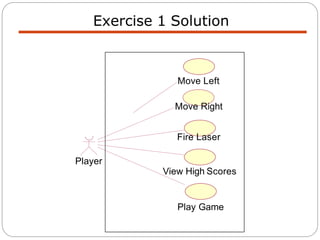
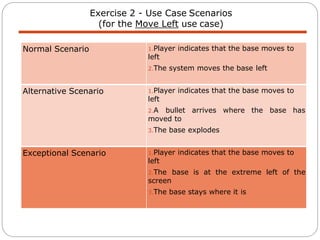
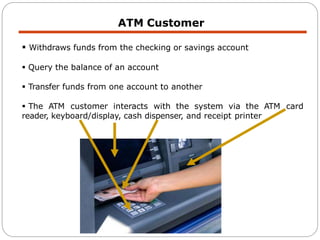
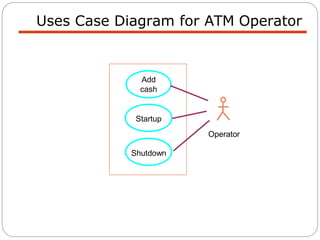
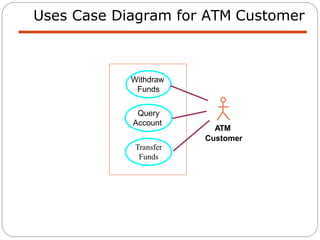
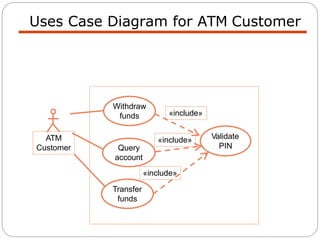
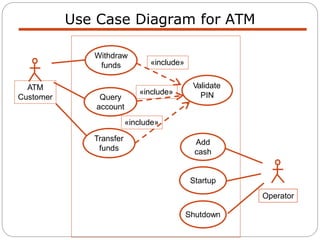
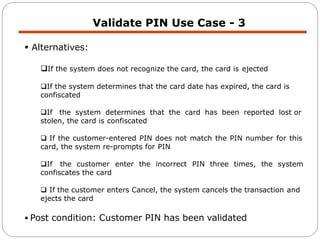
The document discusses use case modeling for software design, including developing use case diagrams and descriptions to identify actors, use cases, and scenarios. It provides examples of a use case diagram and descriptions for making tea and moving left in a space invader game. The document also provides a detailed example of use case modeling for an ATM system involving customers and operators.


![ Normal Scenario:
1. Switch on kettle to boil water. [A1: Kettle empty]
2. Place tea bag and milk in mug.
3. When kettle has boiled pour boiling water into mug.
4. Let tea brew and then remove tea bag and put tea bag in the
bin.
Simple Scenario – Make Tea](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec10usecase-230826181519-12401b46/85/Lec-10Use-Case-pptx-5-320.jpg)