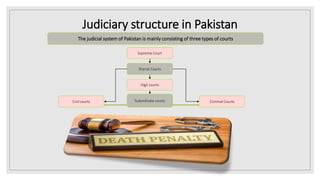
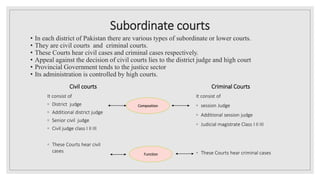
Pakistan's judiciary structure consists of the Supreme Court, five High Courts, Federal Shariat Court, and various subordinate courts. The Supreme Court is the apex court and hears appeals and constitutional matters. It has 17 justices. The five High Courts are provincial courts that exercise appellate jurisdiction and supervise subordinate courts. Subordinate courts include civil courts that hear civil cases and criminal courts that hear criminal cases. Judges are appointed through a judicial commission and parliamentary committee process and can be removed by the Supreme Judicial Council for misconduct or incapability.