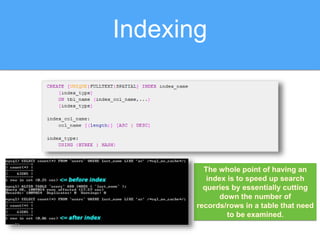
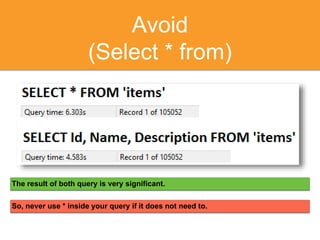
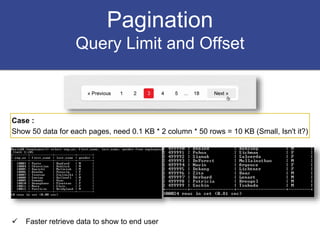
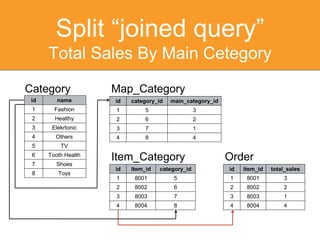
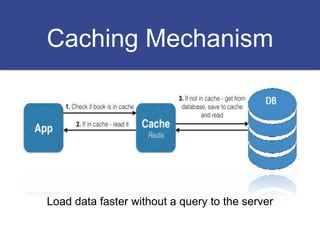
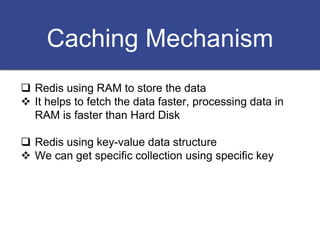
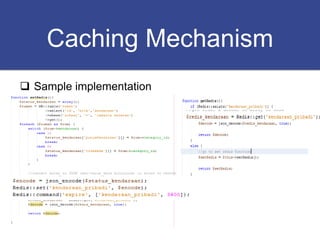
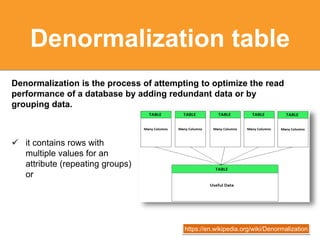
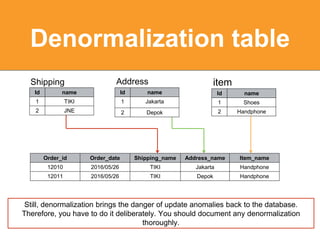
The document discusses strategies for optimizing SQL queries to enhance data retrieval speed for a company's growing database. Key techniques include avoiding 'SELECT *' statements, implementing pagination, splitting complex joined queries, and using caching mechanisms like Redis. It also touches on the importance of documentation when using denormalization to optimize read performance while being cautious of update anomalies.