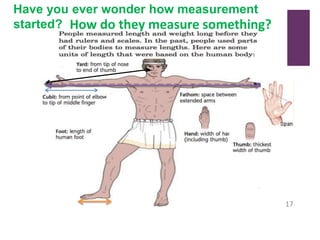
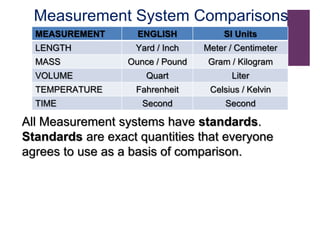
This document provides an introduction to physics and the branches of science. It discusses that science is a systematic body of knowledge based on observation and experimentation. The main branches of science are biological science, social science, and physical science. Physical science deals with the study of non-living things, their composition, nature, characteristics, and changes. The main branches of physical science discussed are chemistry, physics, astronomy, geology, and meteorology. The document then shifts to discussing measurement, defining it as the act of measuring or giving the size of something. It explains the international system of units (SI system) that scientists use for measurements and comparisons.