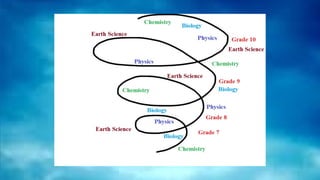
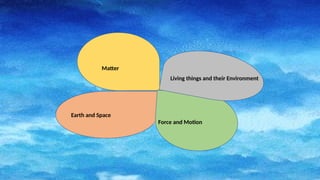
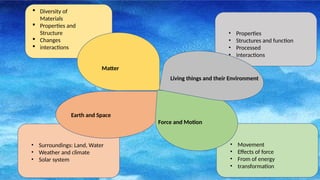
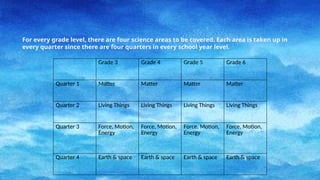
The document outlines the spiral progression of the K-12 elementary science curriculum in the Philippines, focusing on four major disciplines: chemistry, biology, physics, and earth and space. Each grade level from grades 3 to 6 explores specific topics within these disciplines across four quarters, deepening the complexity and understanding of key concepts. It emphasizes the importance of teaching science as a subject in its own right, rather than embedding it in other curricula.