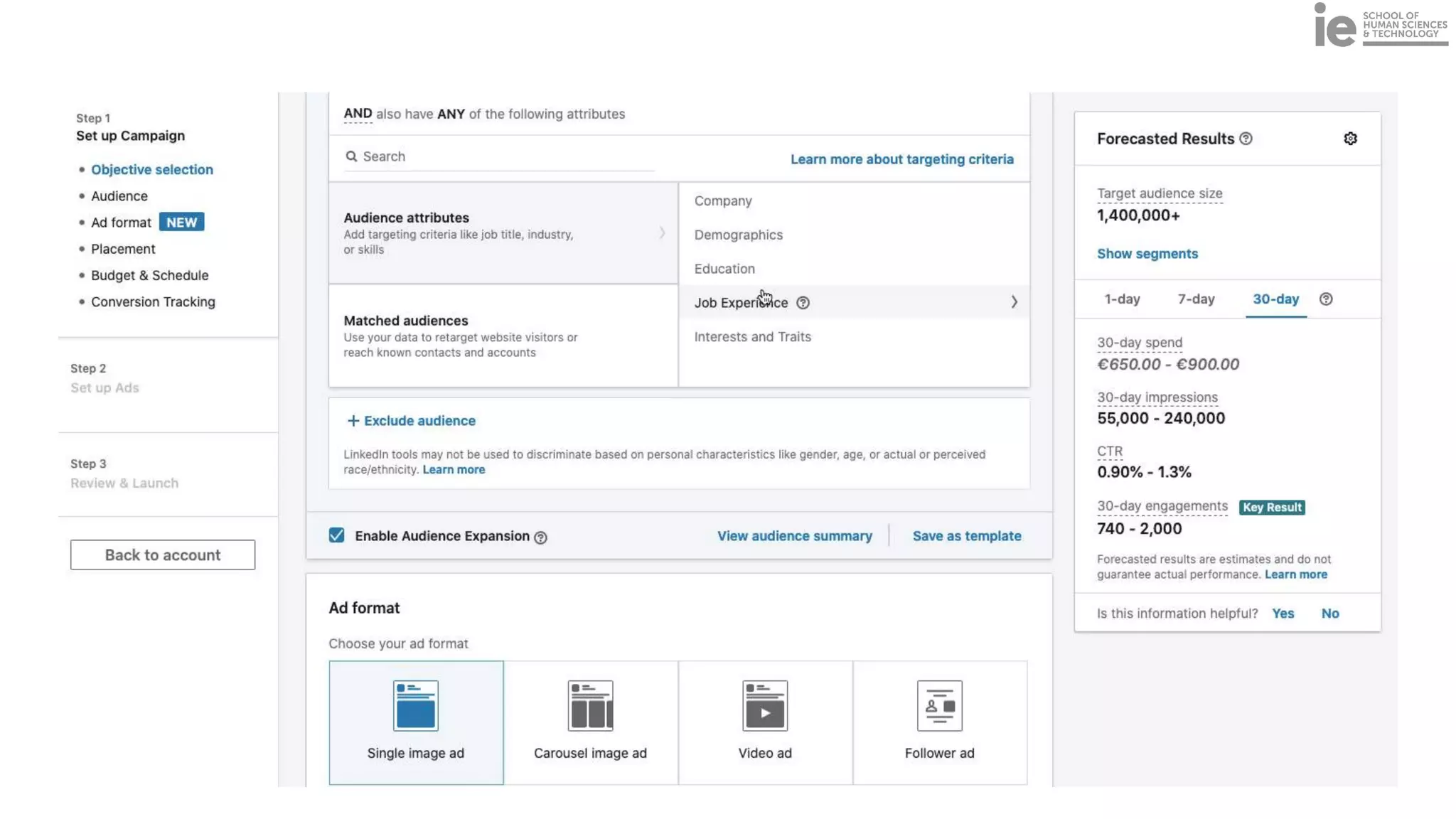
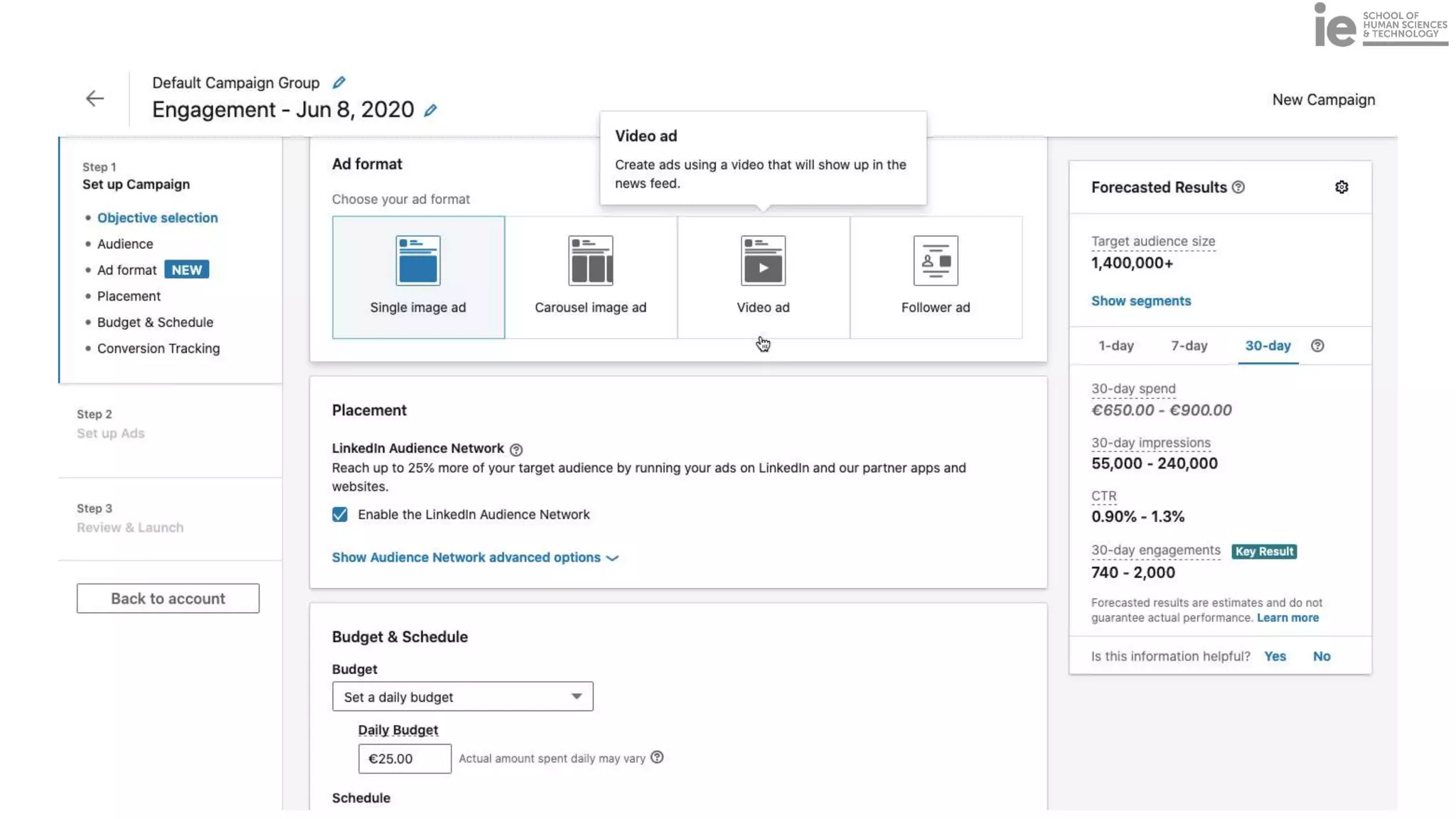
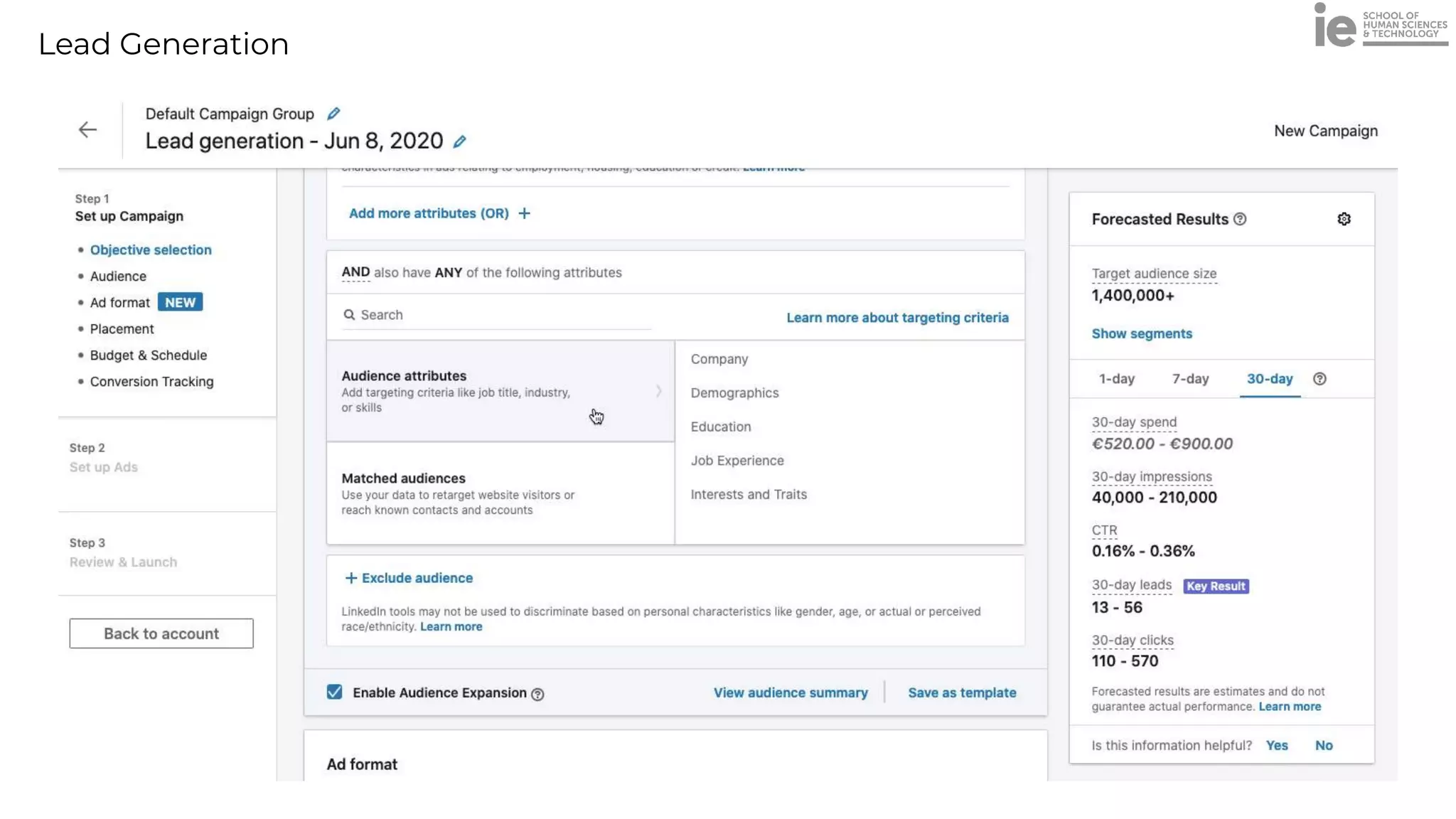
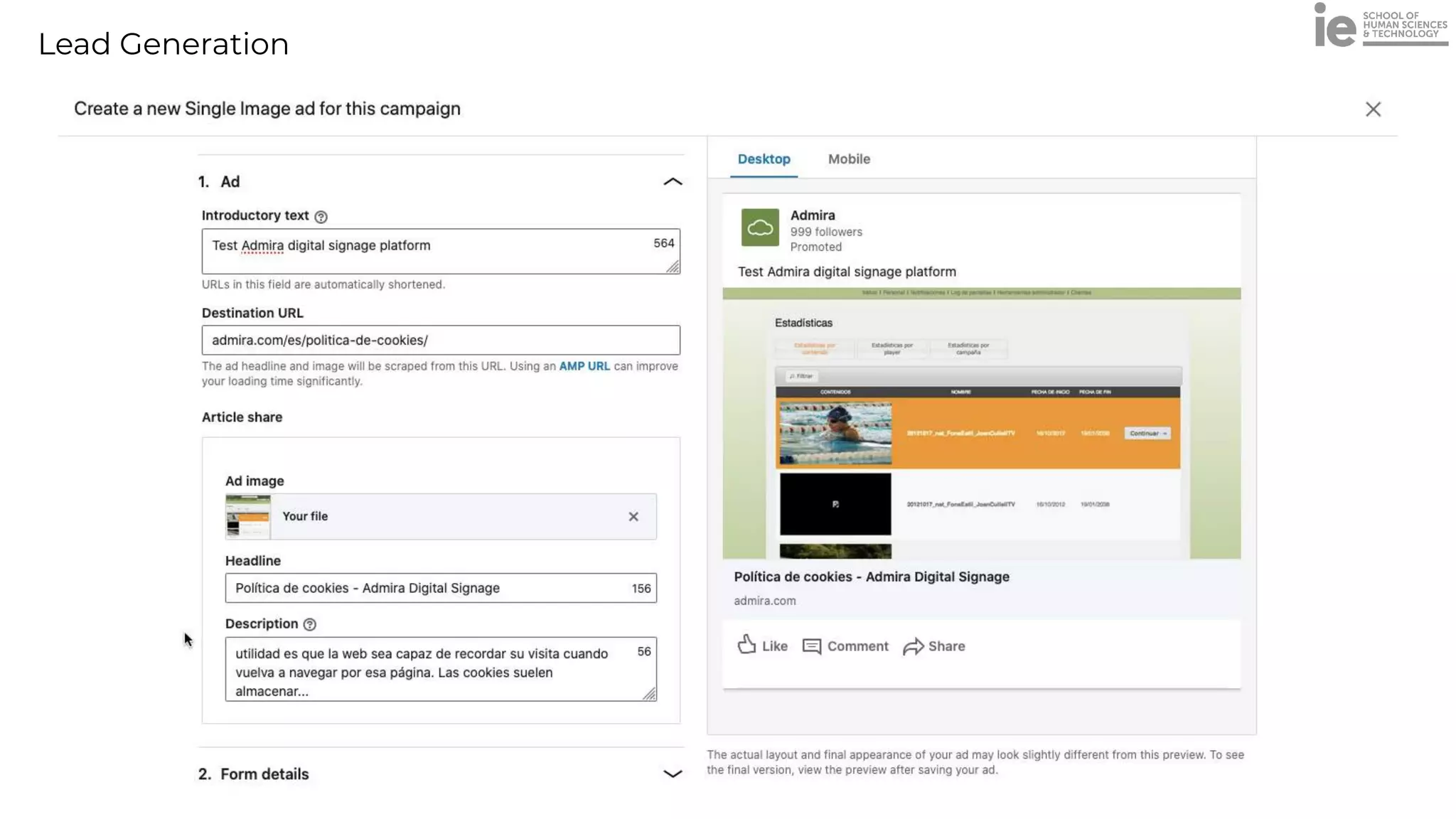
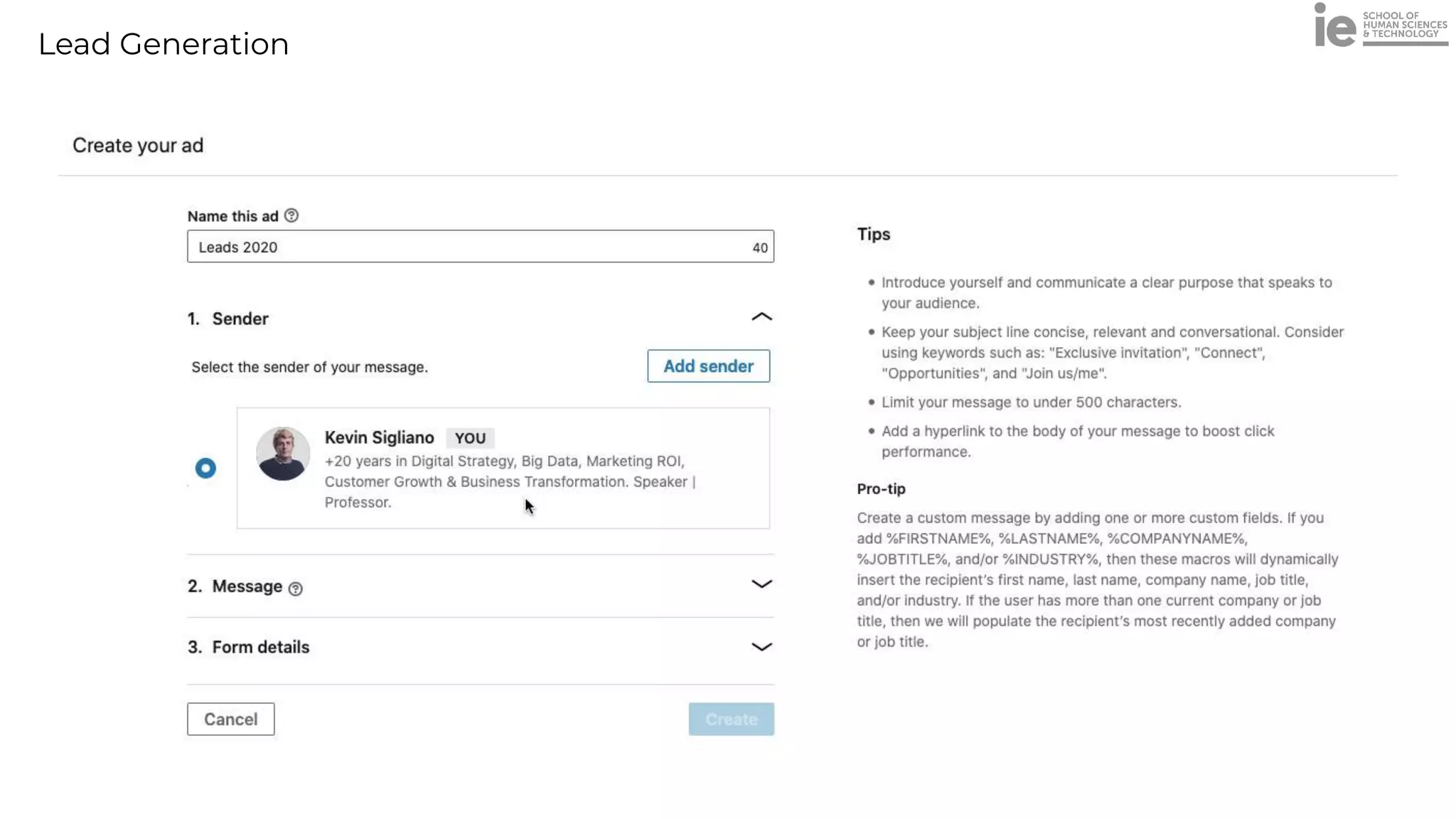
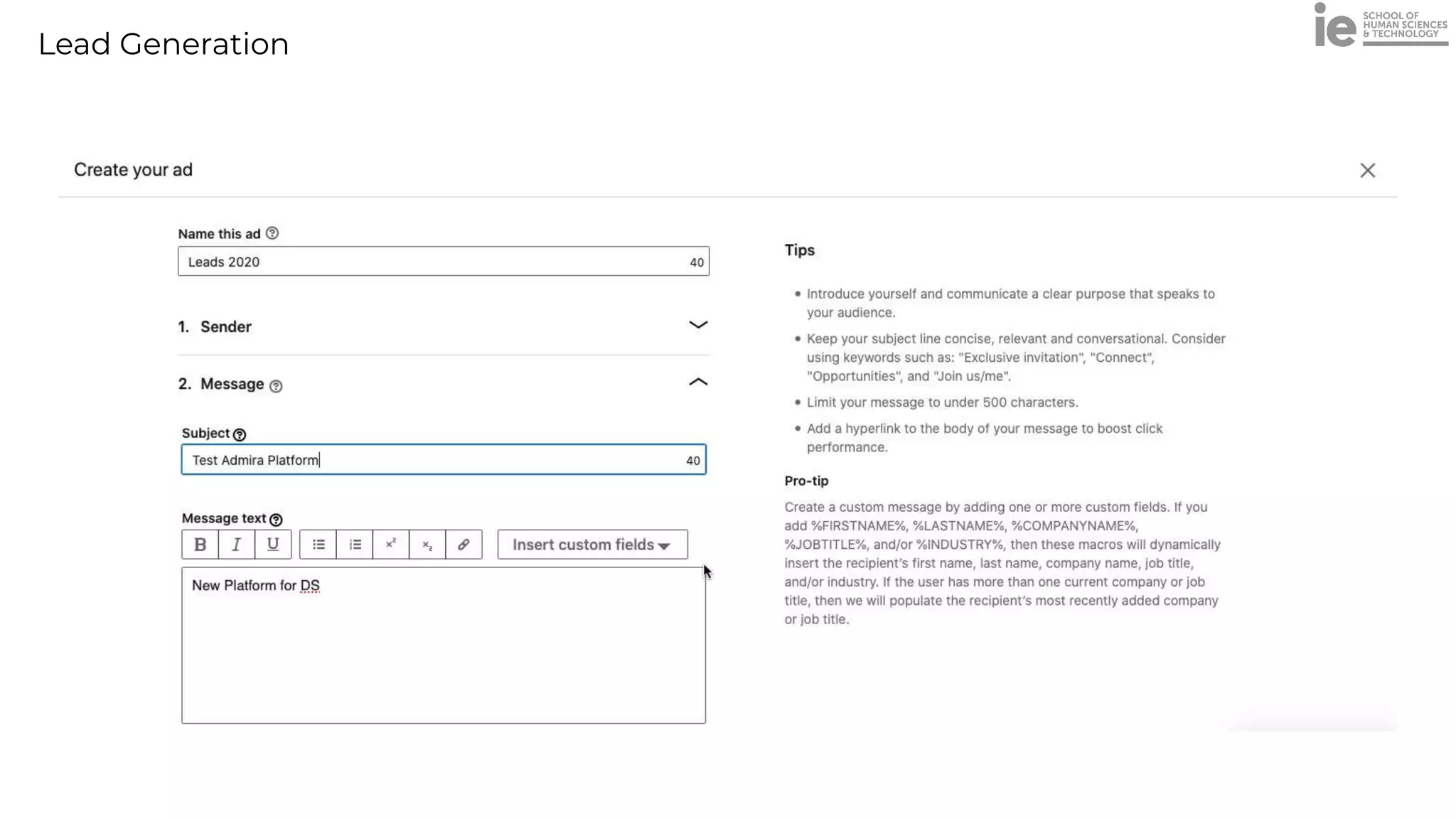
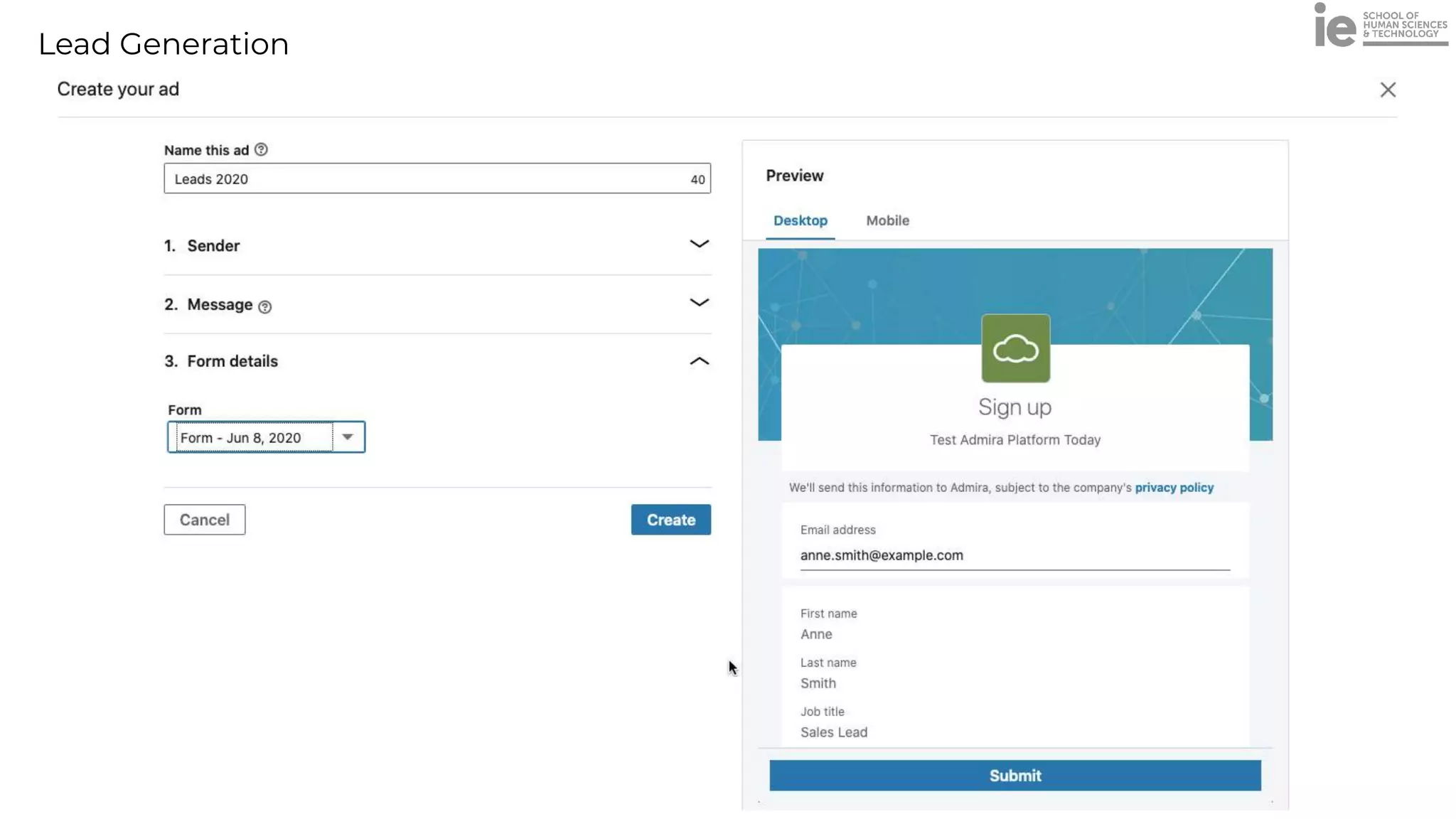
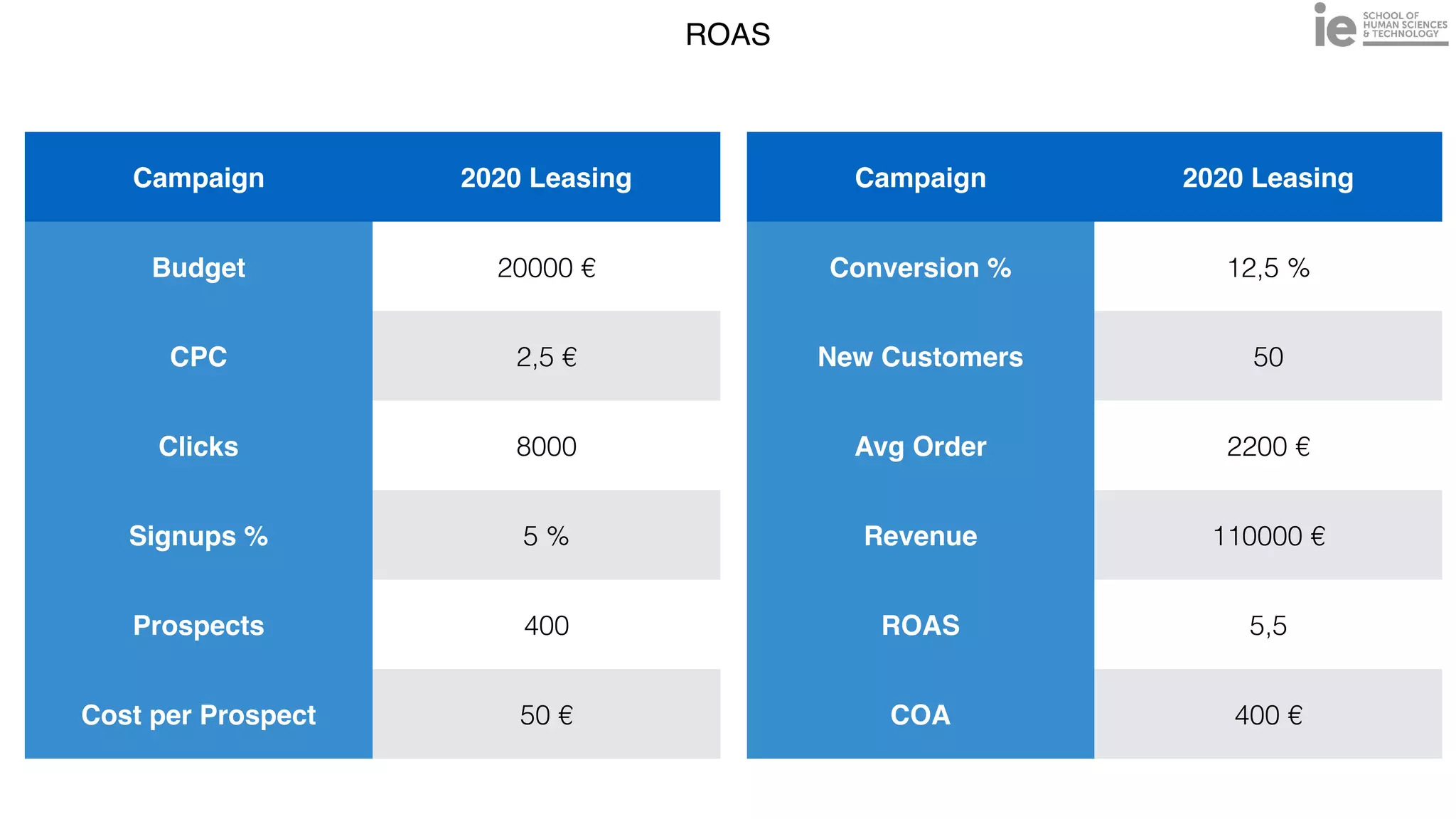
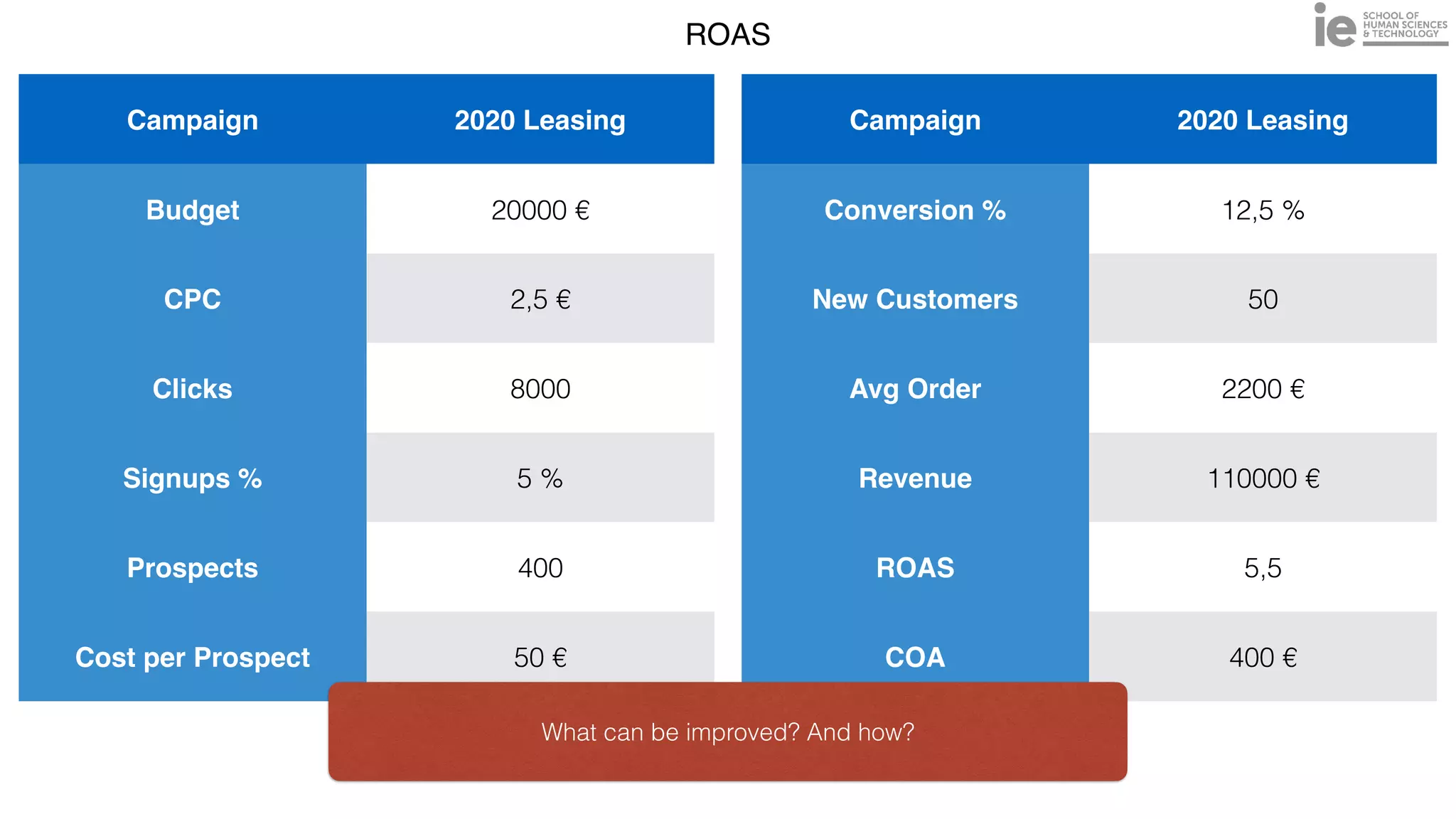
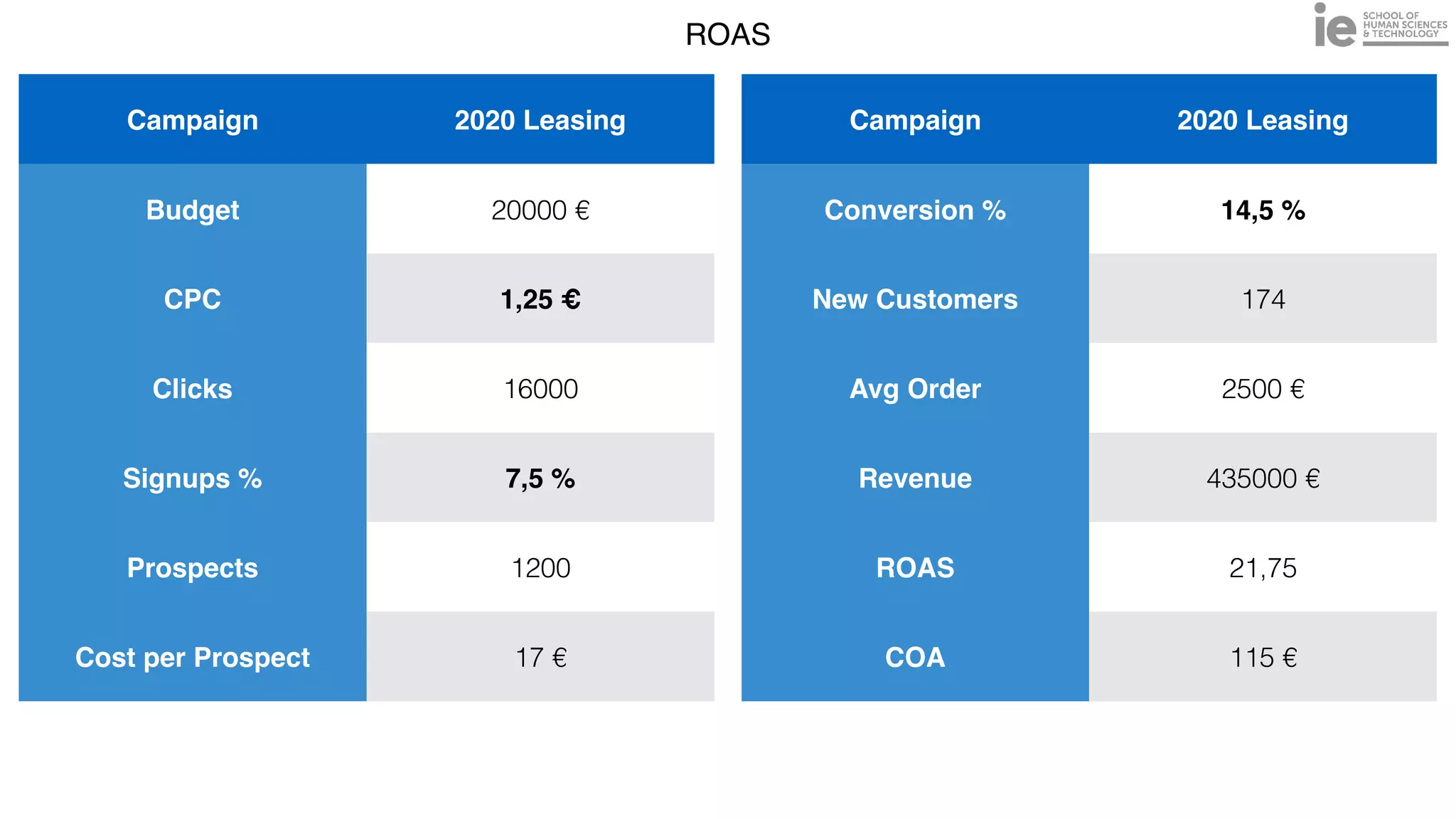
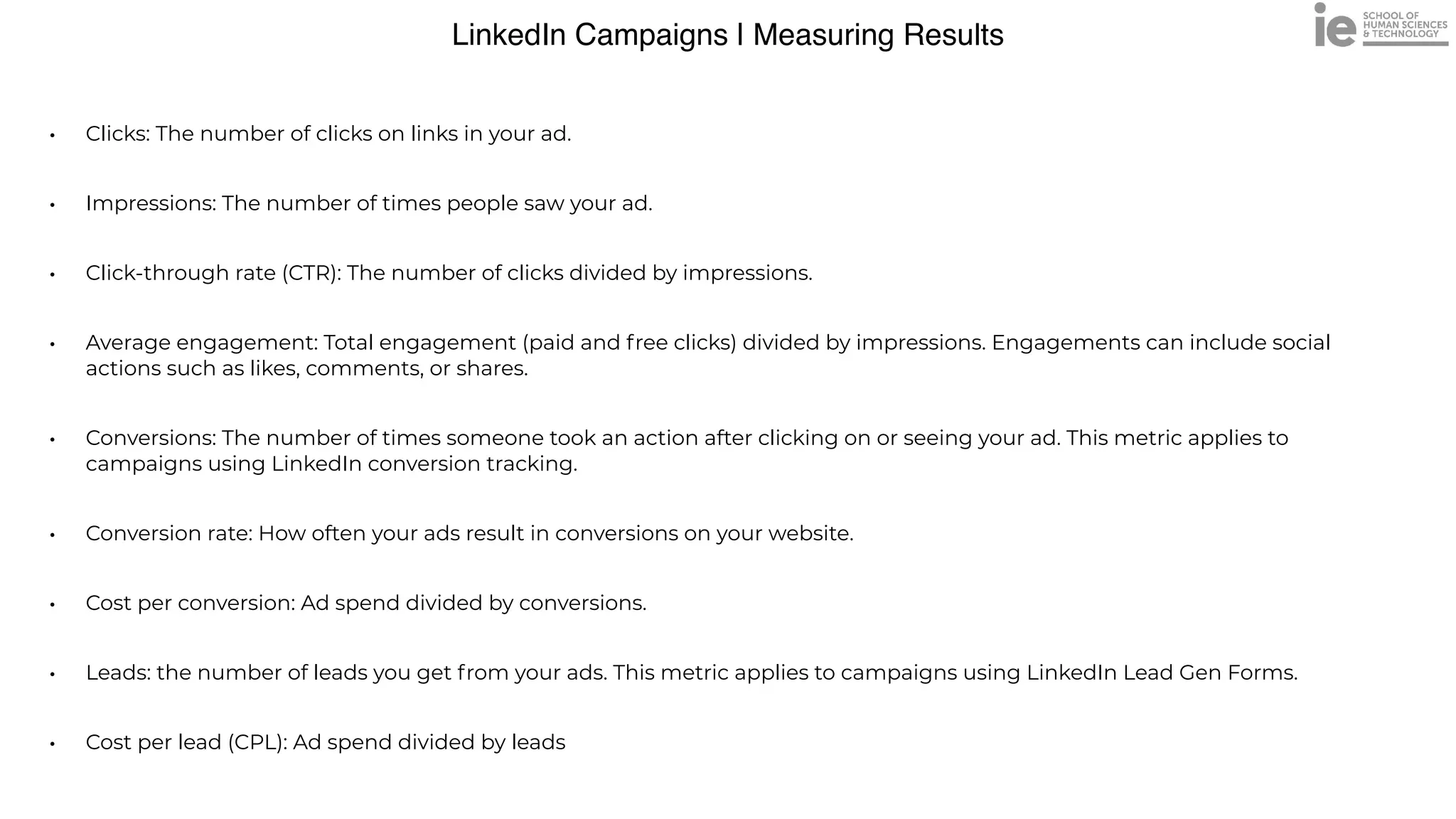
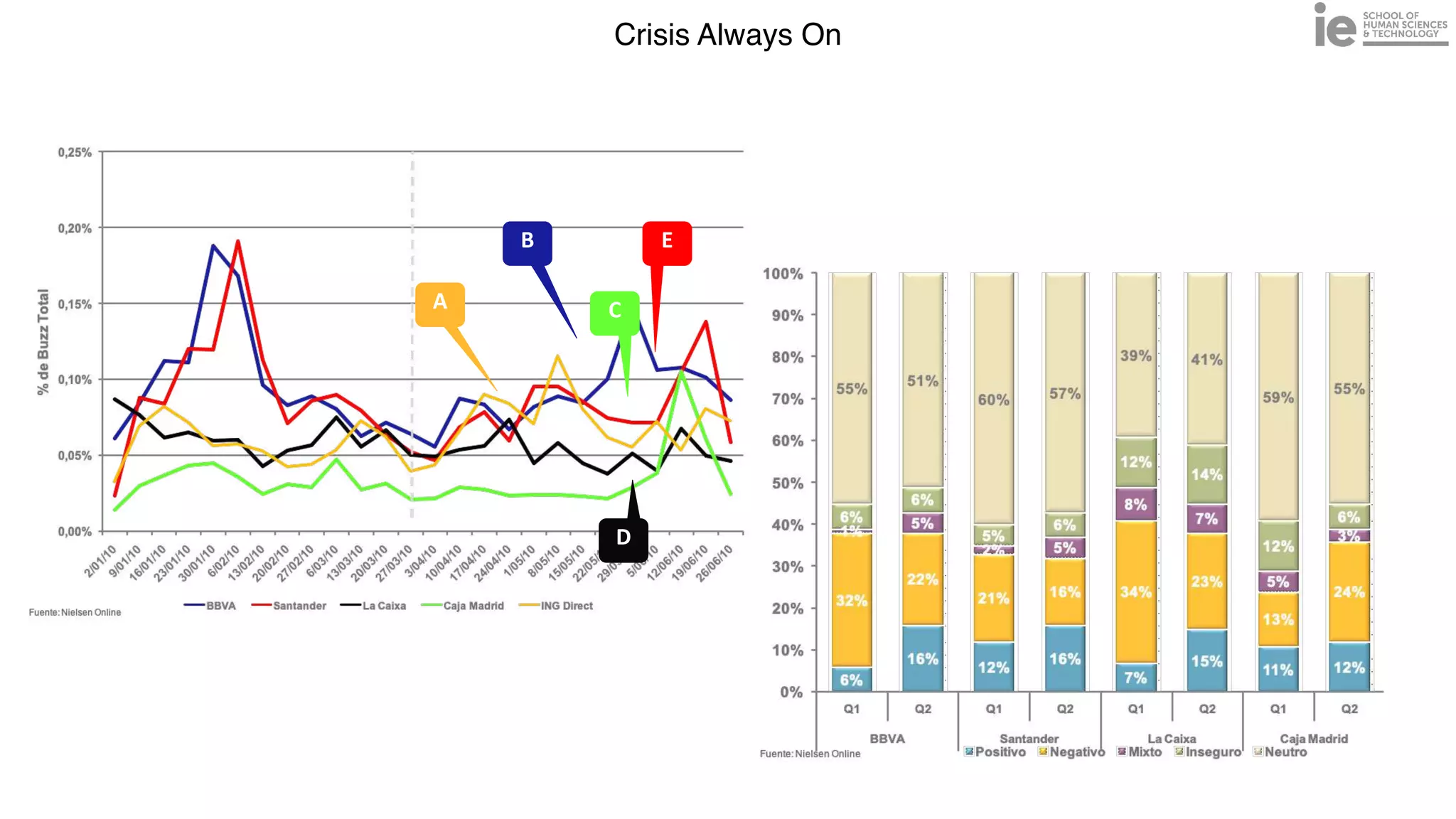
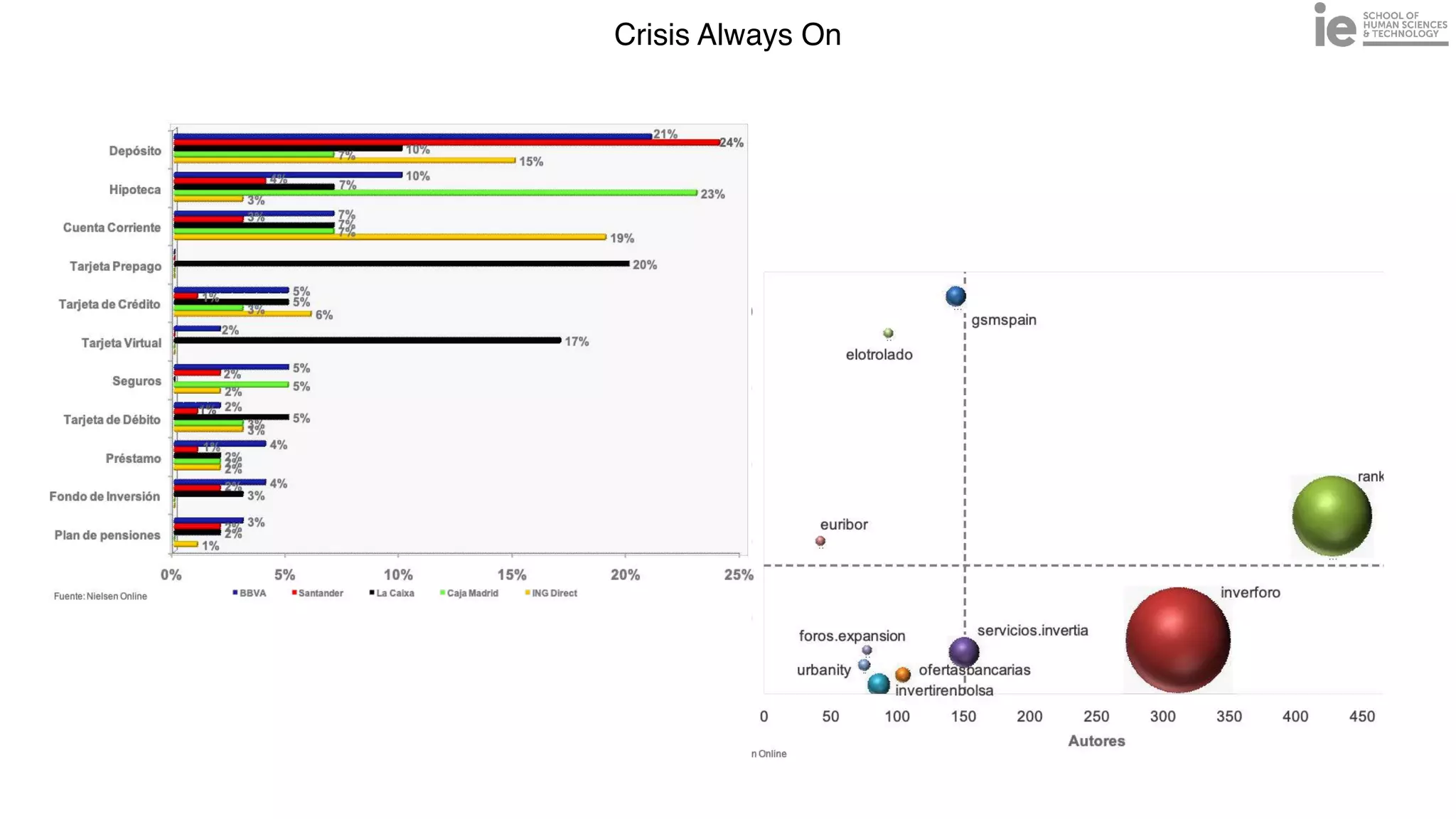
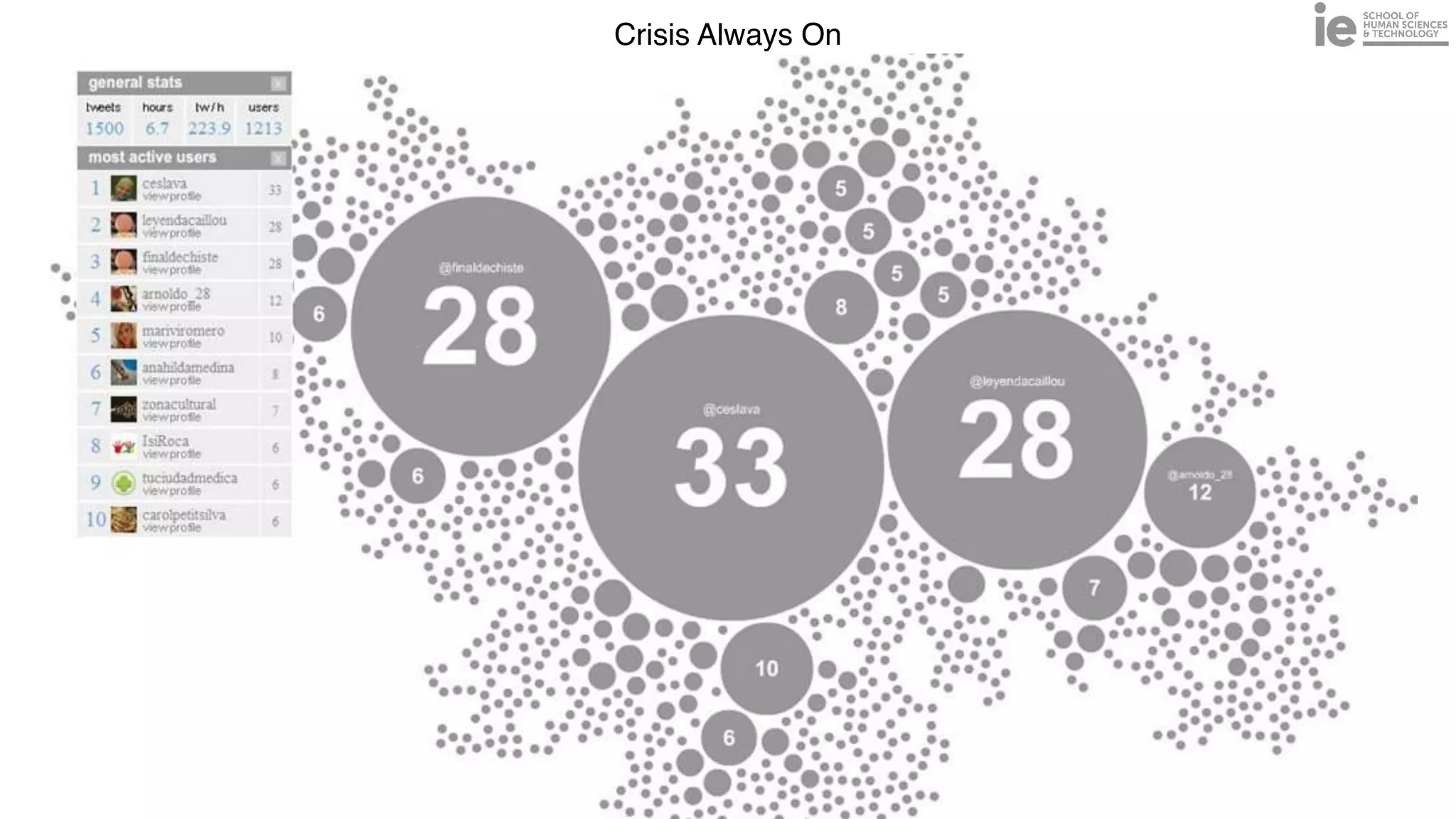
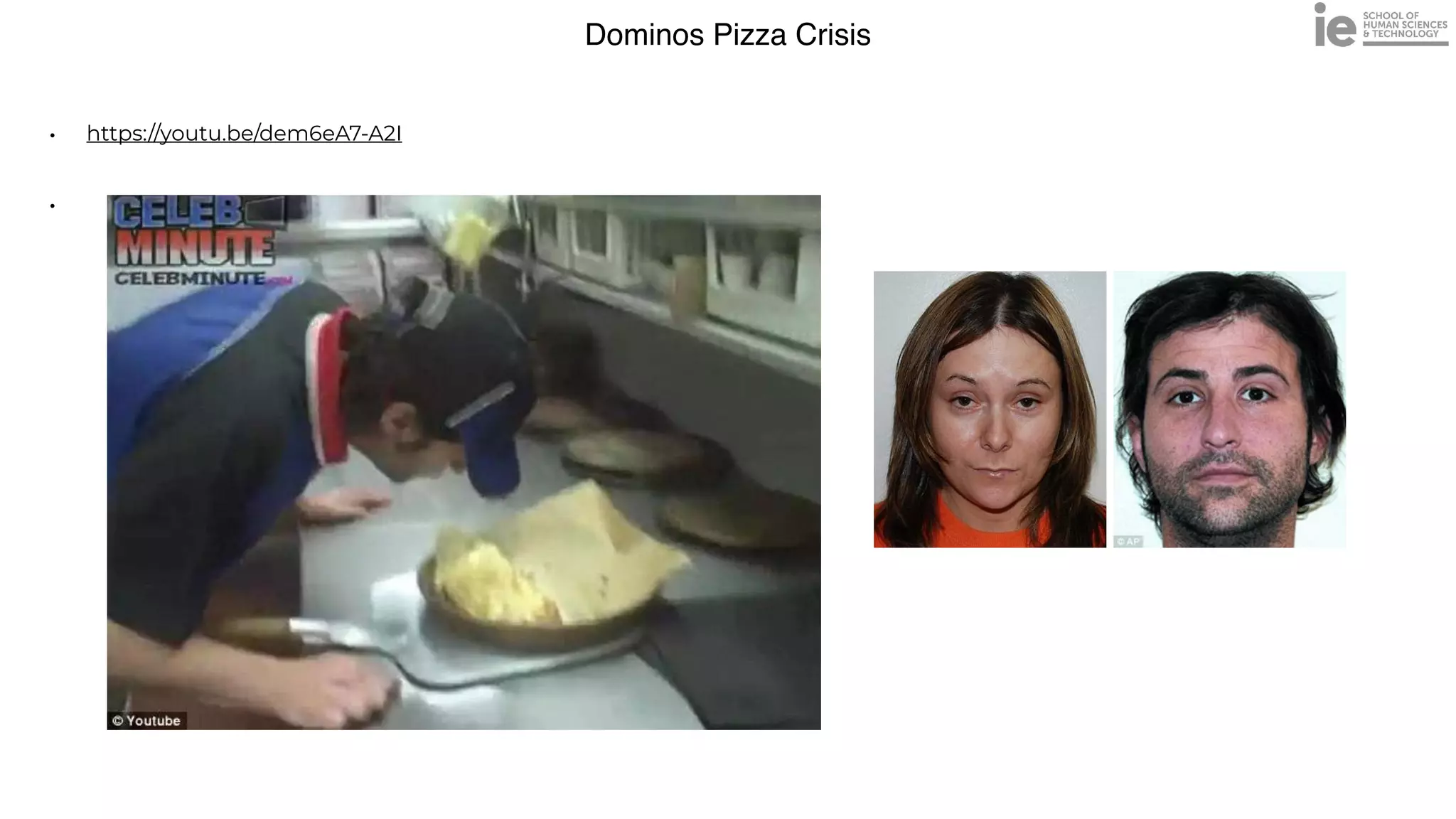
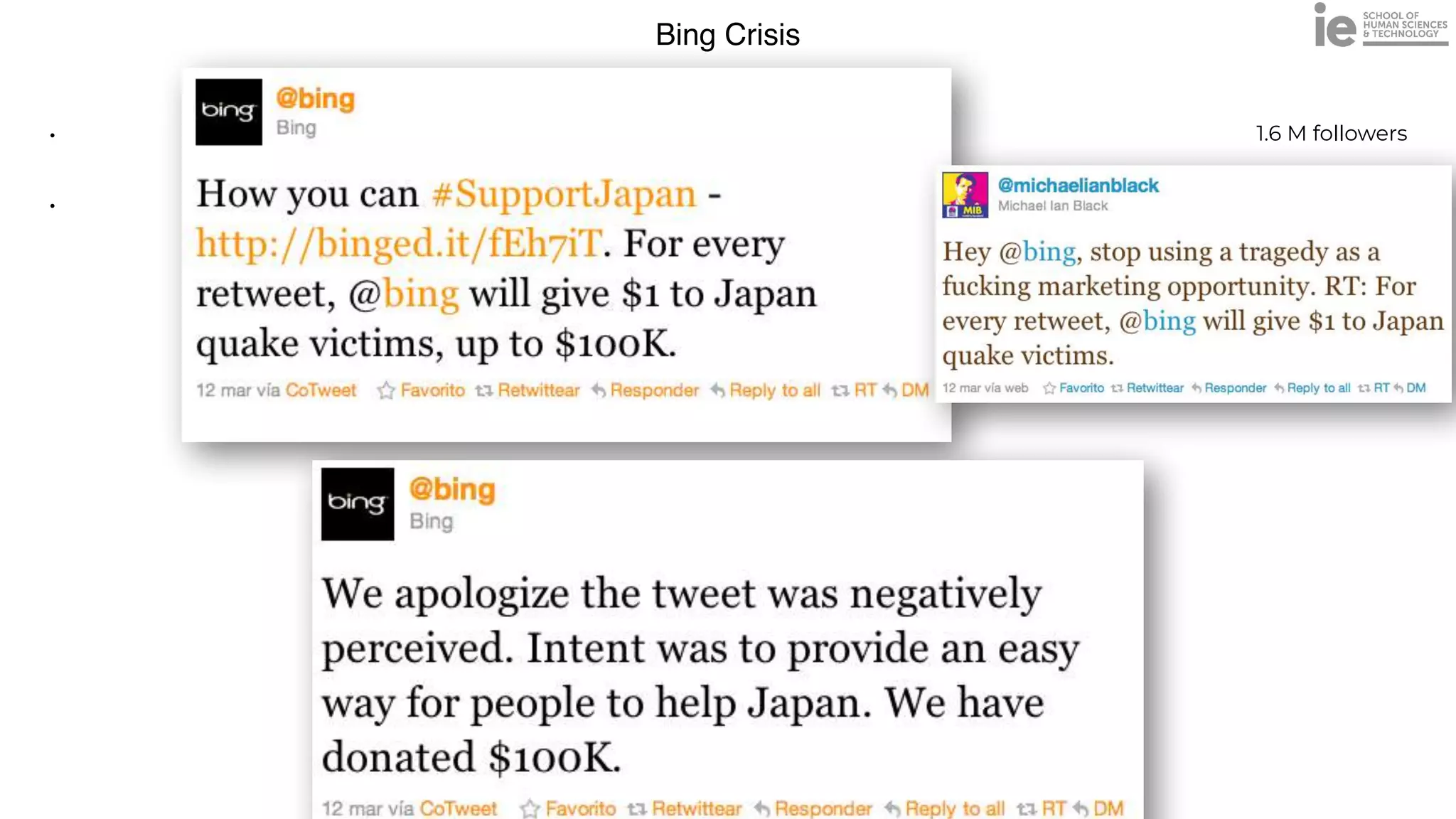
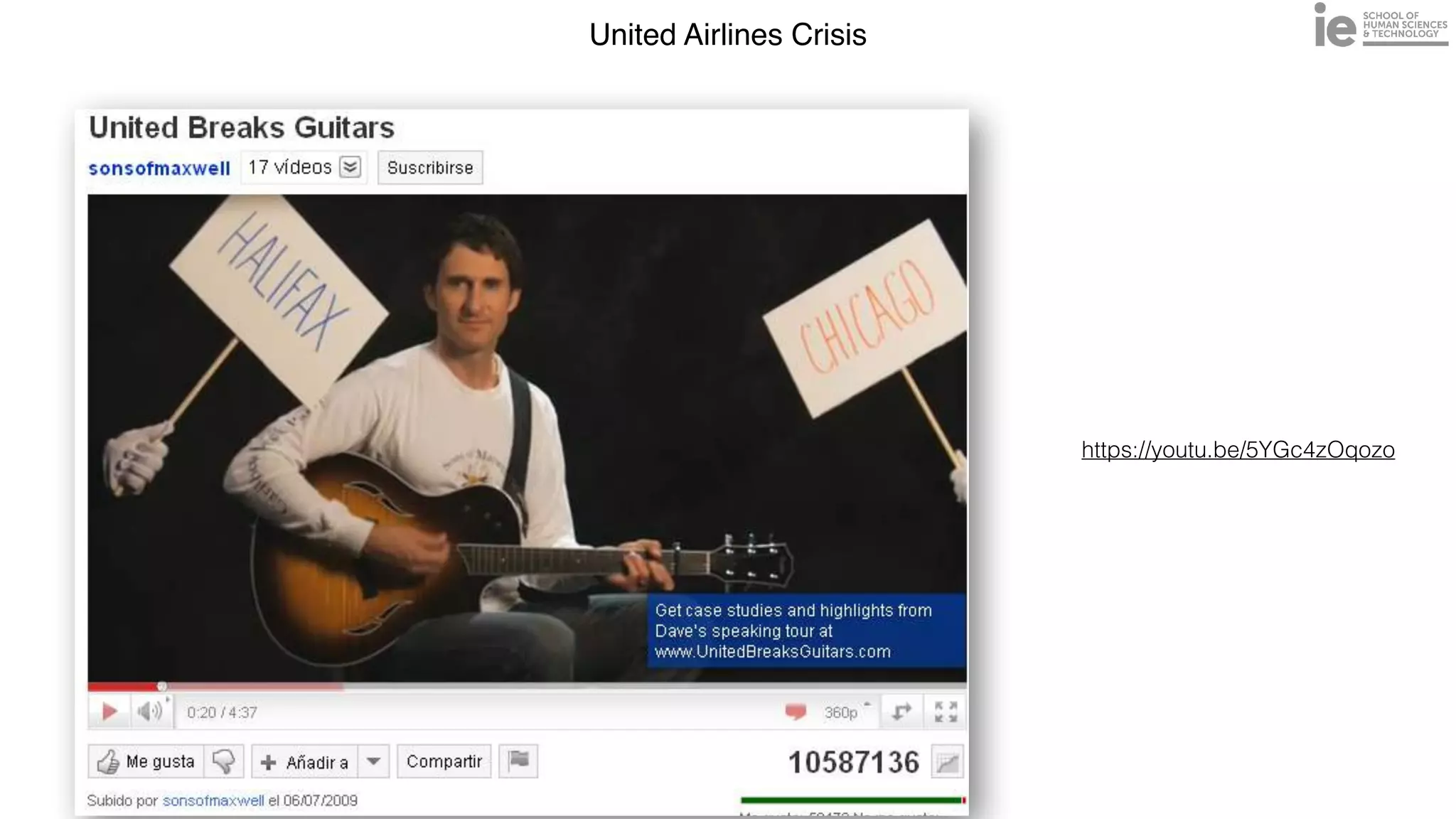
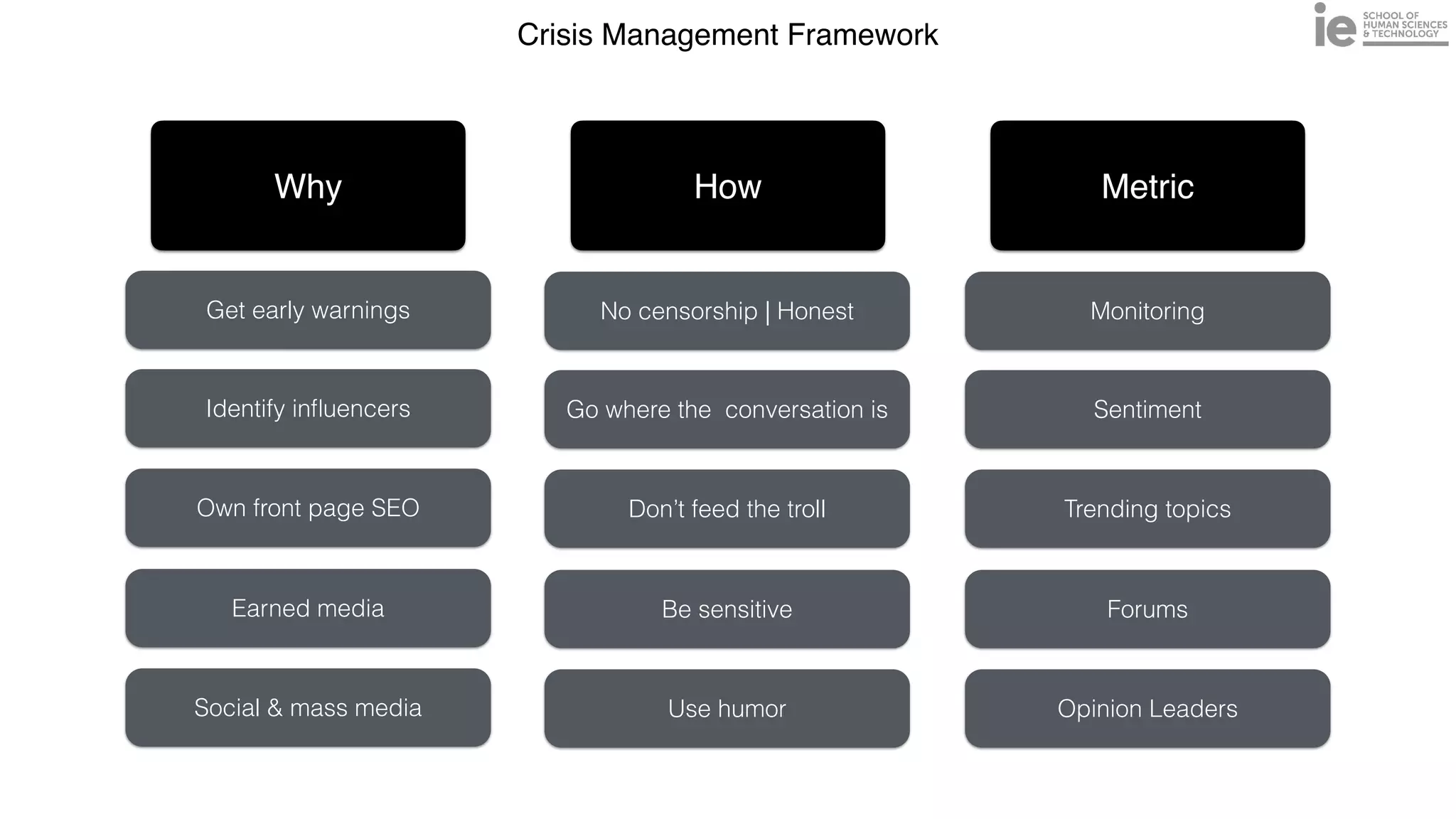
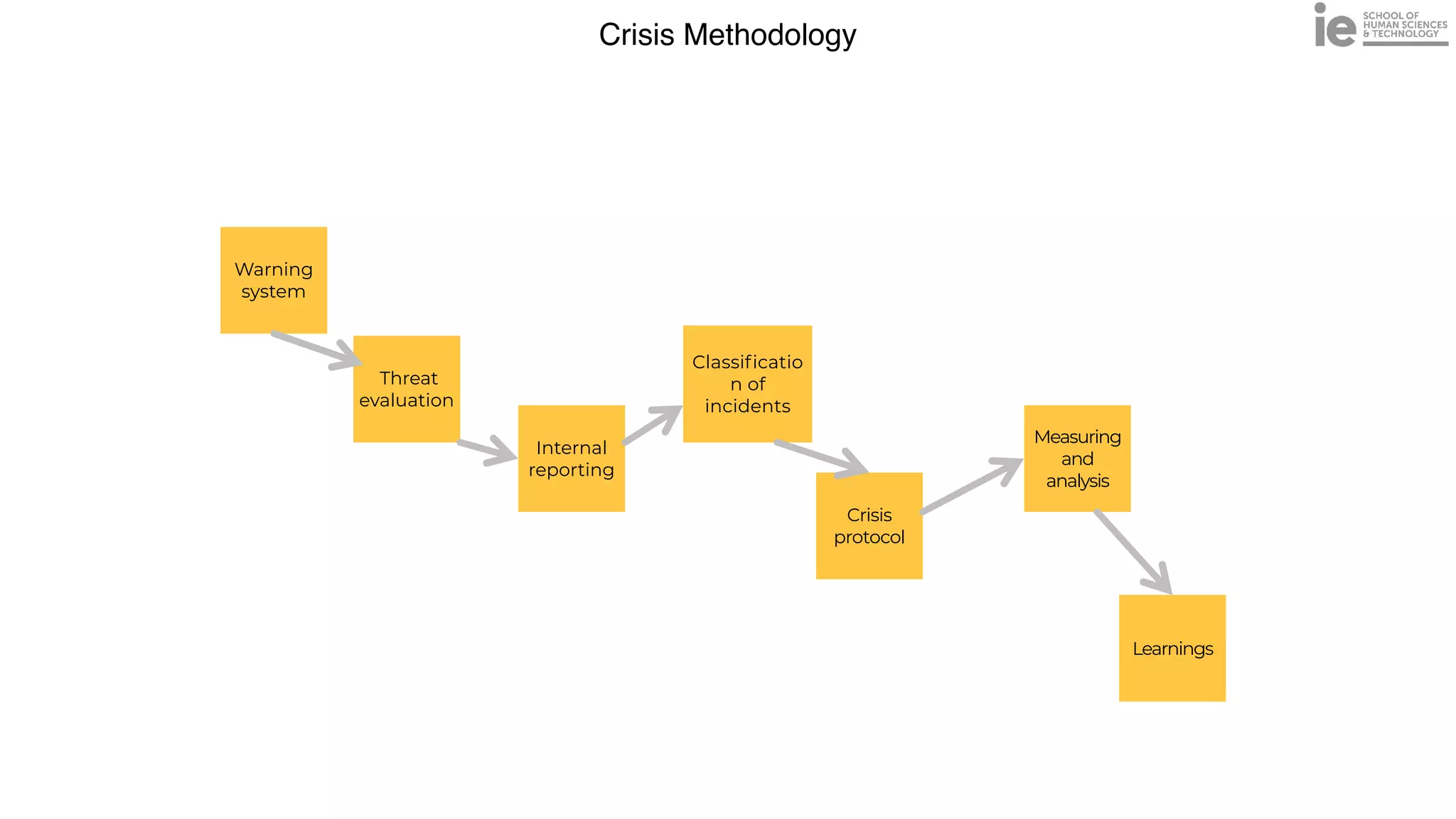
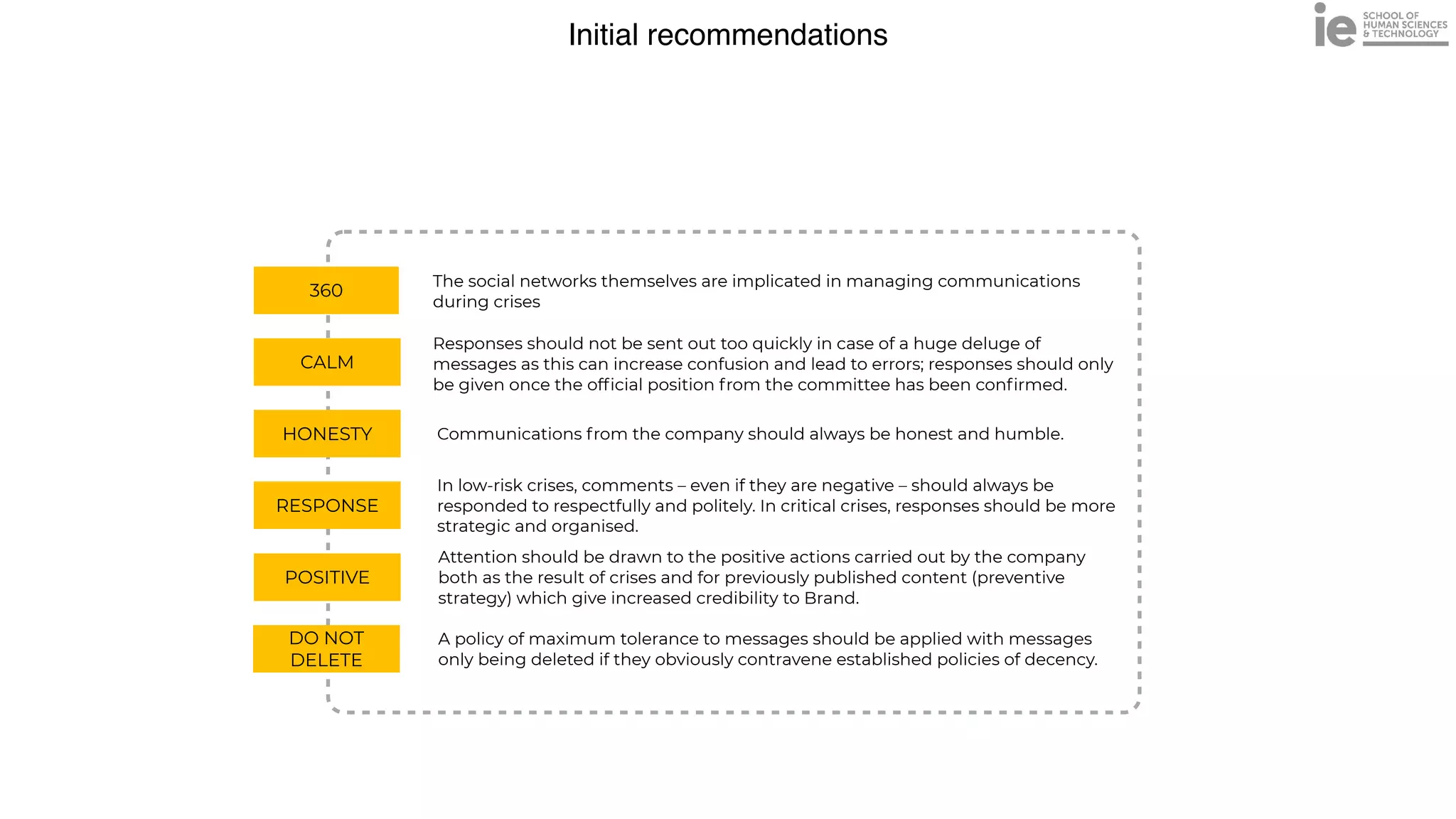
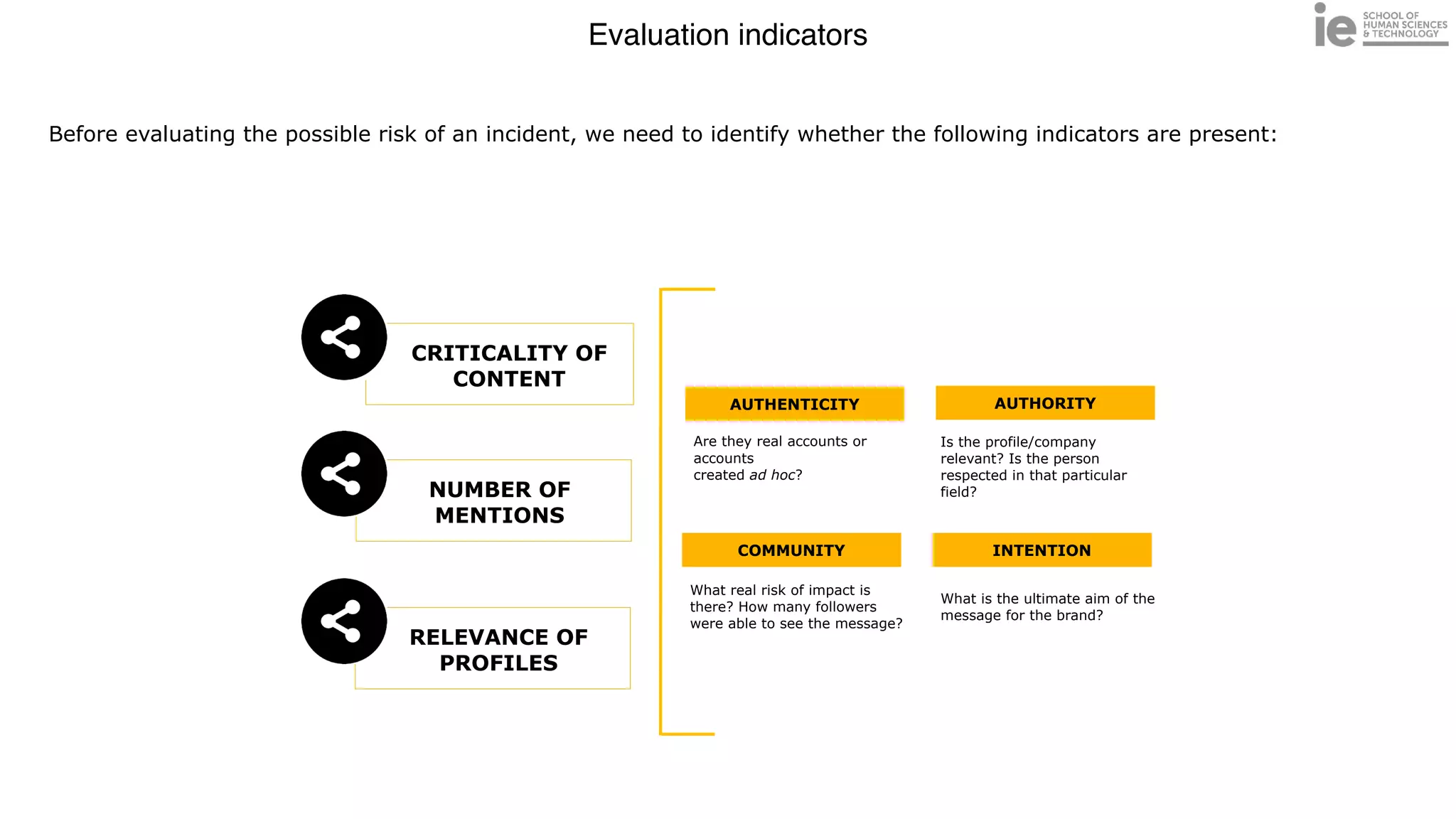
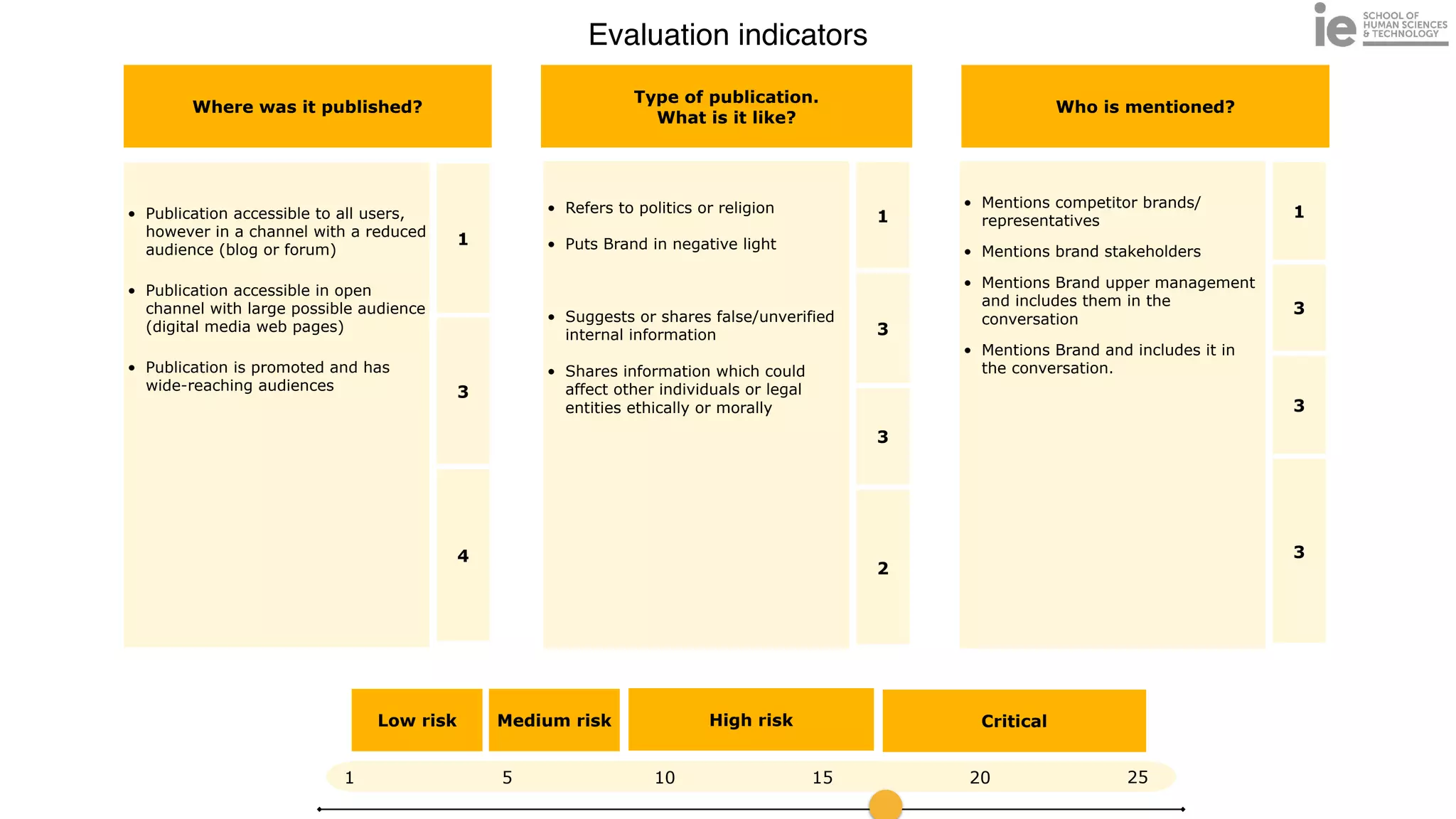
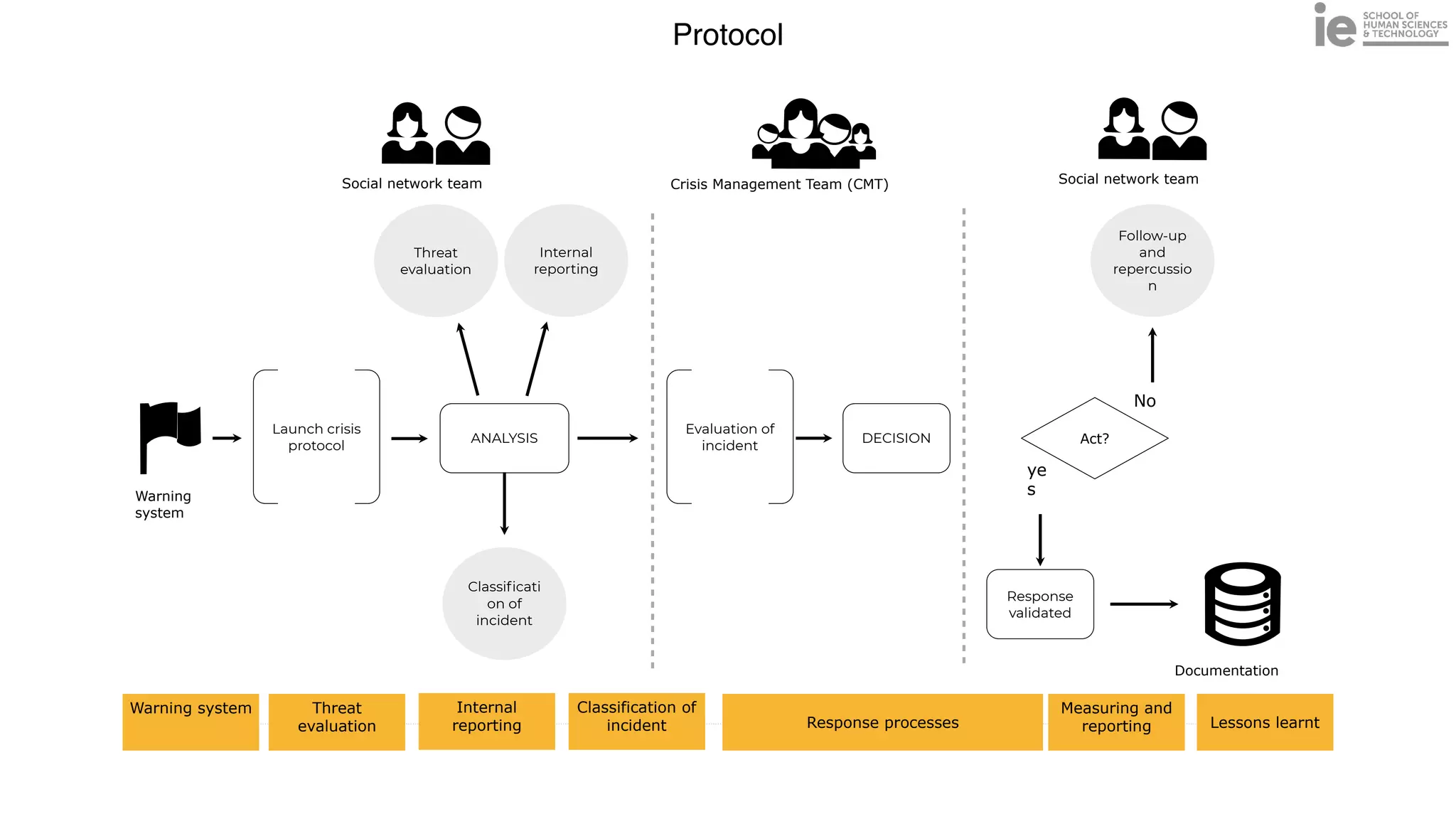
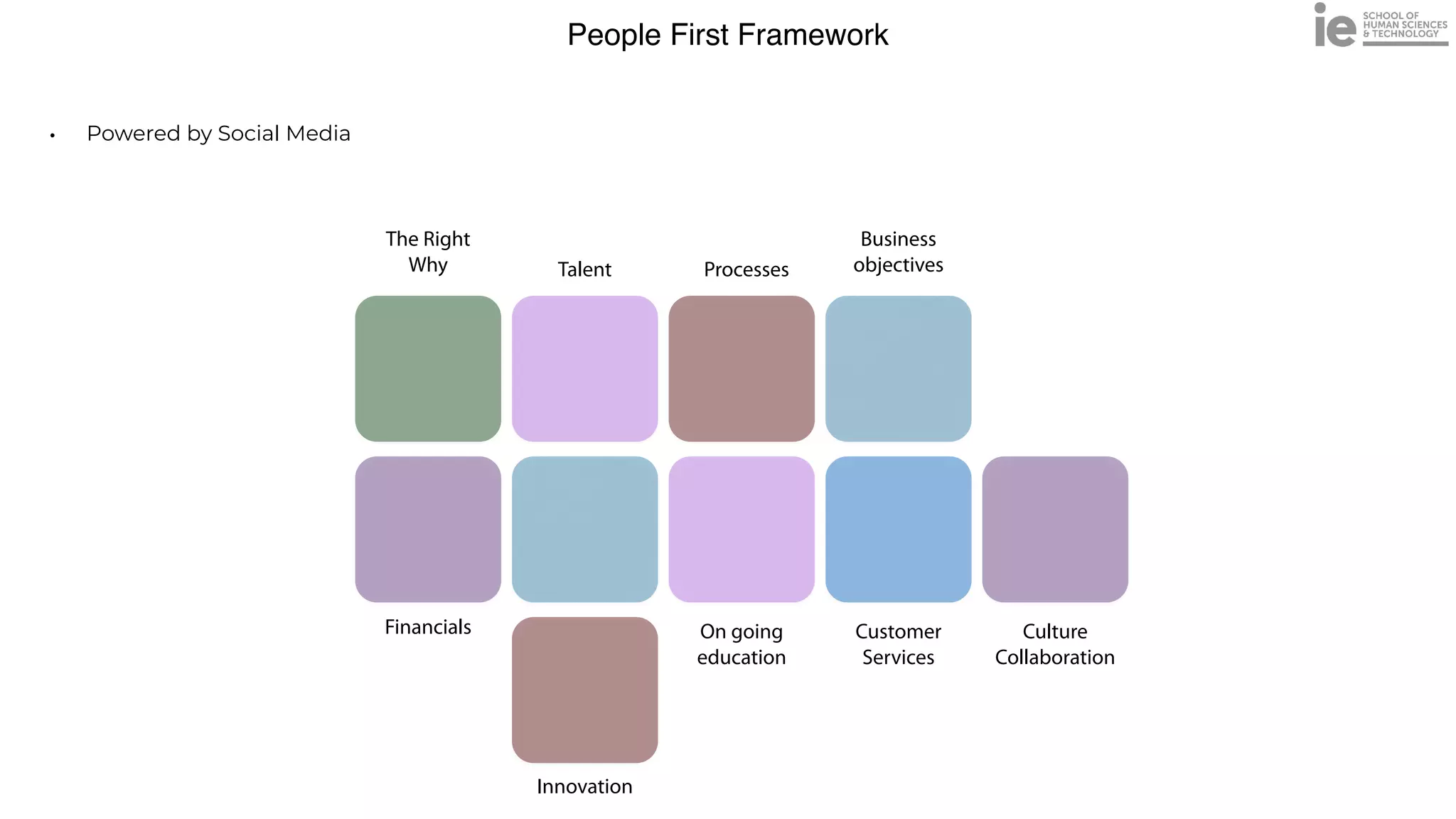
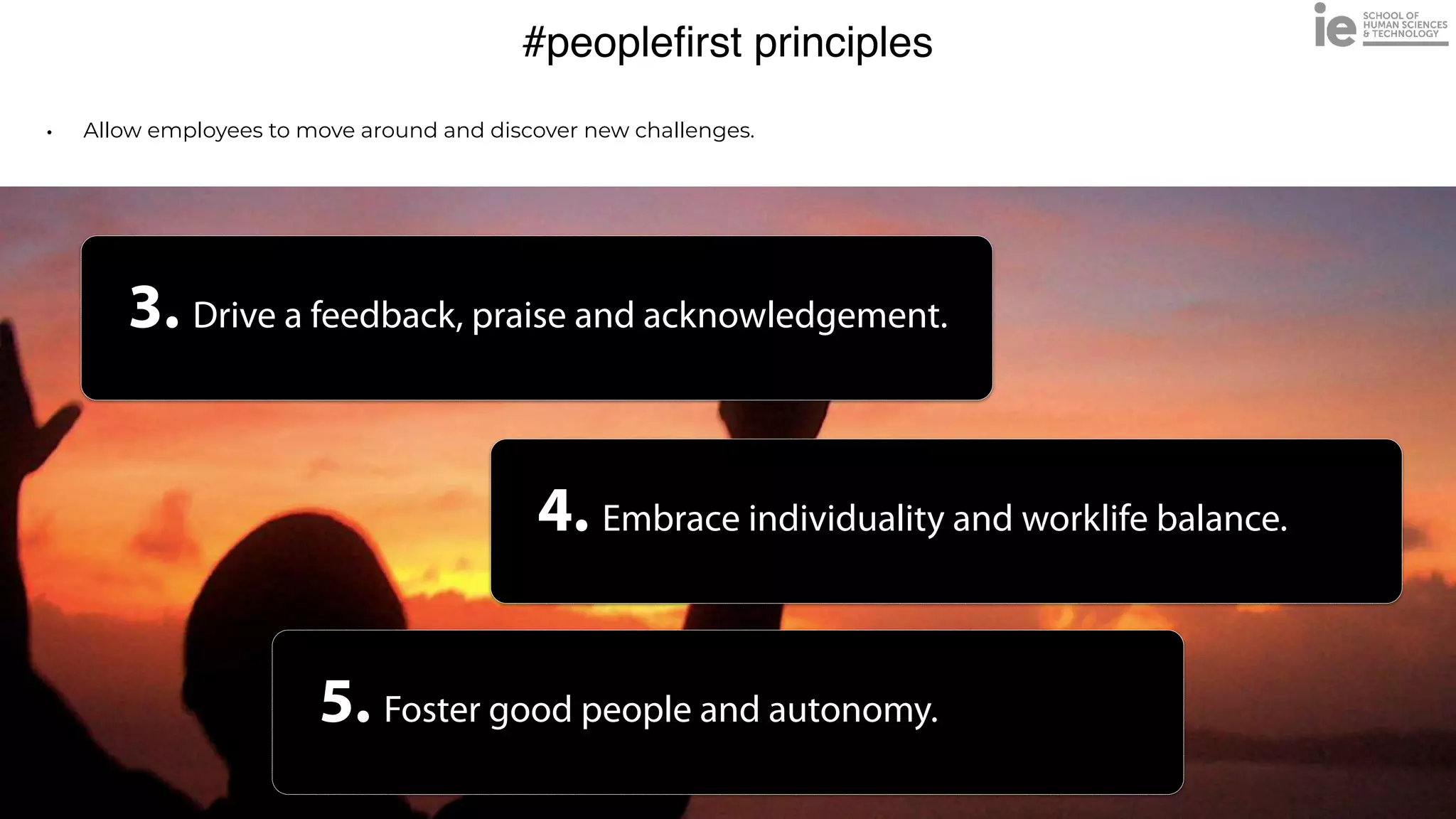
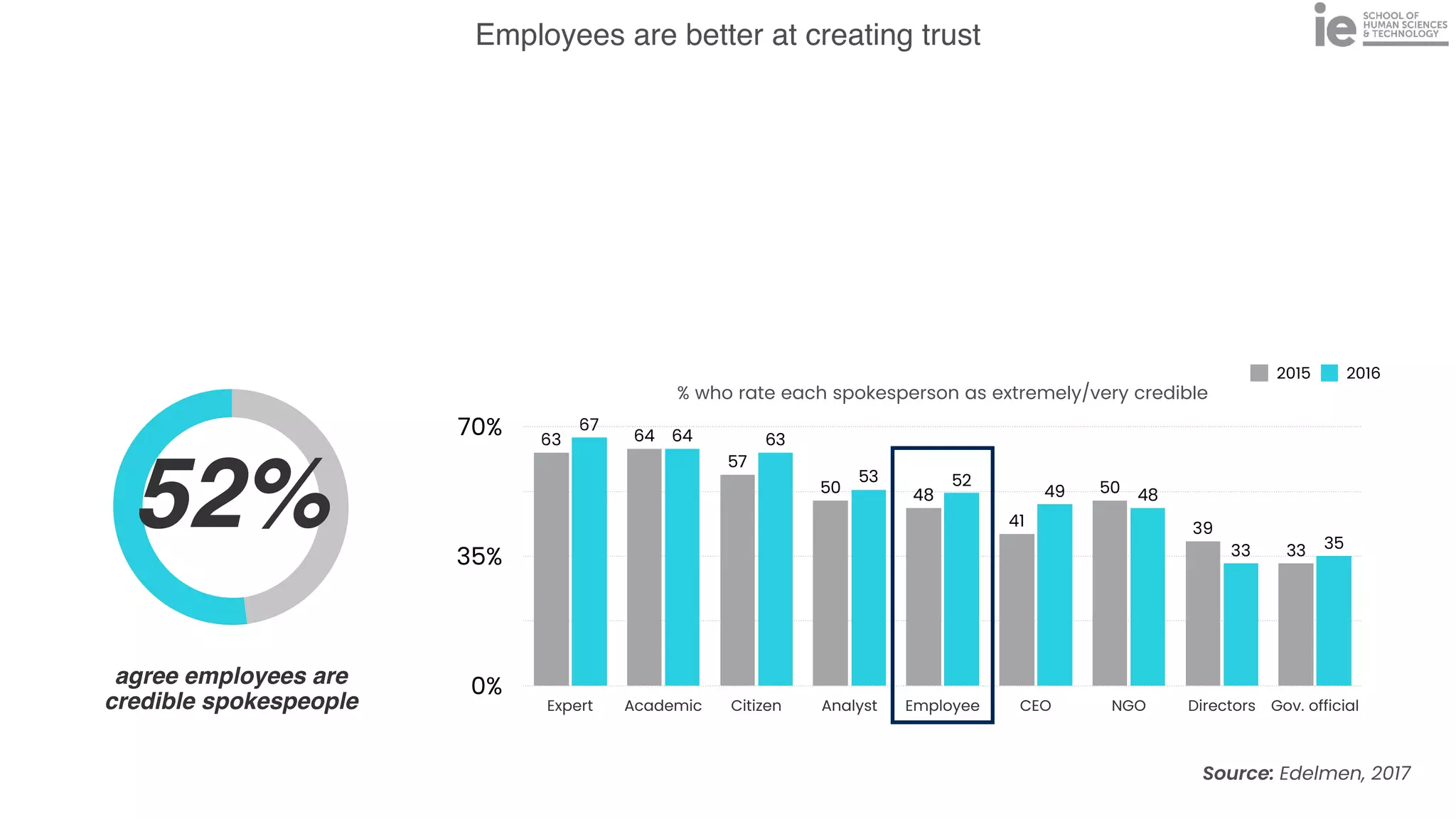
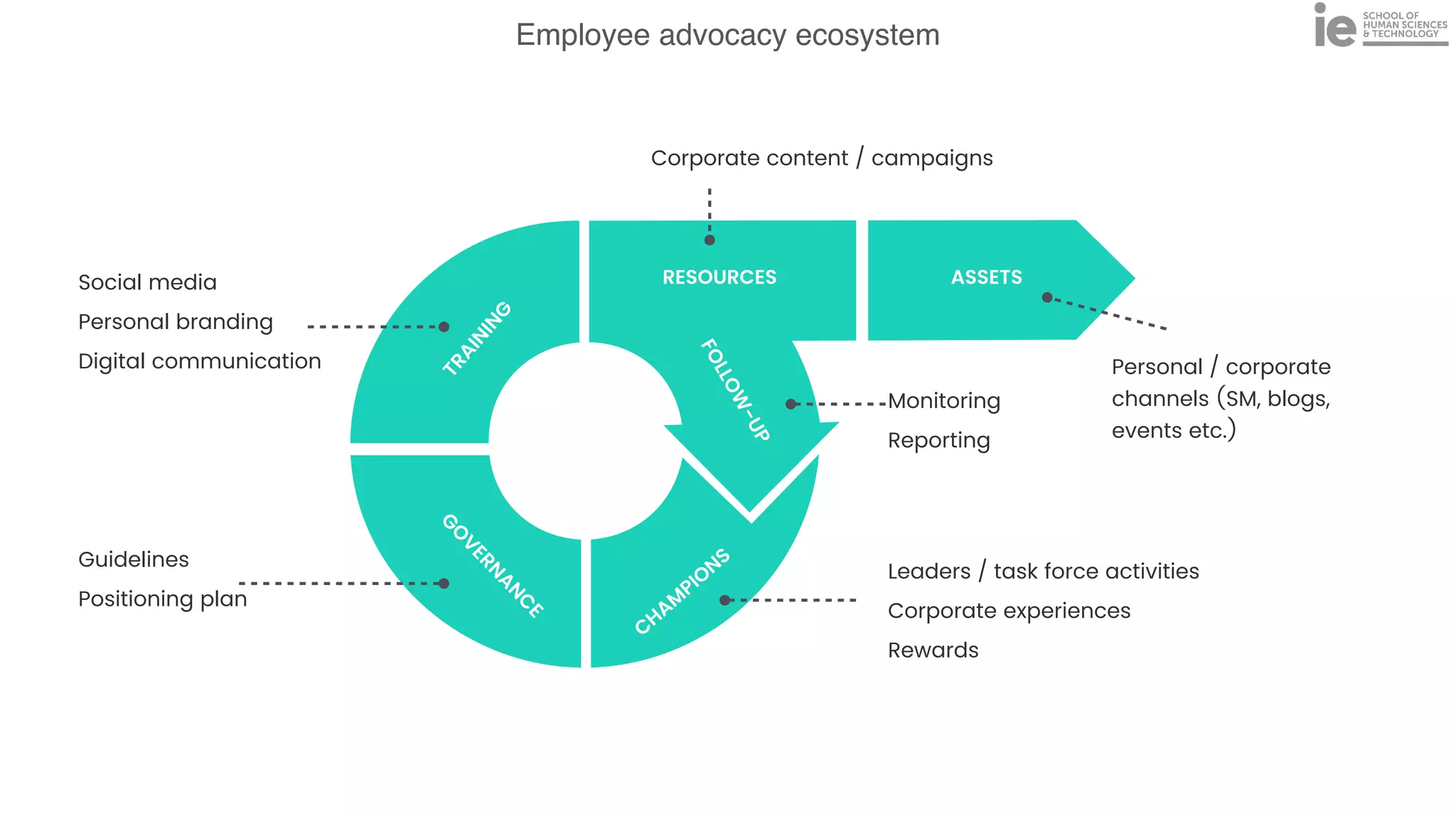
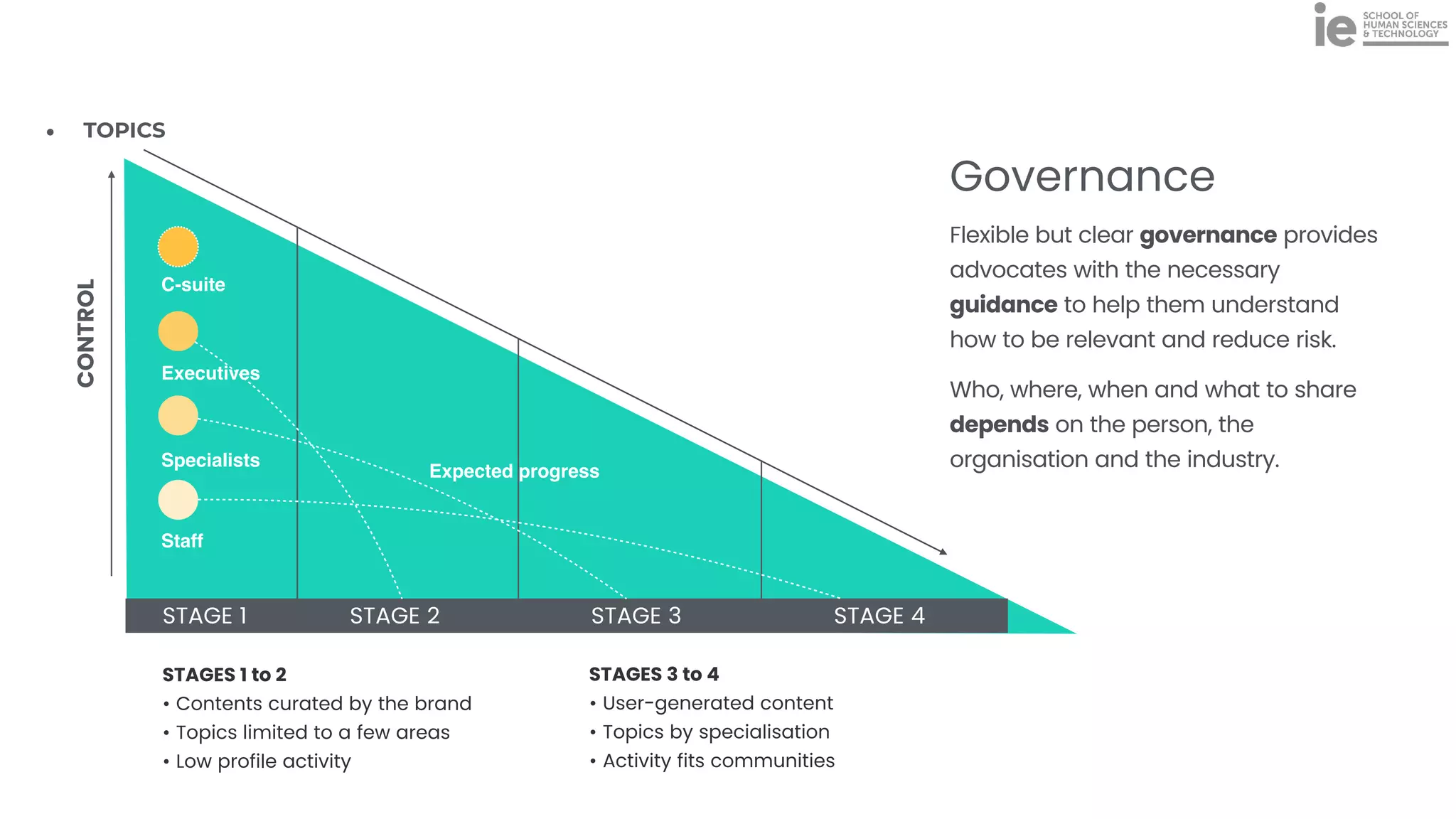
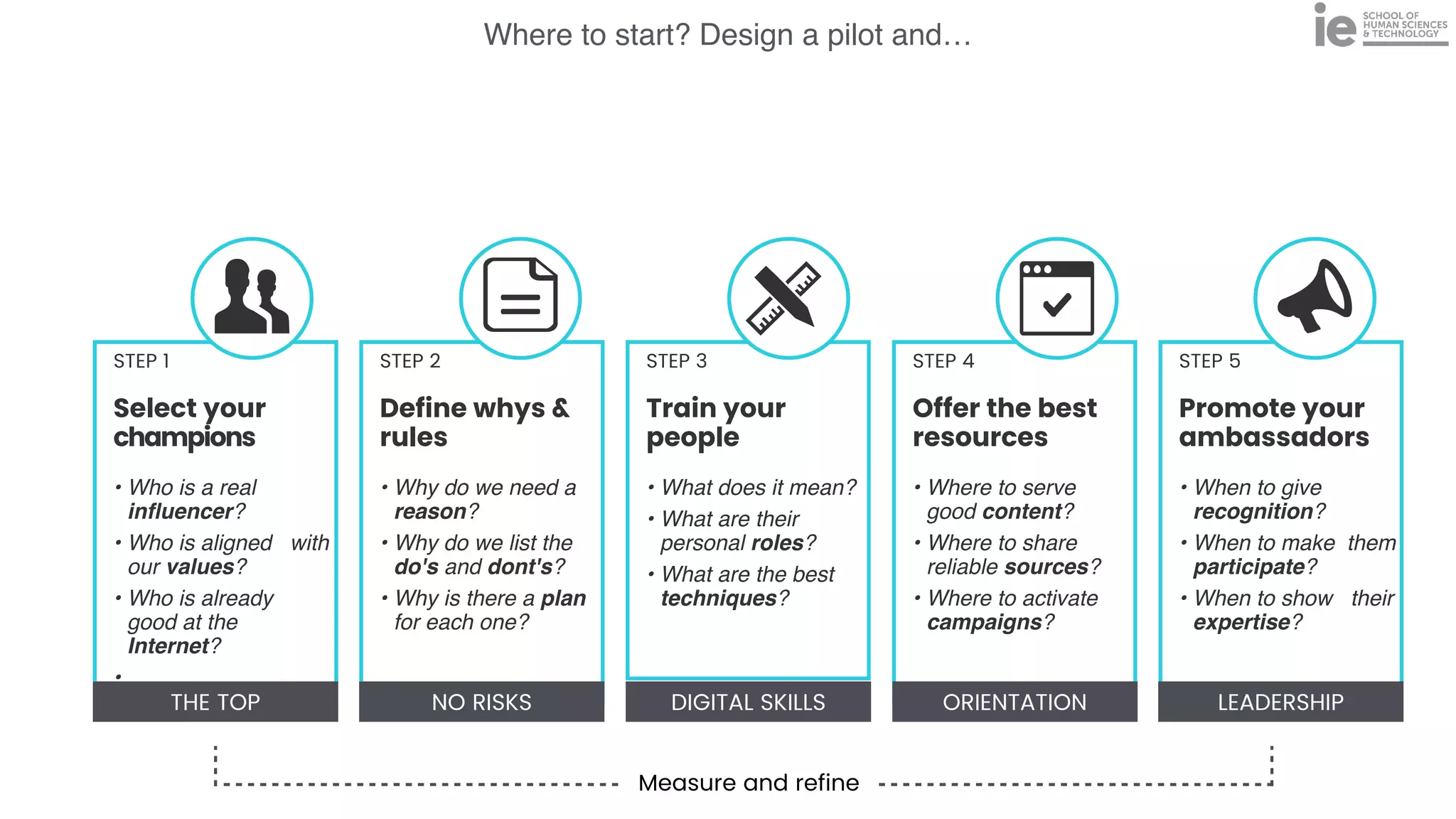
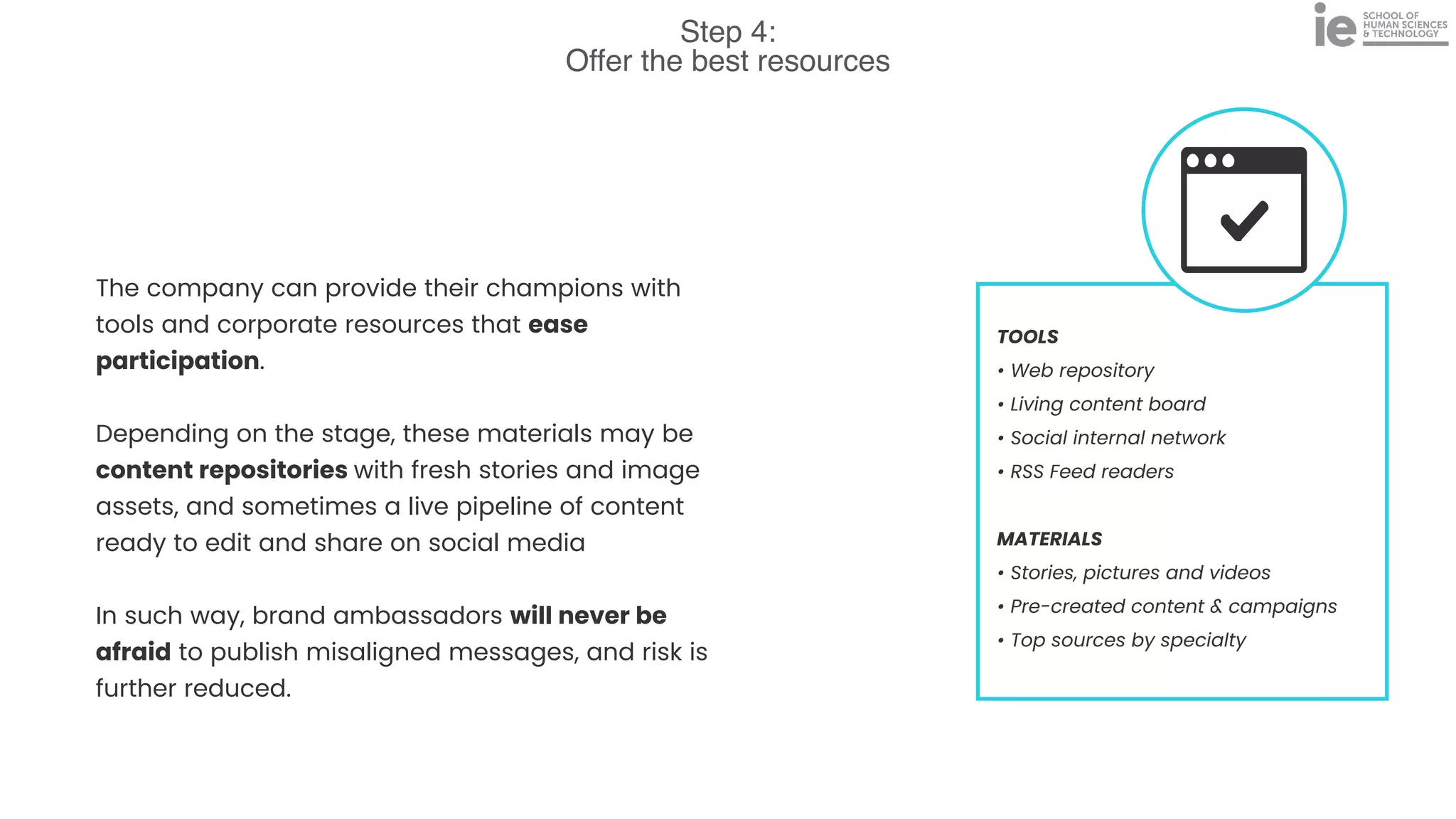
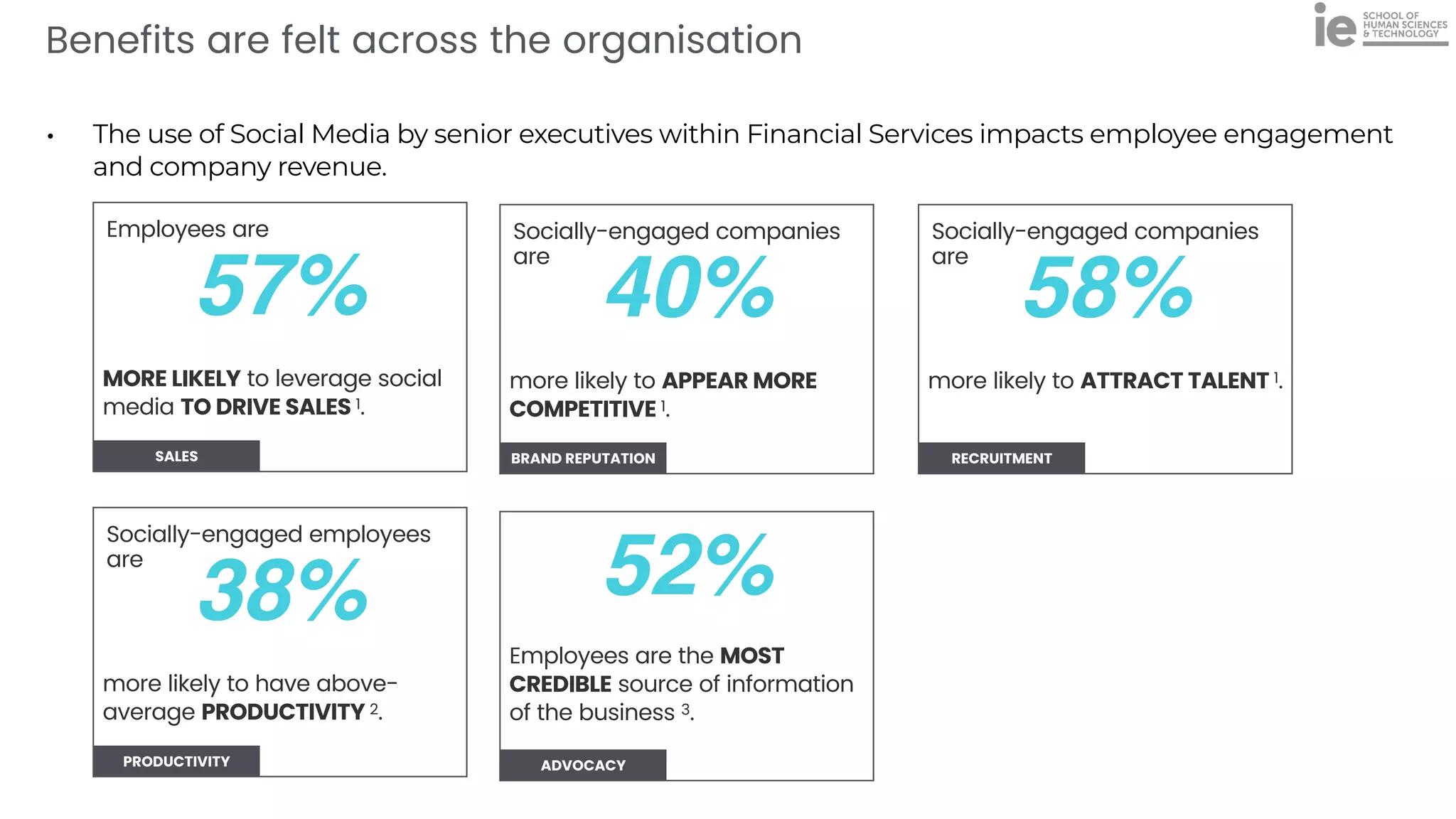
This document discusses best practices for building an employee advocacy program on LinkedIn. It recommends selecting champions who are influential internally, defining program goals and guidelines, providing training to champions on social media and personal branding, offering tools and resources to make participation easy, and promoting champions' activities both internally and externally. It also includes tips for creating a social media policy and guidelines for personal and corporate social media use. The overall goal is to empower employees to become advocates for the company brand in a way that strengthens engagement and trust.











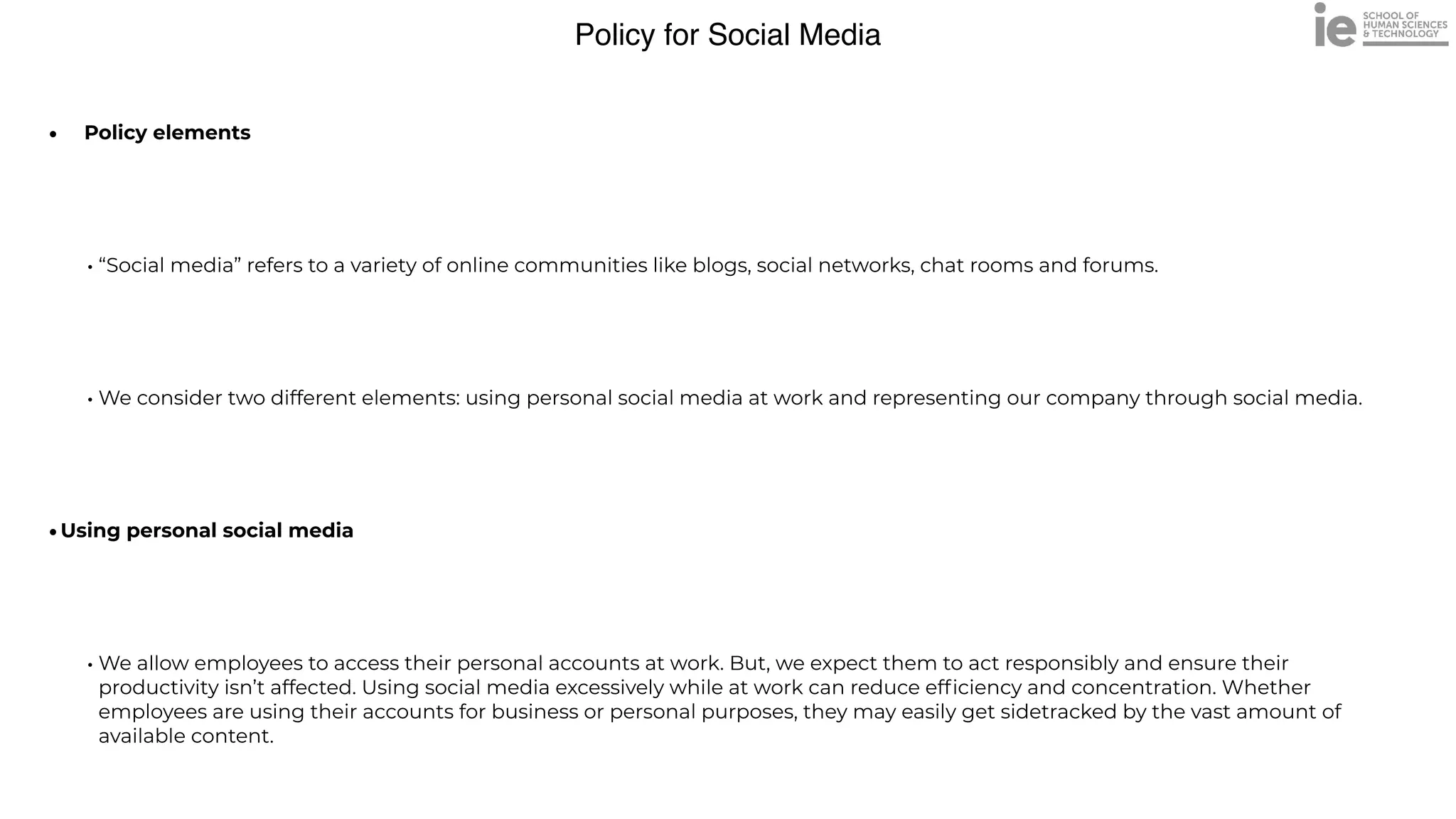


![Policy for Social Media
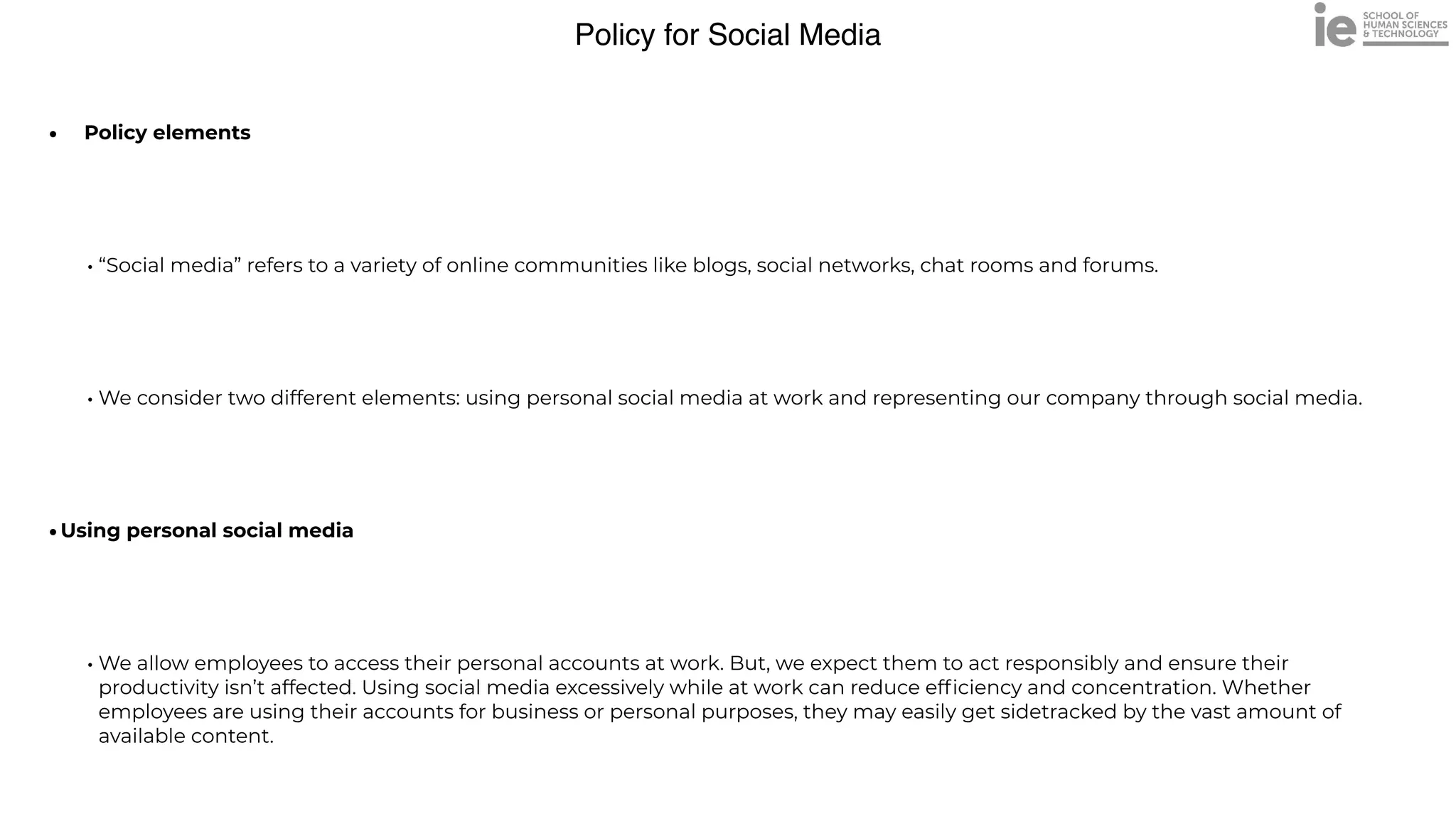
•Representing our company:
• Inform our [PR/Marketing department] when they’re about to share any major-impact content
• Avoid deleting or ignoring comments for no reason. They should listen and reply to criticism.
• Never post discriminatory, offensive or libelous content and commentary
• Correct or remove any misleading or false content as quickly as possible
Disregarding job responsibilities and deadlines to use social media
Disclosing confidential information through personal or corporate accounts
Directing offensive comments towards other members of the online community](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linkedinb2b-2022-220710190021-d731dfc2/75/LinkedIN-B2B-2022-pdf-29-2048.jpg)