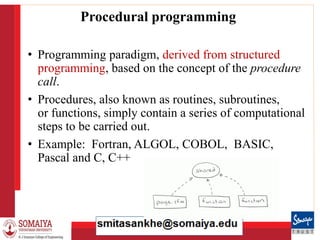
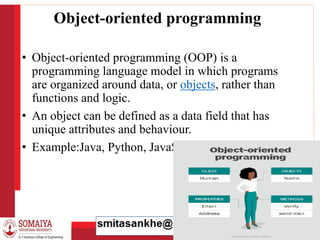
The document is an introduction to object-oriented programming (OOP) and methodologies, detailing programming concepts, languages, and specifically Java's features. It covers different programming approaches, compares C, C++, and Java, and elaborates on OOP principles such as inheritance, polymorphism, abstraction, and encapsulation. Additionally, it highlights Java's characteristics like platform independence, security, and robustness, alongside providing a simple Java program example.



















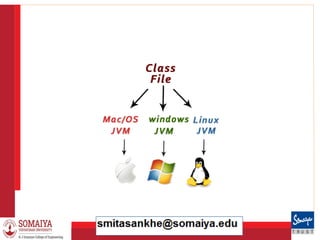







![8/21/2023 37
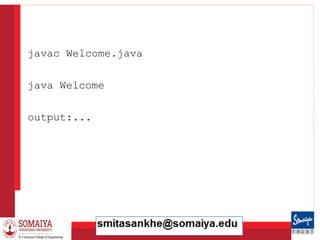
A Simple Java Program
Example 1.1
//This application program prints
Welcome to Java!
public class Welcome
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-1-240422055958-eadf7741/85/lecture-1111111111111111111111111111-pdf-37-320.jpg)