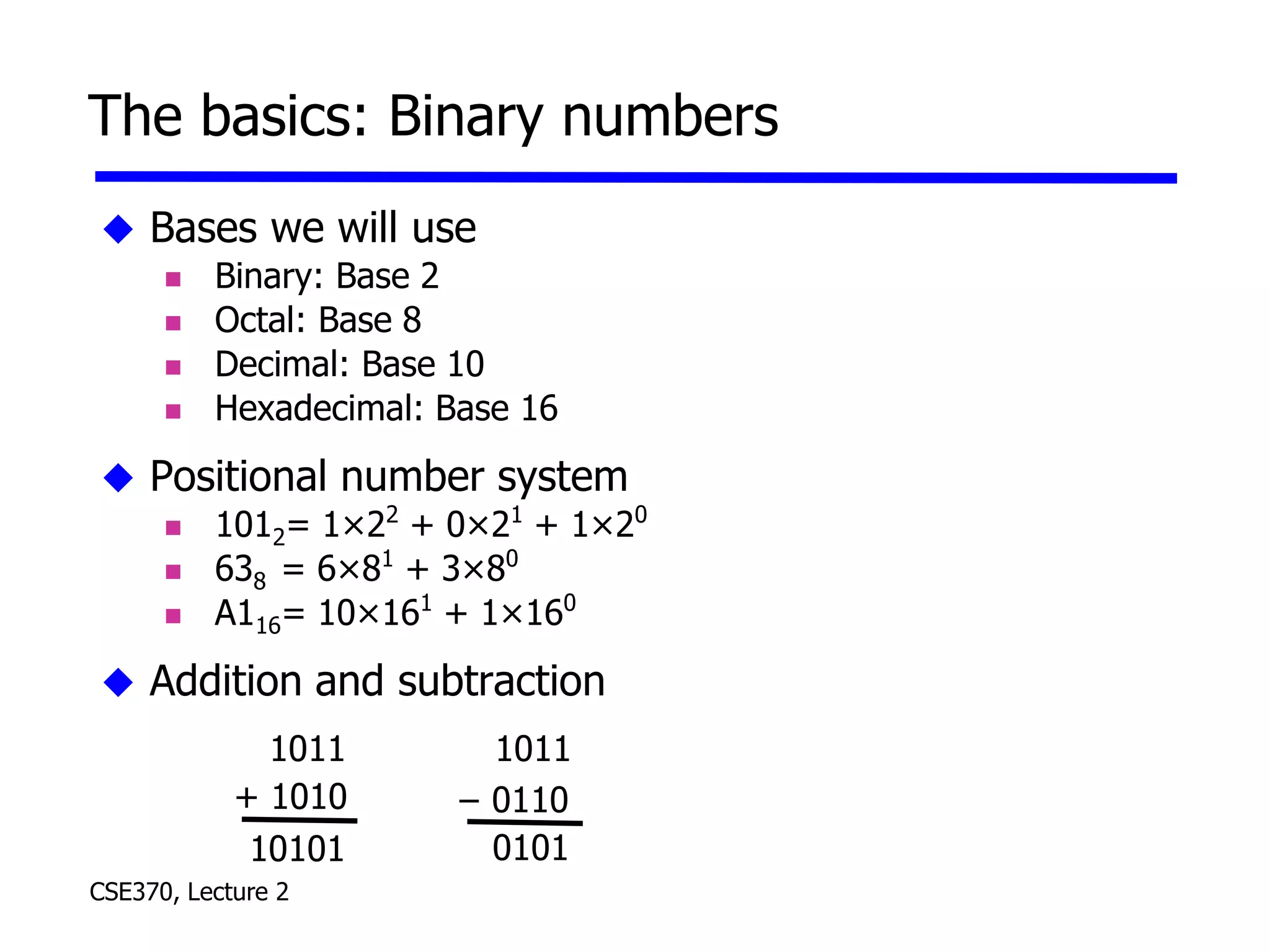
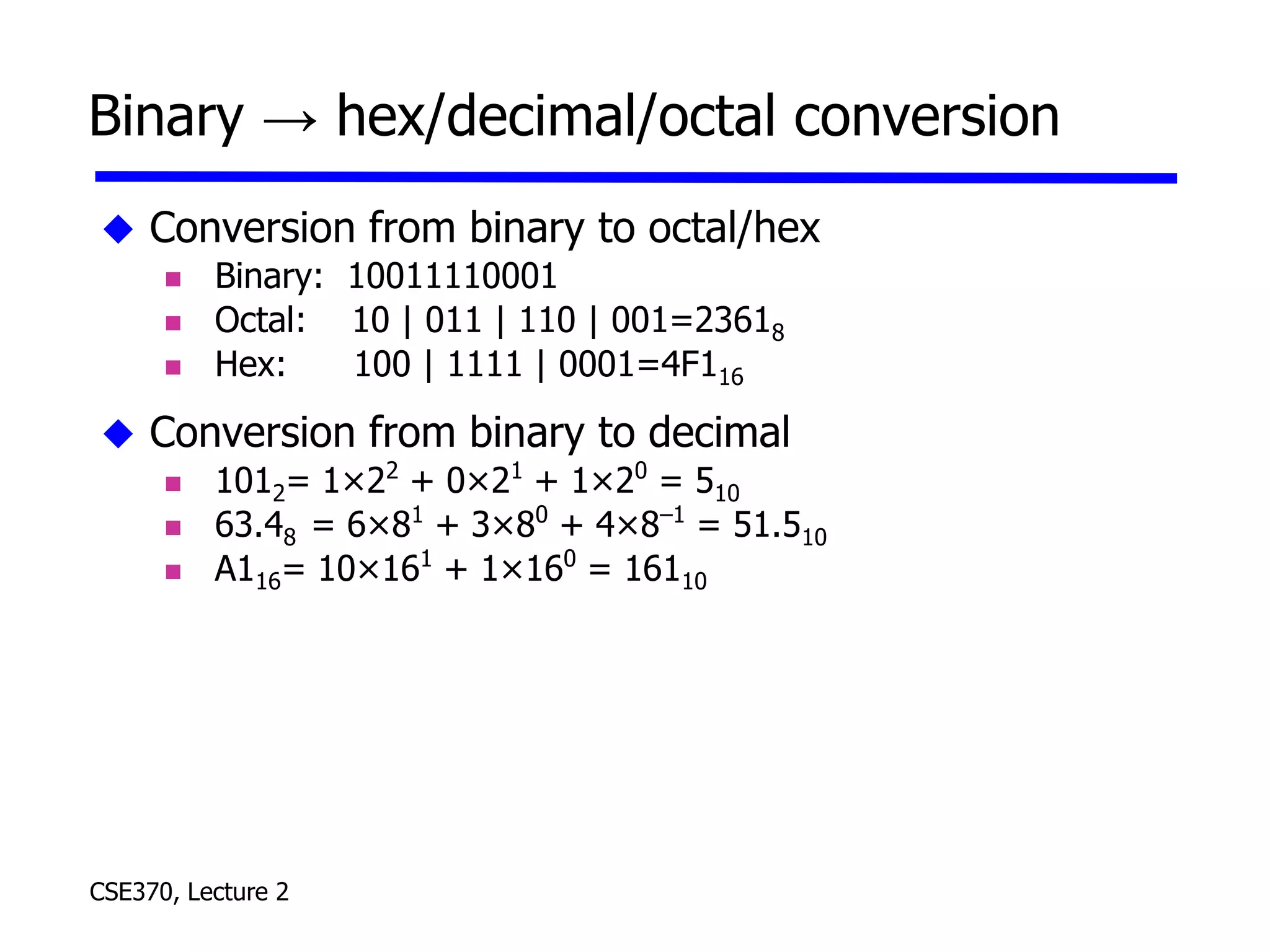
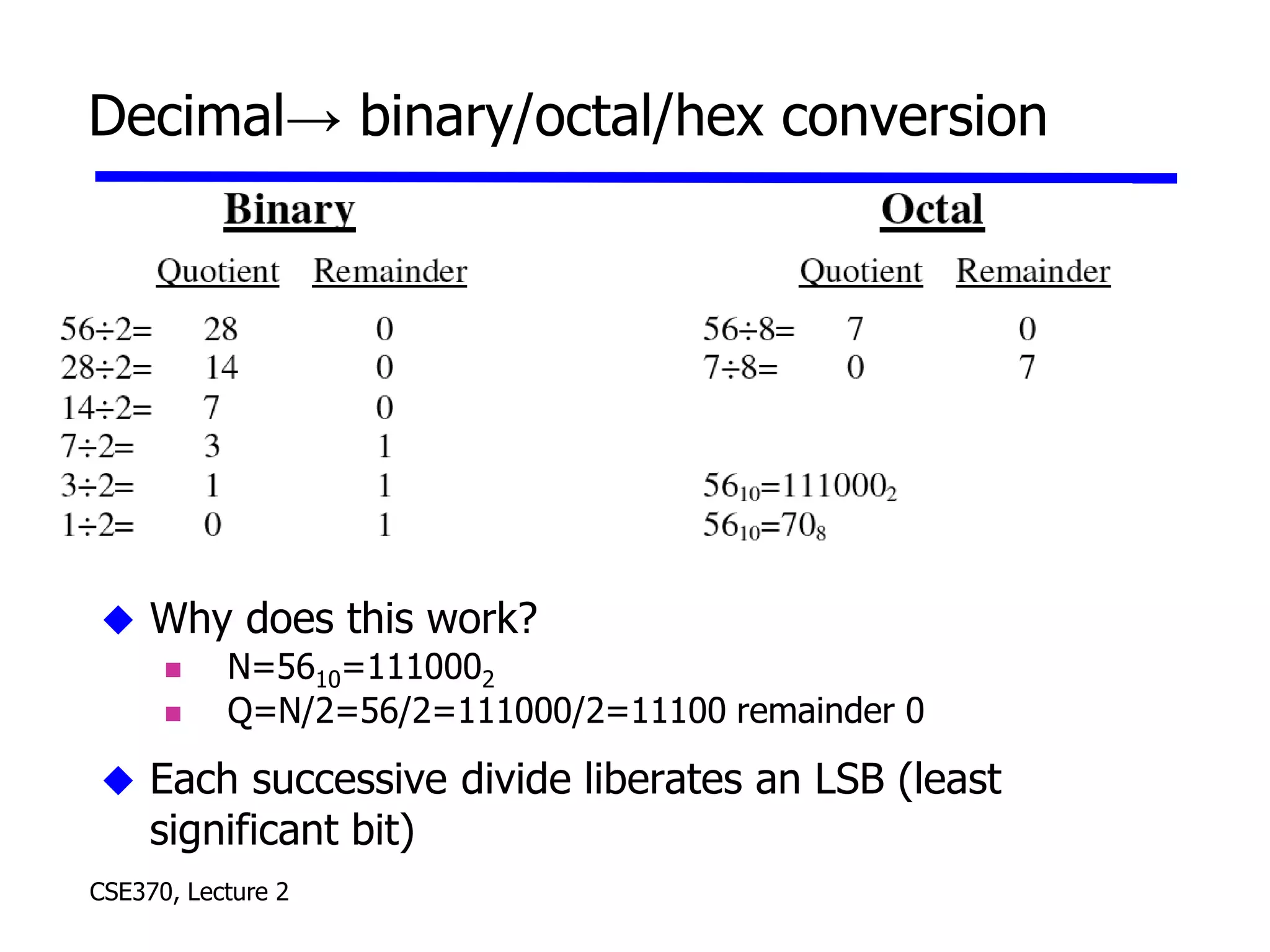
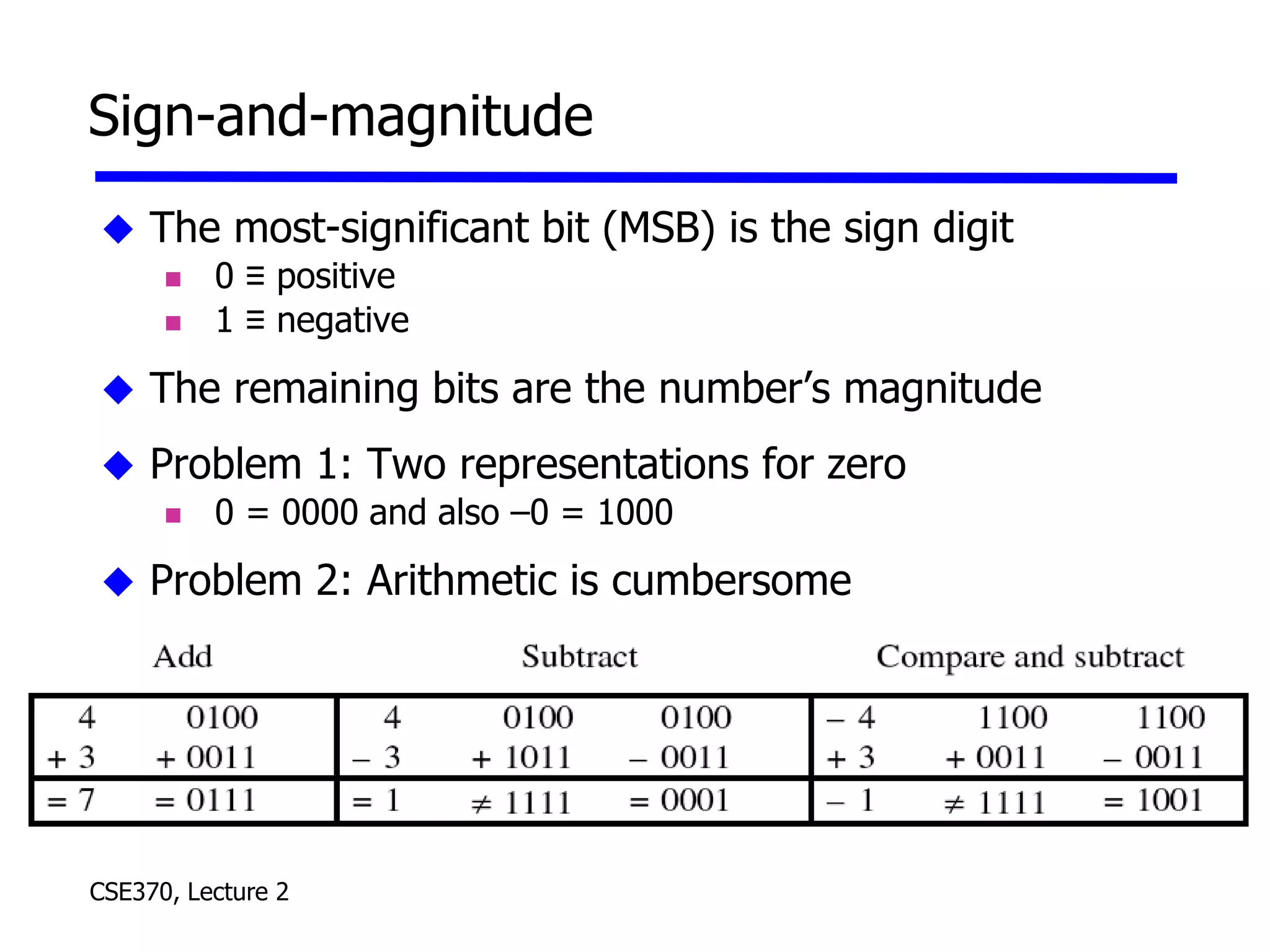
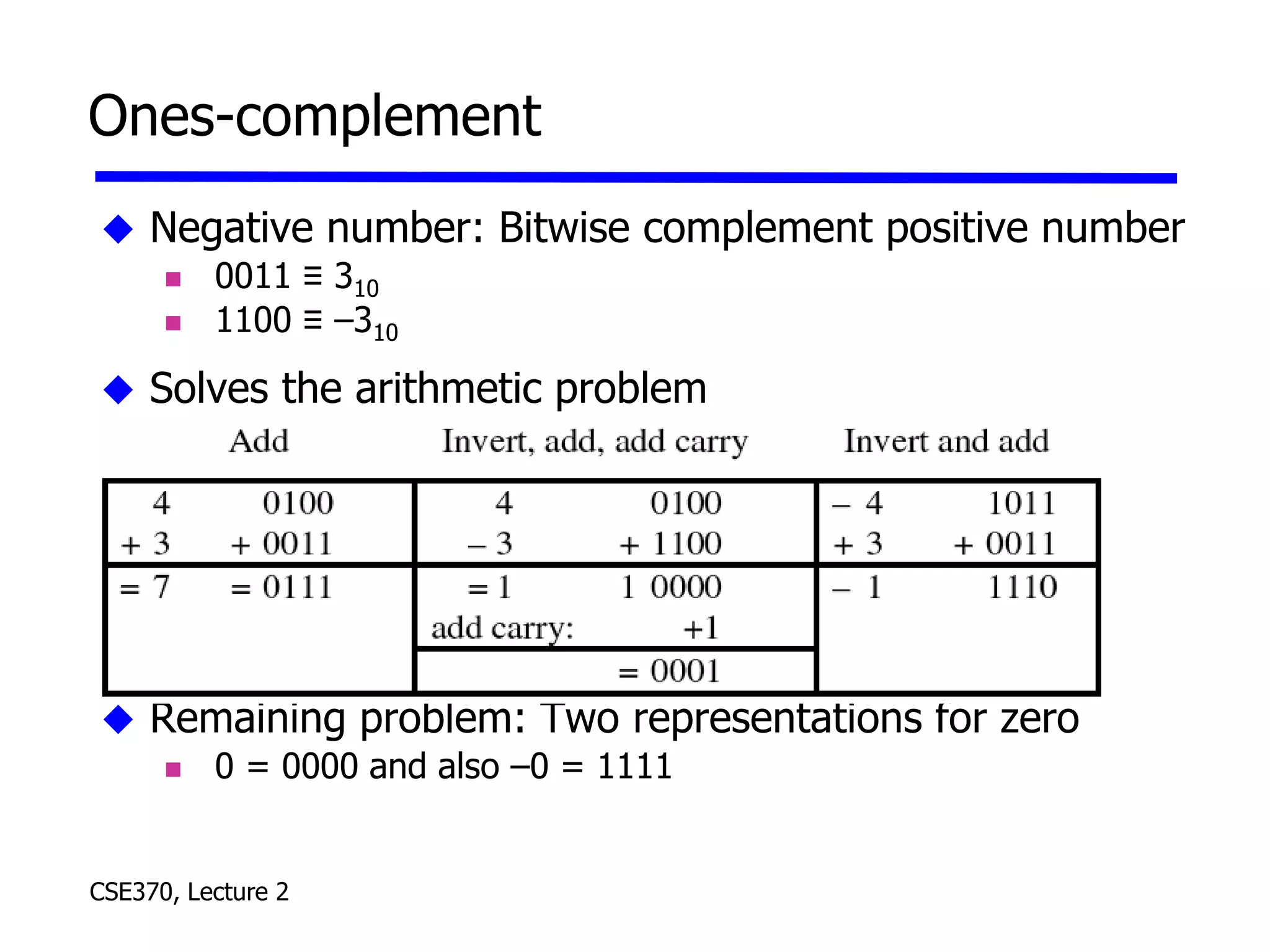
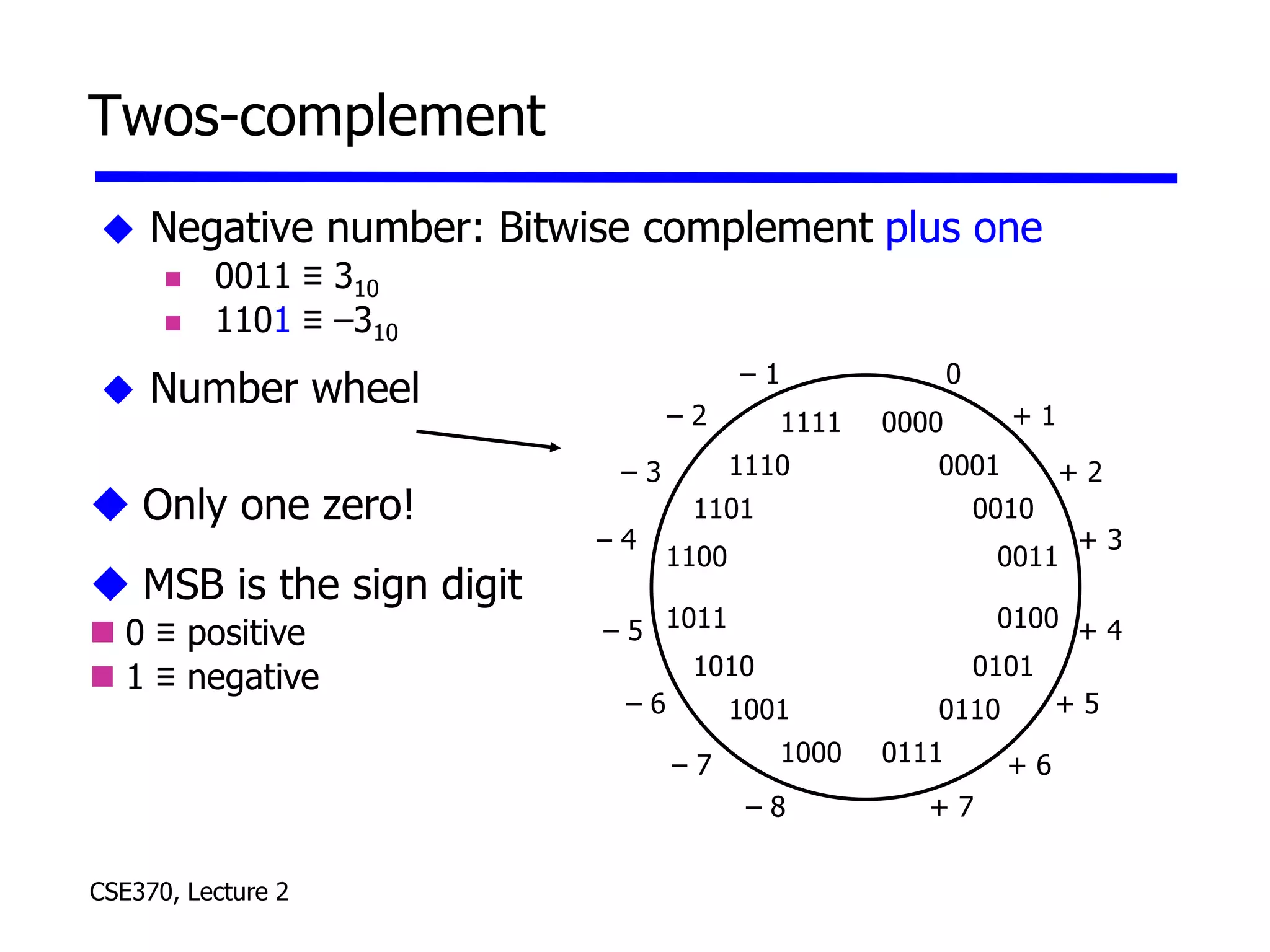
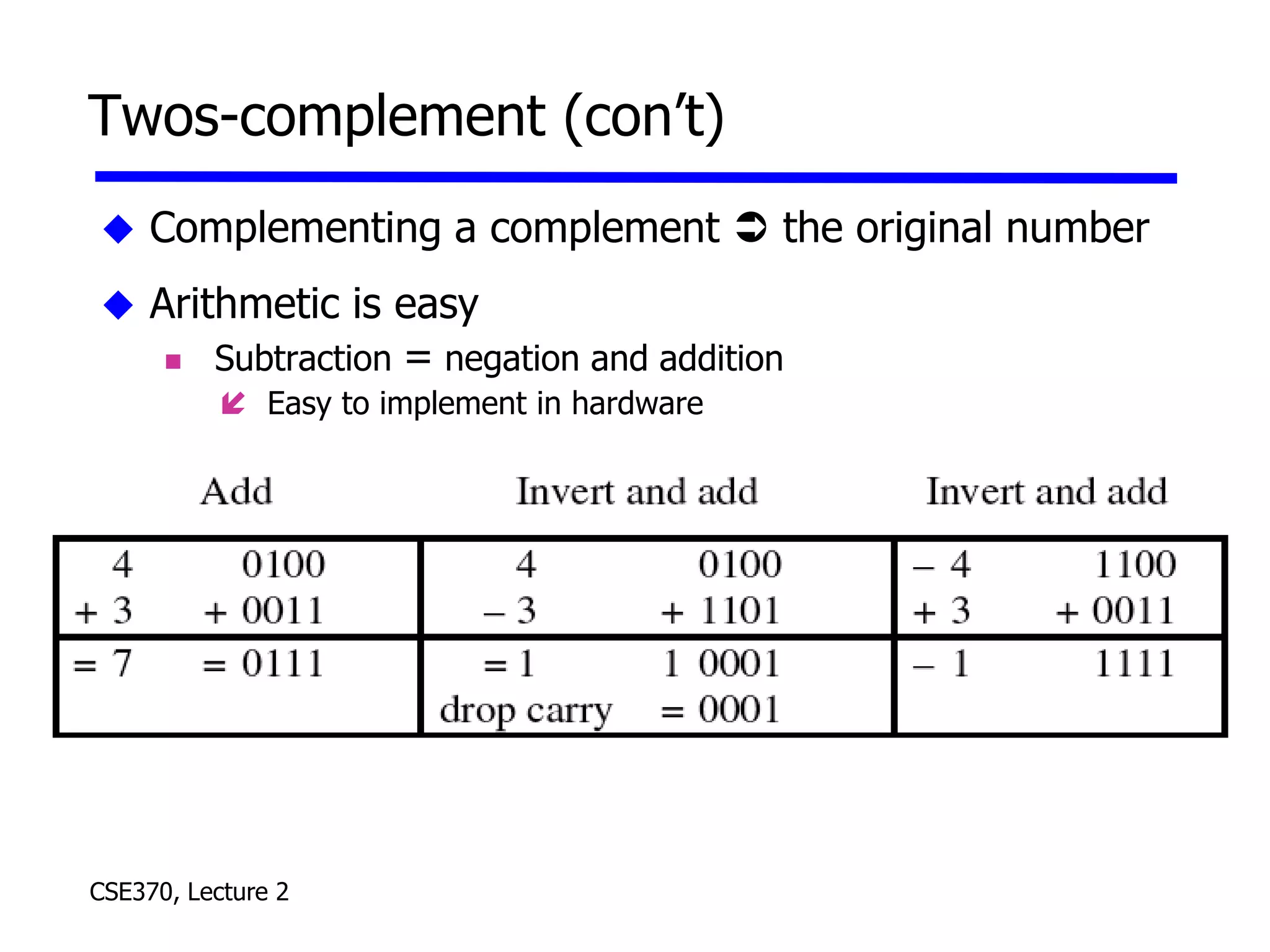
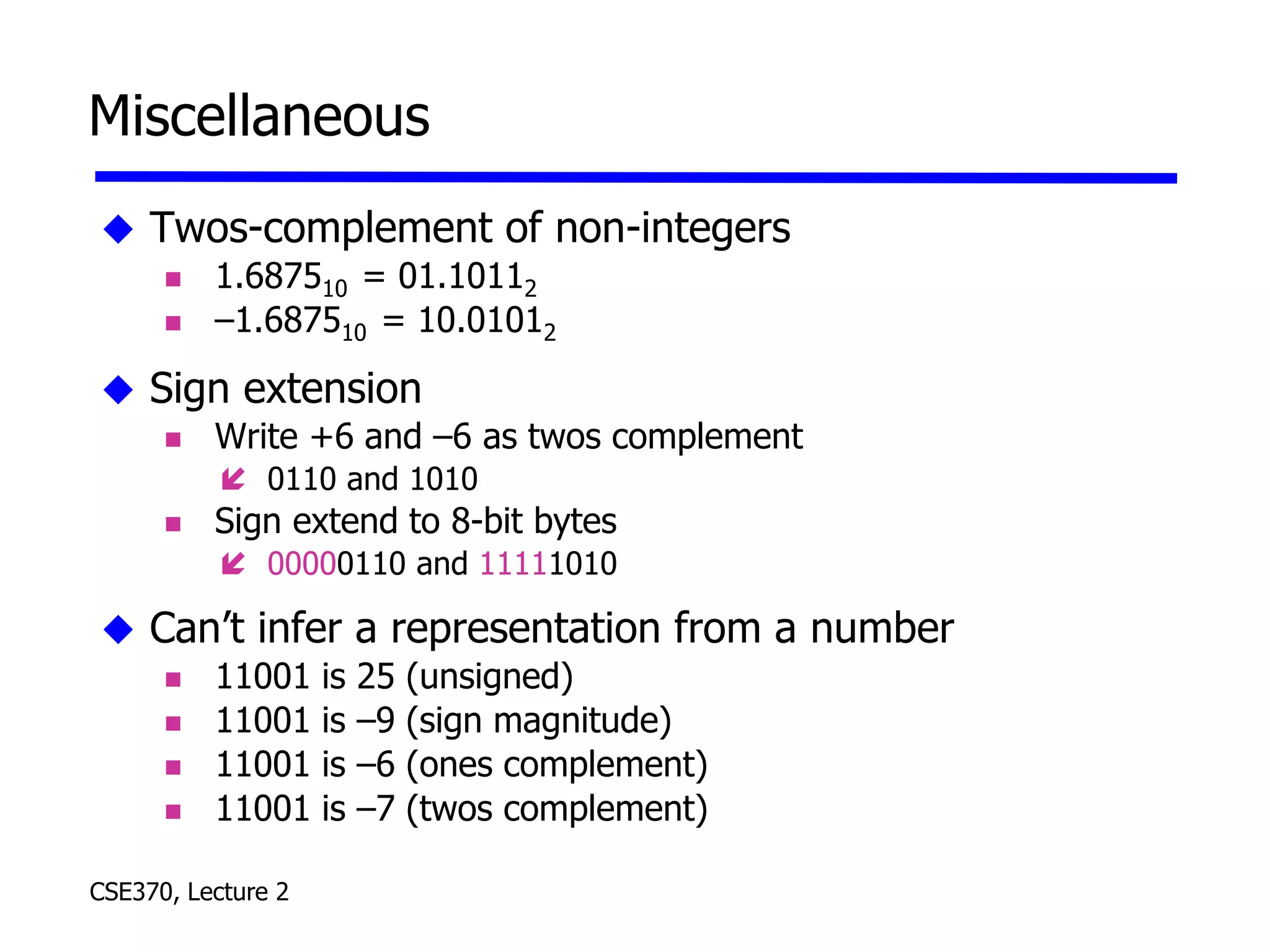
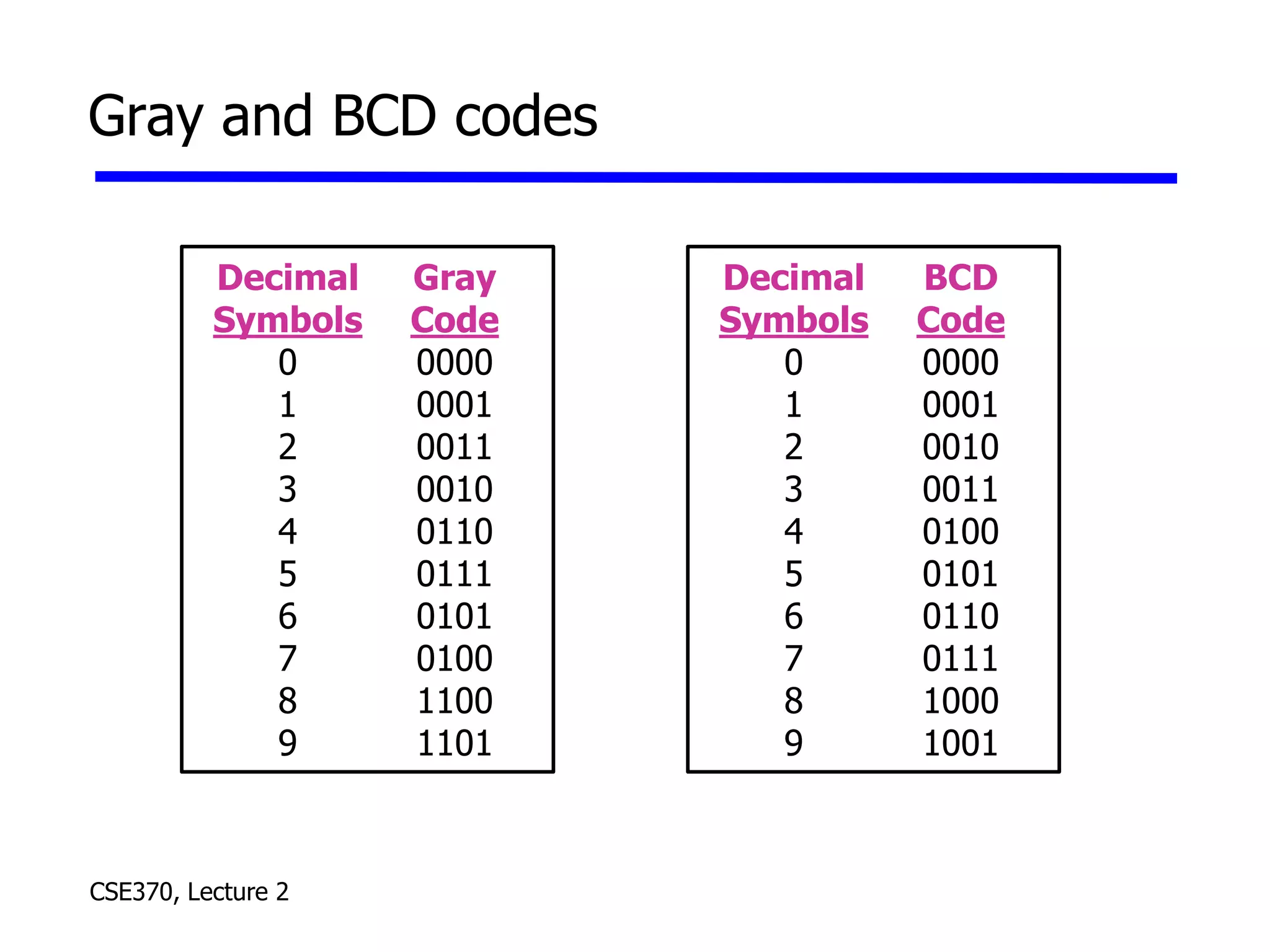
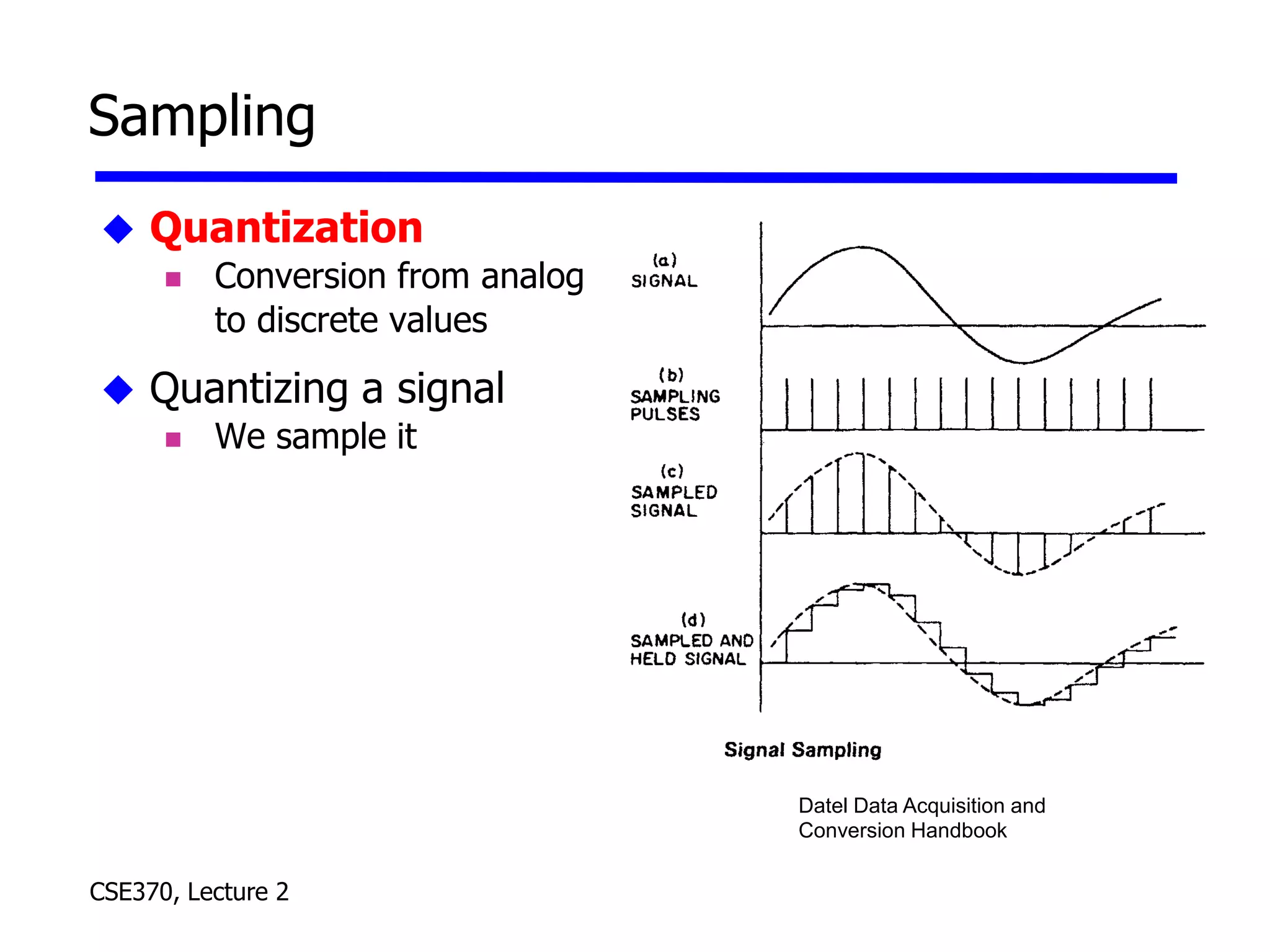
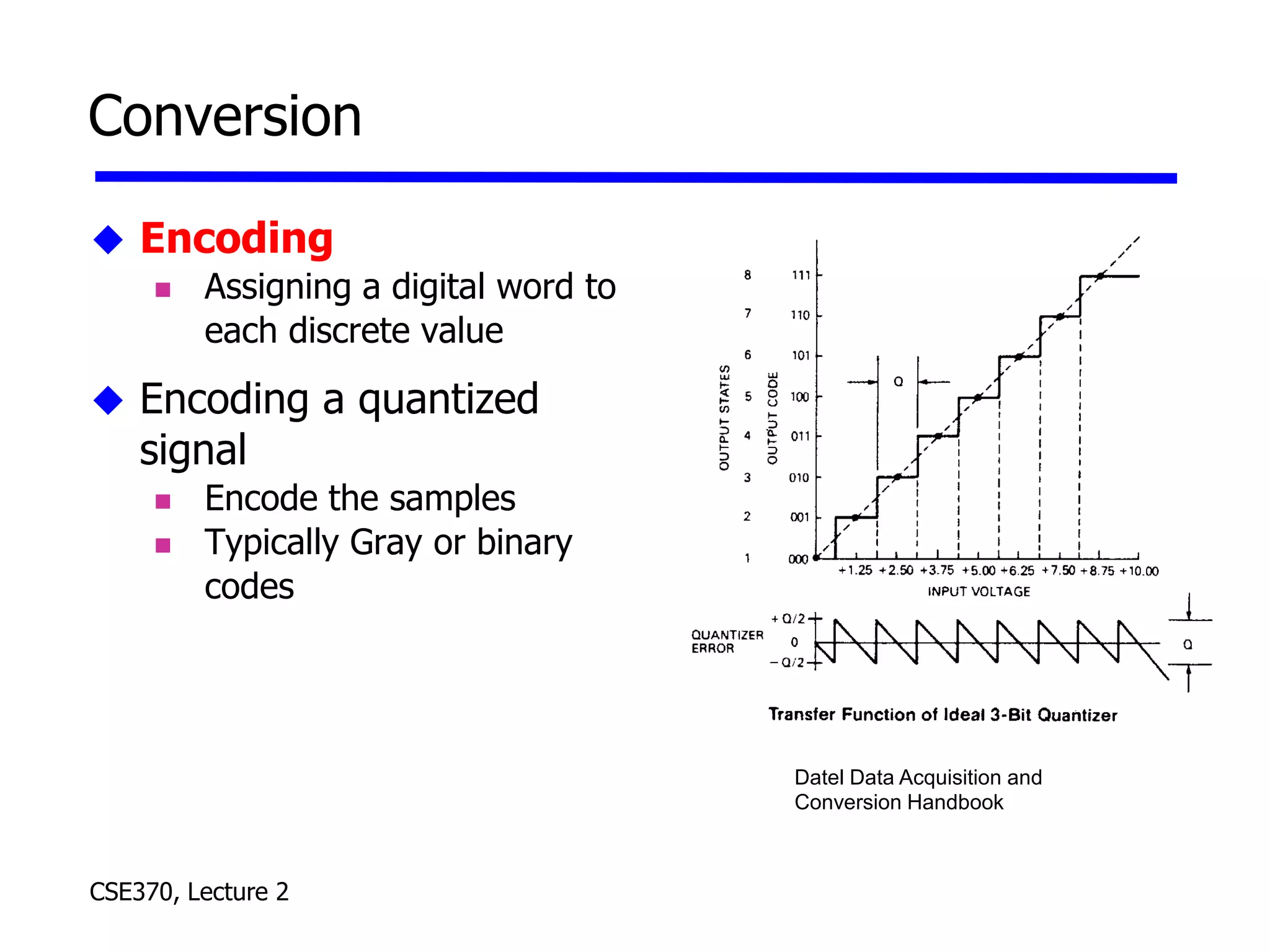
The lecture covered number systems including binary, octal, decimal, and hexadecimal. It discussed how to convert between these number systems. It also covered sign-magnitude, one's complement, and two's complement representations for negative numbers in binary. Finally, it provided an overview of analog to digital conversion and digital to analog conversion to interface between the analog physical world and digital computers.