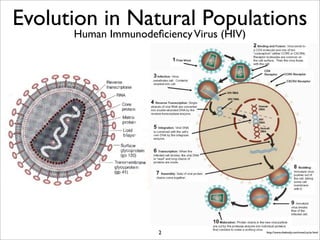
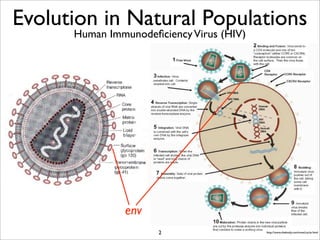
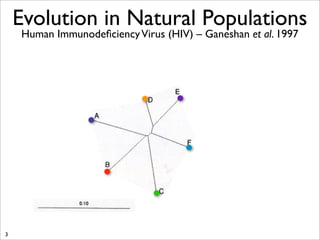
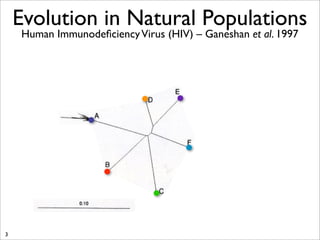
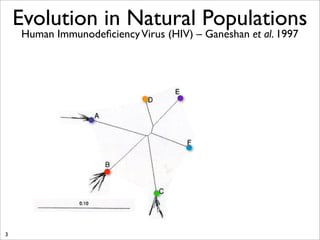
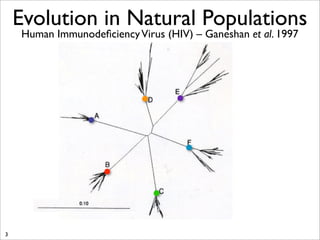
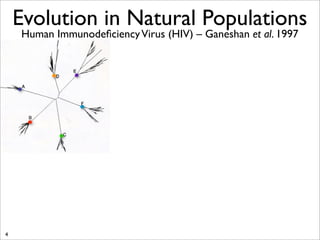
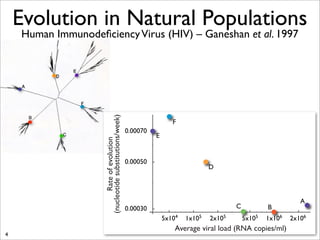
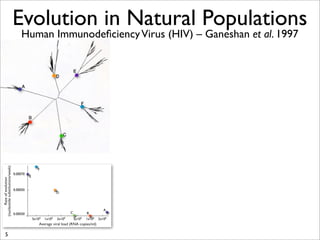
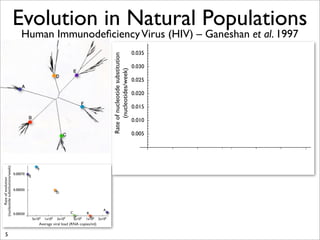
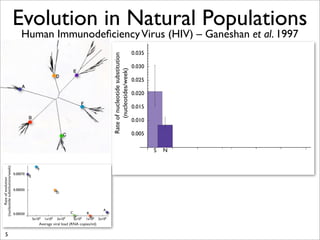
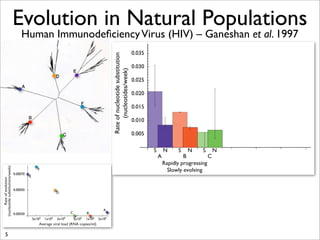
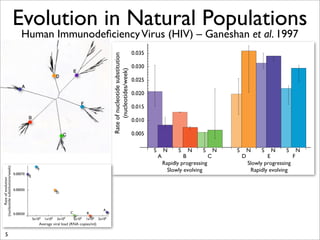
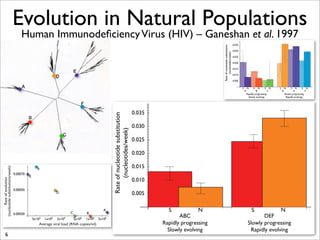
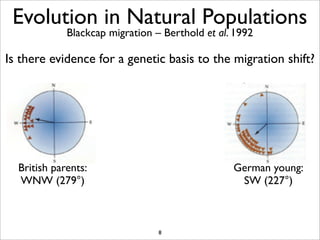
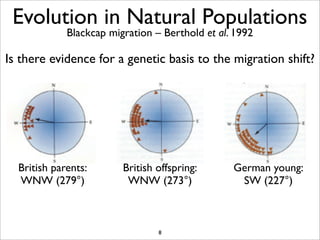
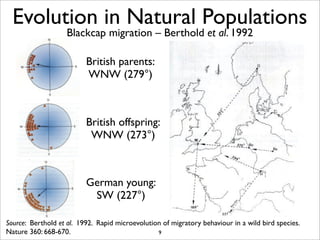
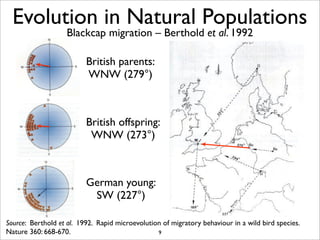
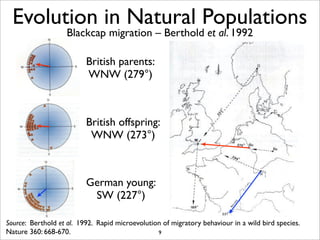
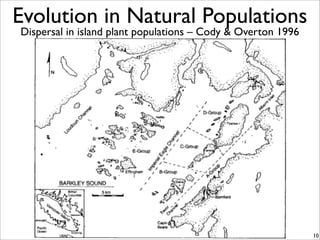
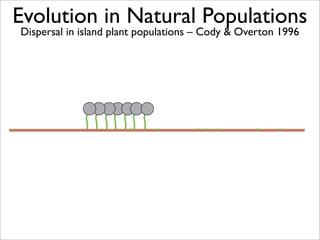
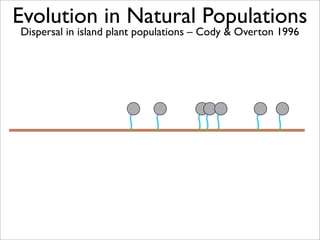
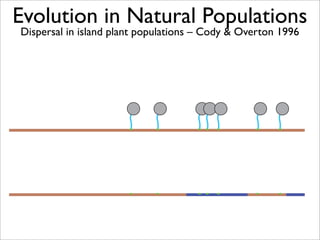
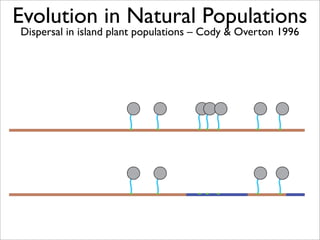
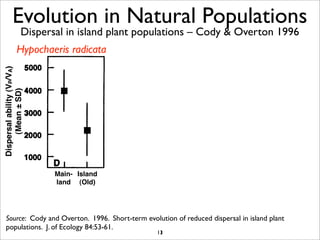
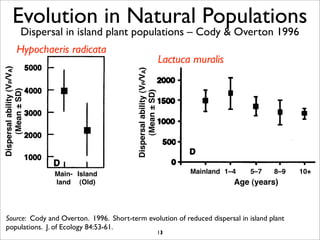
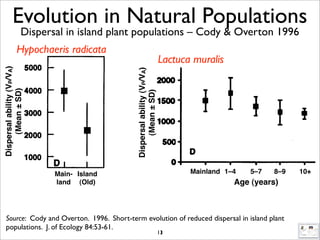
The document lists five lines of evidence that are used to support the theory of evolution:
1. Direct observation of change in natural populations.
2. Direct observation of change under artificial selection.
3. The existence of homologous traits.
4. Homologies tend to be nested or organized in a hierarchical manner.
5. Evidence from the fossil record.