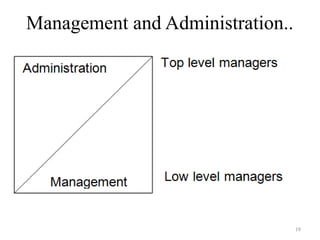
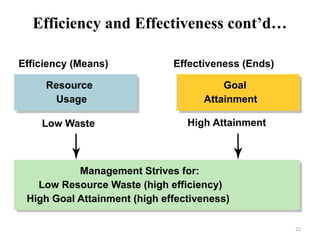
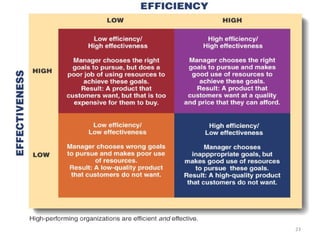
The document provides an overview of management in the health sector, defining key terms and concepts such as health, health services, and management itself. It emphasizes the importance of management for achieving organizational goals and details various principles of management, including effectiveness, efficiency, and the need for structured work relations. Additionally, it discusses how management interacts with both internal and external environments within health service organizations.