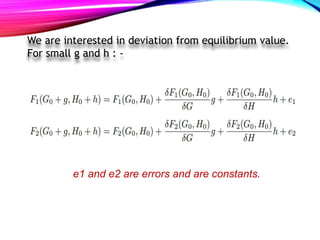
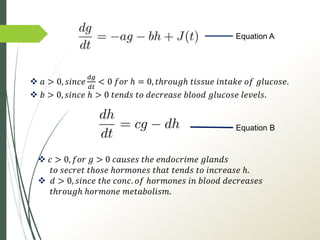
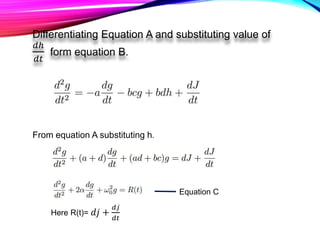
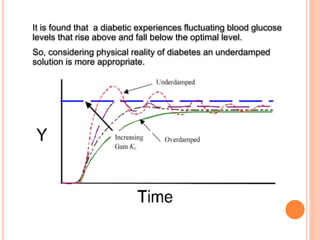
This document presents a mathematical model for detecting diabetes using glucose tolerance tests. The model uses differential equations to represent how glucose and hormone levels in the blood change over time after consuming glucose. It assumes glucose and hormone levels start at equilibrium. The solution shows blood glucose levels will oscillate underdamped for diabetics, reaching abnormal highs and lows. The natural frequency of oscillations can indicate if results are diabetic or non-diabetic.