The document summarizes several theories of international trade:
- Free trade theory holds that countries benefit from specializing in what they have an absolute advantage in producing and trading with other countries.
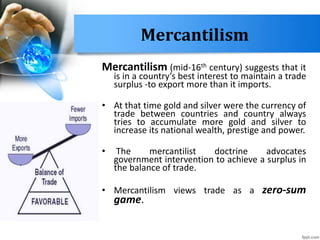
- Mercantilism argued that countries should aim for a trade surplus to accumulate wealth, but views trade as zero-sum.
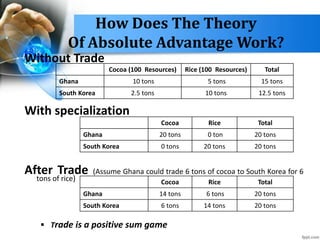
- Adam Smith's absolute advantage theory showed countries gain by specializing in what they produce most efficiently.
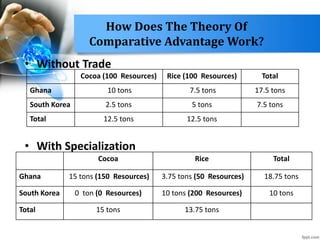
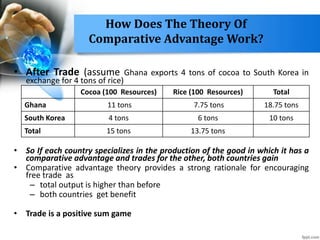
- Ricardo's comparative advantage theory demonstrated even countries without an absolute advantage gain from trade by specializing in their comparative advantage.
- Heckscher-Ohlin theory claims comparative advantage arises from differences in factor endowments like capital and labor. It predicts trade in factor-intensive goods