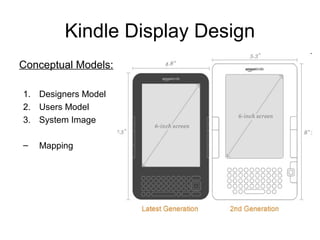
This document discusses the design of the Kindle e-reader according to conceptual models of designers' goals, users' expectations, and the system itself. It examines how the Kindle's display design maps these models and considers affordances like buttons, keyboard, and screen, citing studies on their usability. Constraints of early Kindles like mobility and note-taking are addressed, as well as improvements in newer versions like page navigation and browsing capabilities, though small screen size remains an issue.