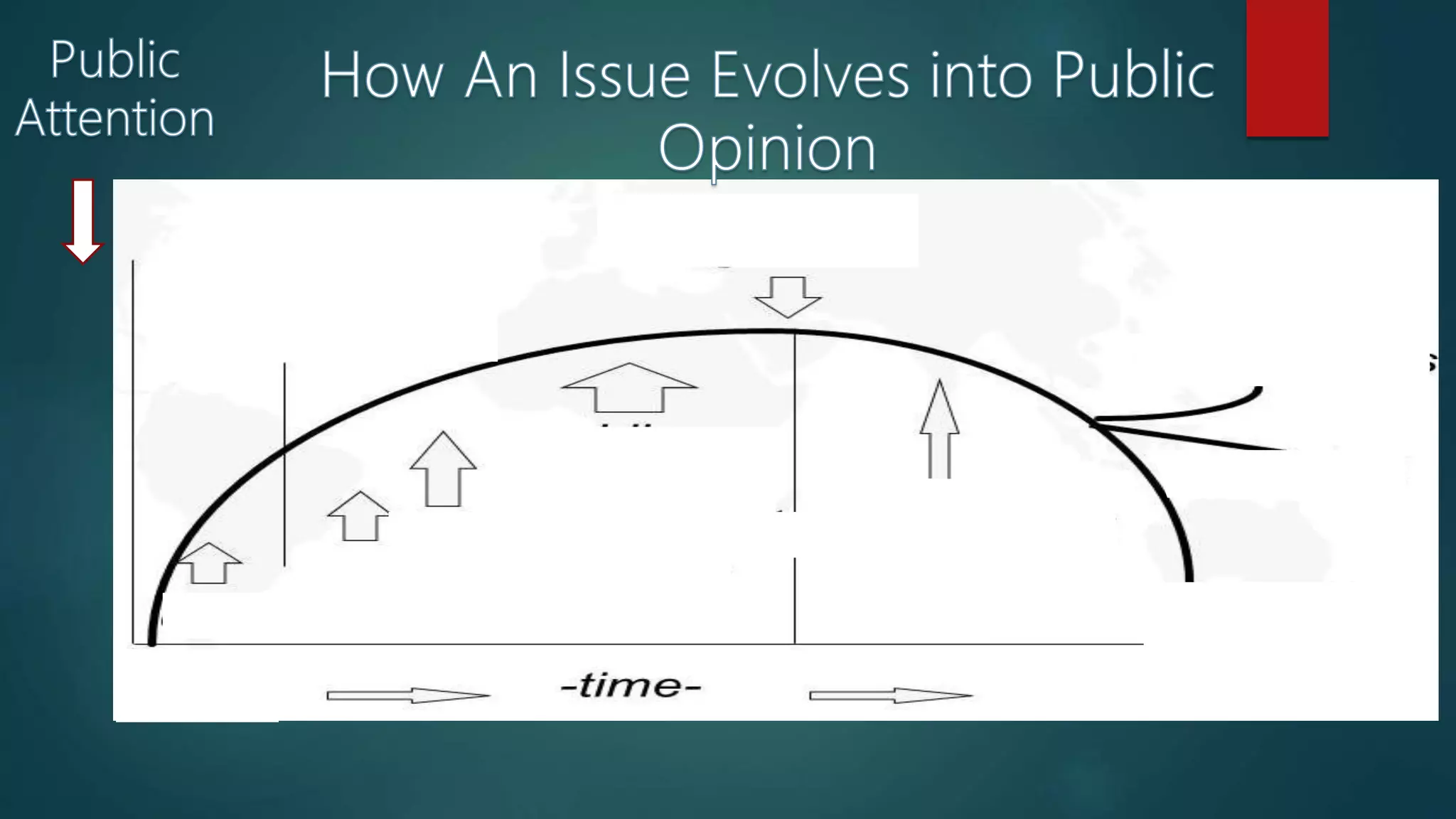
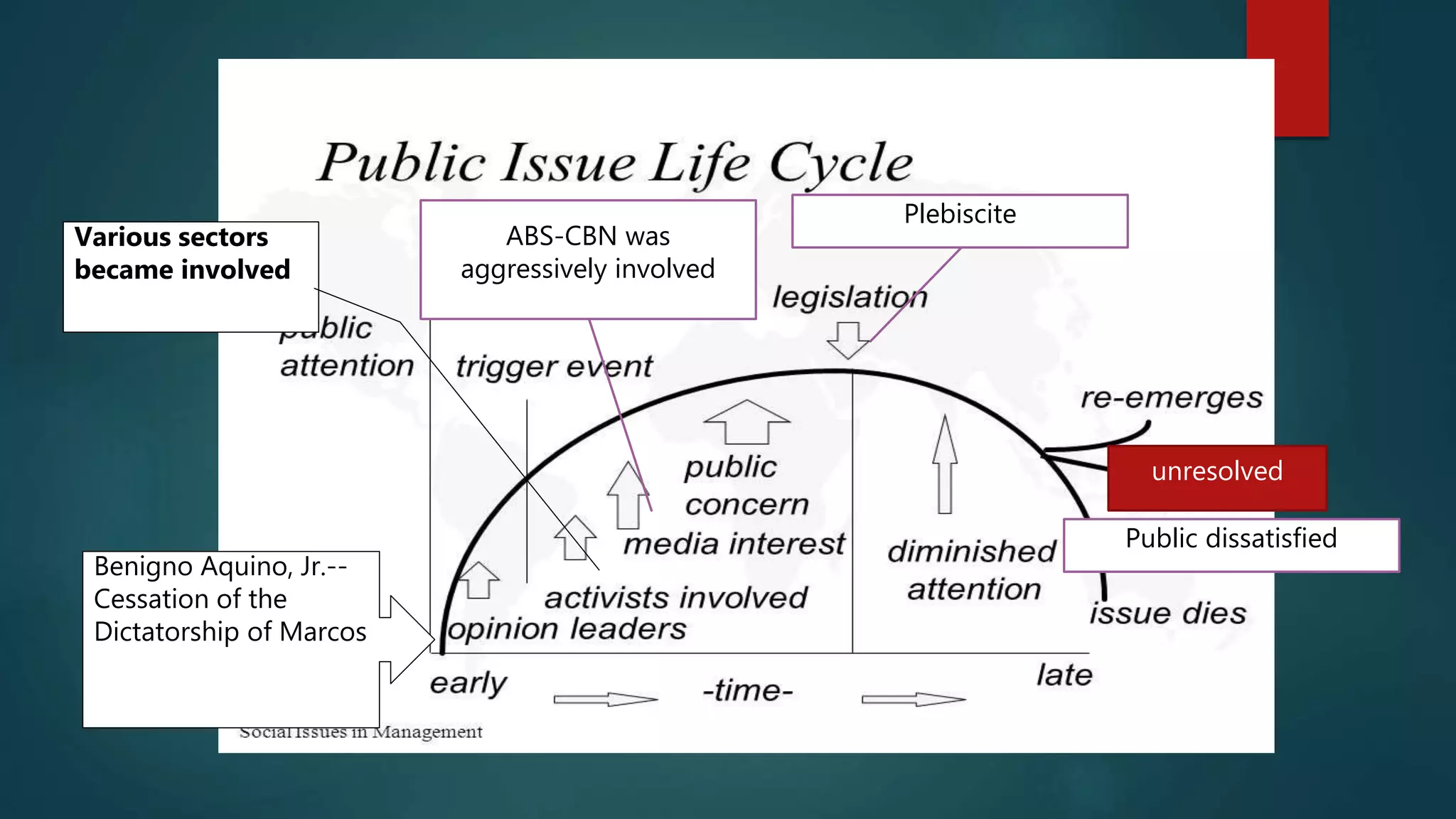
The life cycle of a public issue involves several stages:
1) Definition of the issue as groups raise concerns about issues affecting their interests and opinion leaders discuss the issue publicly.
2) Increased public awareness as the issue is debated generating media coverage and more people get involved with differing opinions.
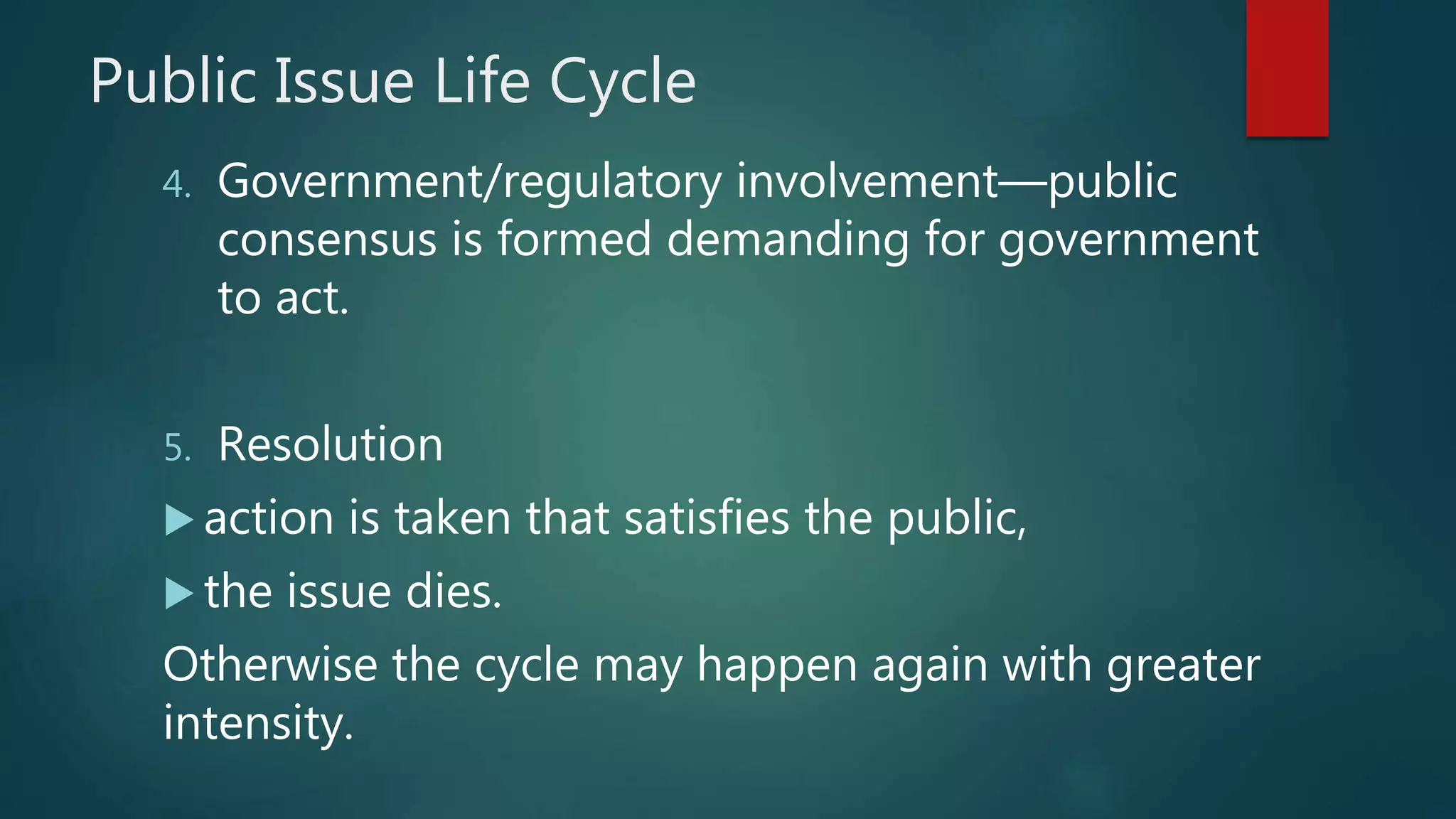
3) Formation of public consensus demanding government action to resolve the issue.
4) Resolution through government action that satisfies the public concern or the issue remains unresolved and the cycle continues with greater intensity.