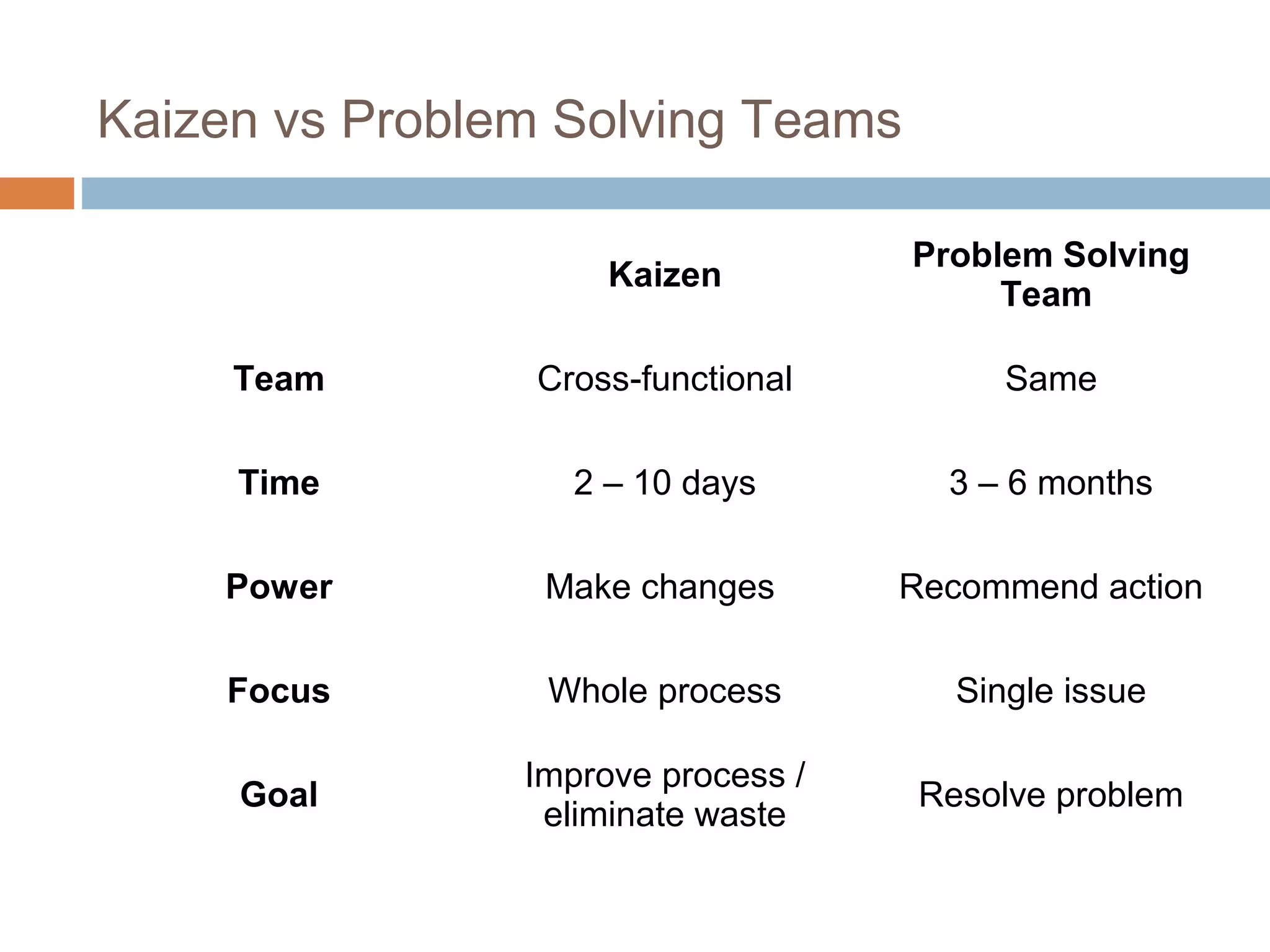
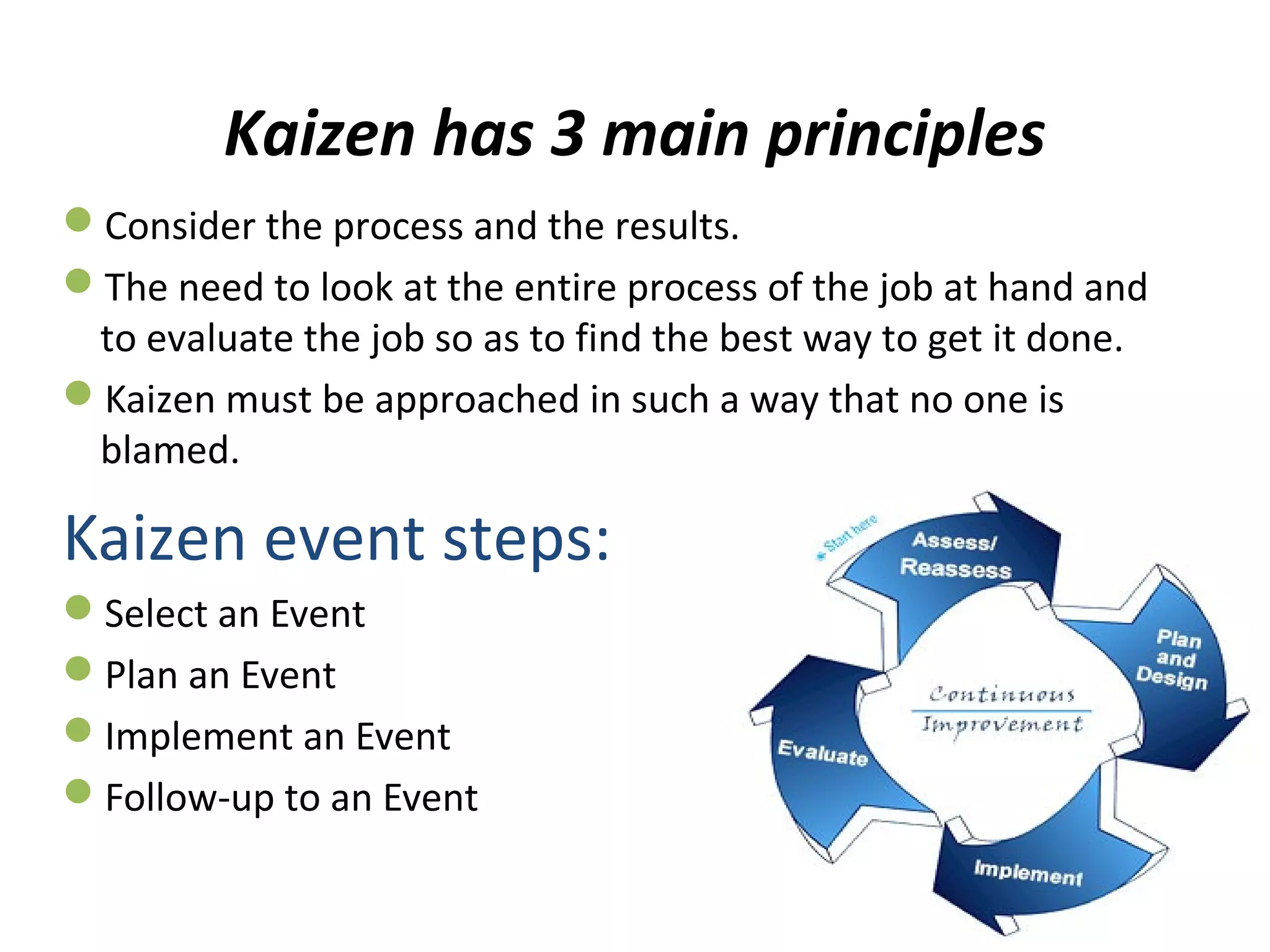
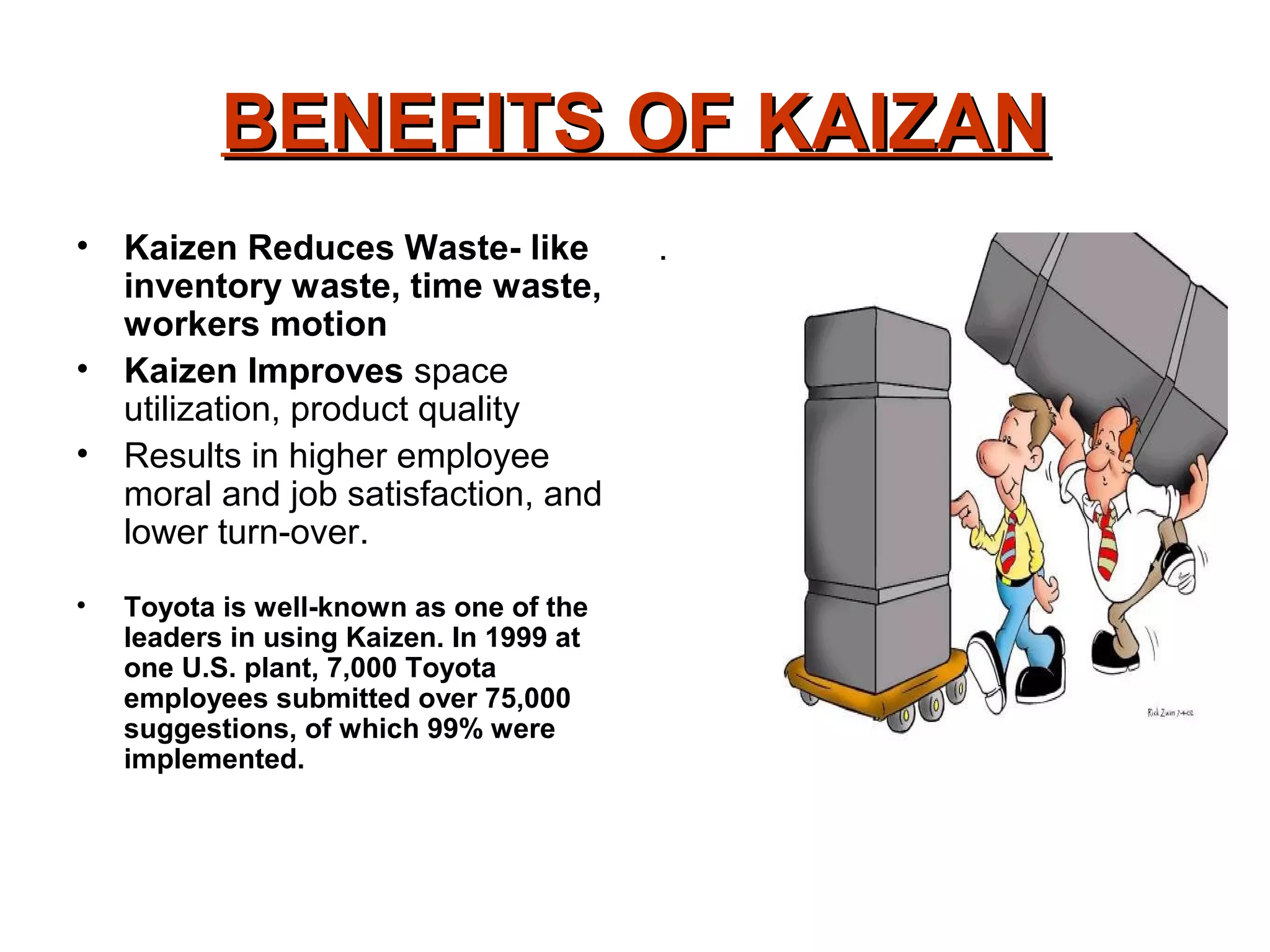
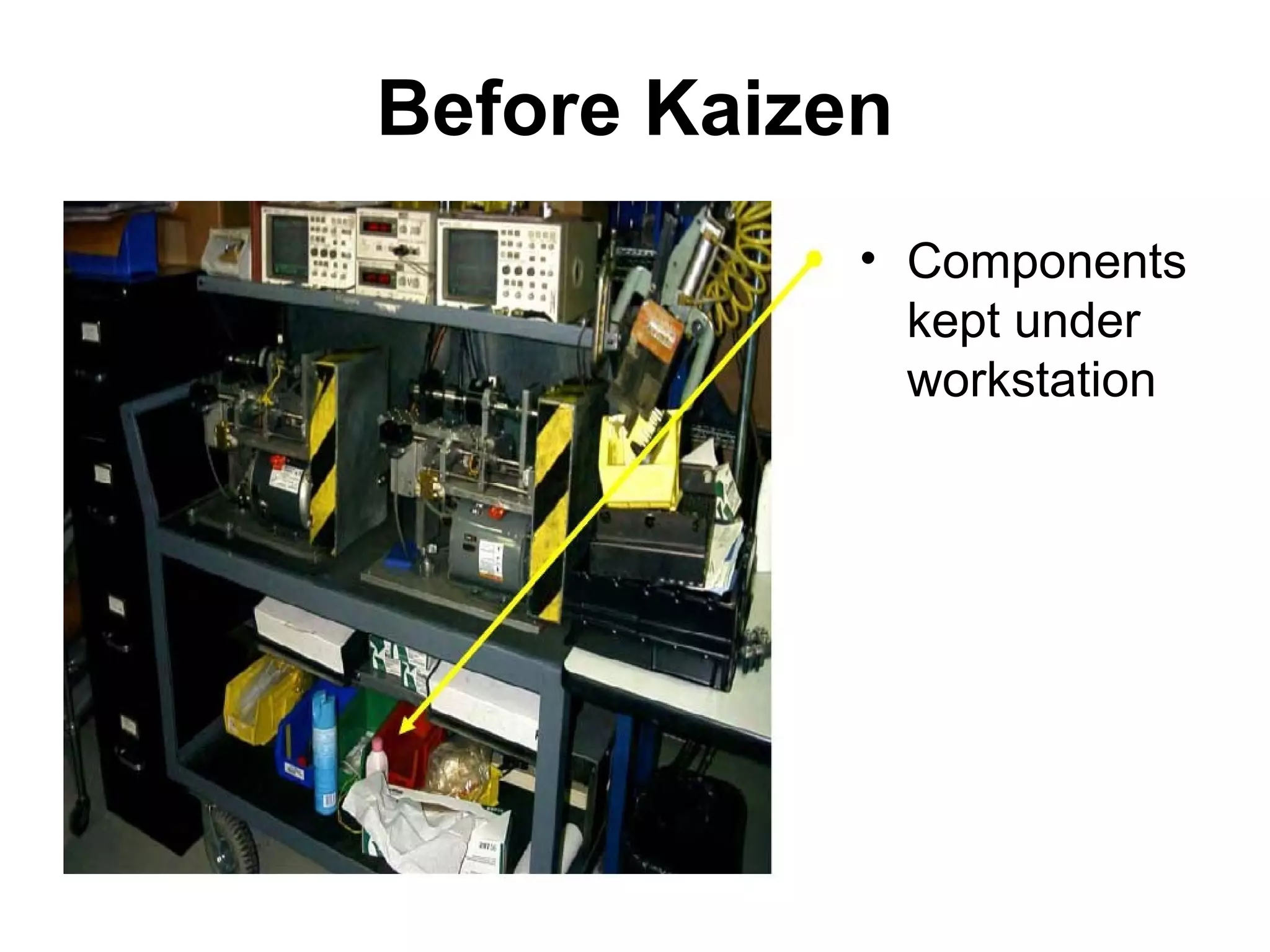
Kaizen refers to continuous incremental improvement. It is a Japanese philosophy that focuses on continuous improvement involving everyone in the organization on an ongoing basis. The goal of Kaizen is to eliminate waste through small, incremental changes to processes. It aims to improve all aspects of an organization over time. Kaizen emphasizes identifying and eliminating non-value added activities and focusing on activities that customers are willing to pay for. The 5S methodology is a tool used in Kaizen to organize and standardize the workplace. Toyota popularized Kaizen as part of their lean manufacturing system to drive cost reductions and quality improvements.