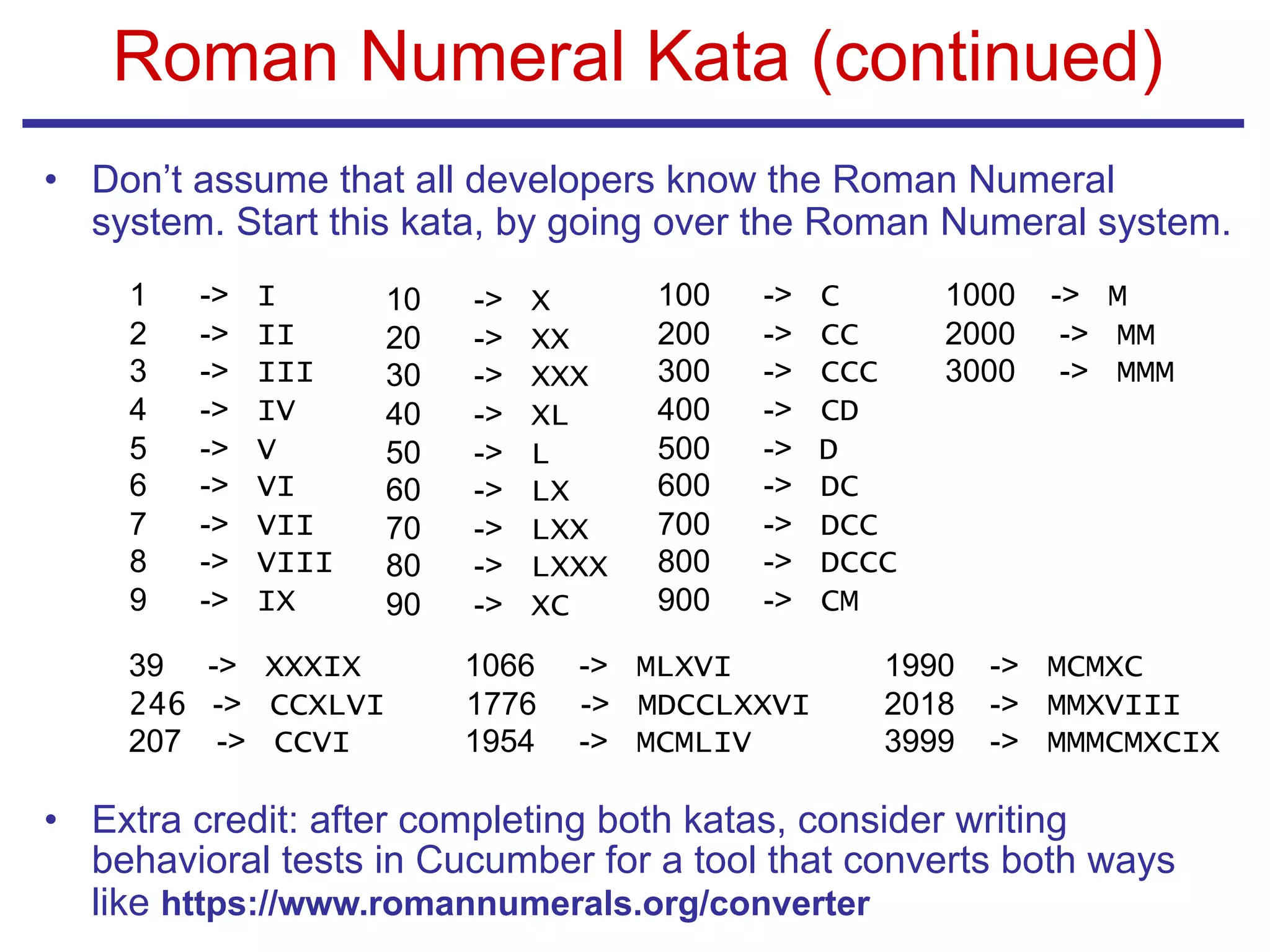
The document outlines the concept of code katas, emphasizing their role in enhancing software craftsmanship through practice, specifically in test-driven development (TDD) and pair programming. It details the structure and benefits of conducting code katas in dojos, provides guidance on selecting katas, and introduces several examples such as FizzBuzz and Coin Changer. Additionally, it highlights the importance of good facilitation and offers resources for further learning on TDD and refactoring.





























![Coin Changer Kata
Simulate providing change for 1 to 99 cents:
• Develop tests and a method that given an integer (or int)
returns the minimal number of coins to make that change.
• Use this version of Coin Change kata (it’s simpler), instead
of the one that asks for all possible combinations.
• Coins are quarters, dimes, nickels and pennies. Ignore half
dollars.
• Before starting, choose a way to represent the coins. Either
as an array of strings [“quarter”, “dime”, “dime”, “penny”] or
as single string “QDDP”, e.g.:
1 -> [“penny”] or “P”
2 -> [“penny”, “penny”] or “PP”
67 -> [“quarter”, “quarter”, “dime”, “nickel”, ”penny”, ”penny”] or “QQDNPP”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/katayourwaytoswcraftsmanship20190805-190806010132/75/Kata-Your-Way-to-SW-Craftsmanship-33-2048.jpg)