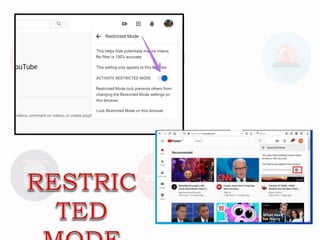
The document provides information on internet safety, security, and ethics. It discusses internet threats like malware, spam, and phishing. It emphasizes the importance of protecting one's reputation online through careful posting and sharing of information. Students should learn to consider safety, avoid dangers, use social media responsibly, and properly reference online sources.