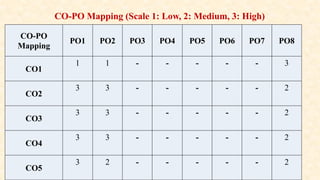
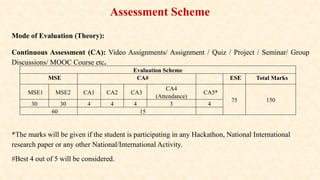
The document outlines the syllabus for a course on Operating Systems, aimed at MCA students in their first semester. It includes course objectives, outcomes, and detailed content covering topics such as process management, memory management, and I/O management. The document also specifies evaluation criteria and references for further reading.