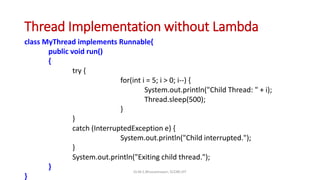
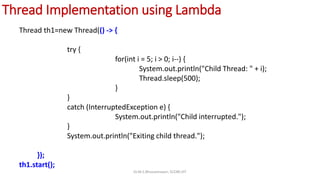
The document explains lambda expressions in Java, describing them as anonymous methods that implement functional interfaces. It outlines the syntax, components, and rules for using lambda expressions, as well as providing examples for implementation. Additionally, it contrasts traditional thread implementations with those using lambda expressions for streamlined code.







![Lambda Expression Example1
Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
interface FuncIntf {
public int getValue();
}
class ClsIntf implements FuncIntf
{
public int getValue()
{
return 20;
}
}
class MyClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FuncIntf intfRef = new ClsInft();
System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.getValue());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-240707080146-84abf75f/85/Lambda-Expression-For-anyone-that-needs-Java-Lambda-notes-10-320.jpg)
![Lambda Expression Example1
Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
interface FuncIntf {
int getValue();
}
class MyClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FuncIntf intfRef = new ClsInft();
System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.getValue());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-240707080146-84abf75f/85/Lambda-Expression-For-anyone-that-needs-Java-Lambda-notes-11-320.jpg)
![Lambda Expression Example1
Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
interface FuncIntf {
int getValue();
}
class MyClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FuncIntf intfRef = ;
System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.getValue());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-240707080146-84abf75f/85/Lambda-Expression-For-anyone-that-needs-Java-Lambda-notes-12-320.jpg)
![Lambda Expression Example1
Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
interface FuncIntf {
int getValue();
}
class MyClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FuncIntf intfRef = () -> 20;
System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.getValue());
}
}
Lambda Expression () -> 20
================
• Implements the method getValue() in FuncIntf
• Returns an instance of the class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-240707080146-84abf75f/85/Lambda-Expression-For-anyone-that-needs-Java-Lambda-notes-13-320.jpg)
![Lambda Expression with parameters - Example2
Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
interface FuncIntf
{
int findSum(int a,int b);
}
class MyClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FuncIntf intfRef = (x,y)-> {int c=x+y;return c;};
System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.findSum(6,8));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-240707080146-84abf75f/85/Lambda-Expression-For-anyone-that-needs-Java-Lambda-notes-14-320.jpg)
![Lambda Expression with parameters type- Example3
Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
interface FuncIntf
{
int findSum(int a,int b);
}
class MyClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FuncIntf intfRef = (int x, int y)-> {int c=x+y;return c;};
System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.findSum(6,8));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-240707080146-84abf75f/85/Lambda-Expression-For-anyone-that-needs-Java-Lambda-notes-15-320.jpg)
![Lambda Expression with parameters type- Example4
Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
interface FuncIntf
{
int findSum(int a,int b);
}
class MyClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FuncIntf intfRef = (int x, int y)-> {int c=x+y;return c;}; //with return(with multiple statements)
System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.findSum(6,8));
FuncIntf intfRef1 = (int x,int y)-> (x+y); //without return(with only one statement)
System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef1.findSum(6,8));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-240707080146-84abf75f/85/Lambda-Expression-For-anyone-that-needs-Java-Lambda-notes-16-320.jpg)