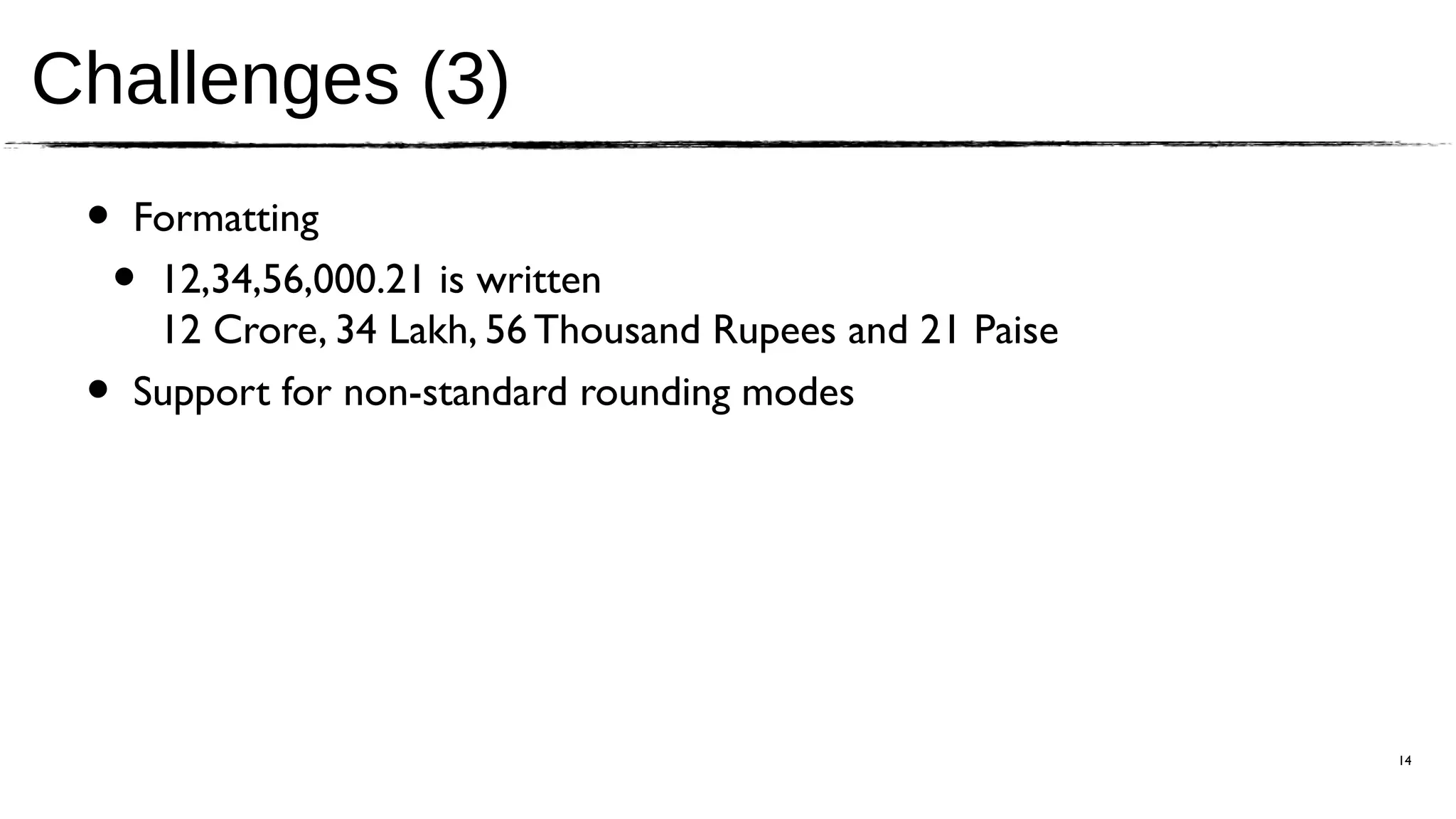
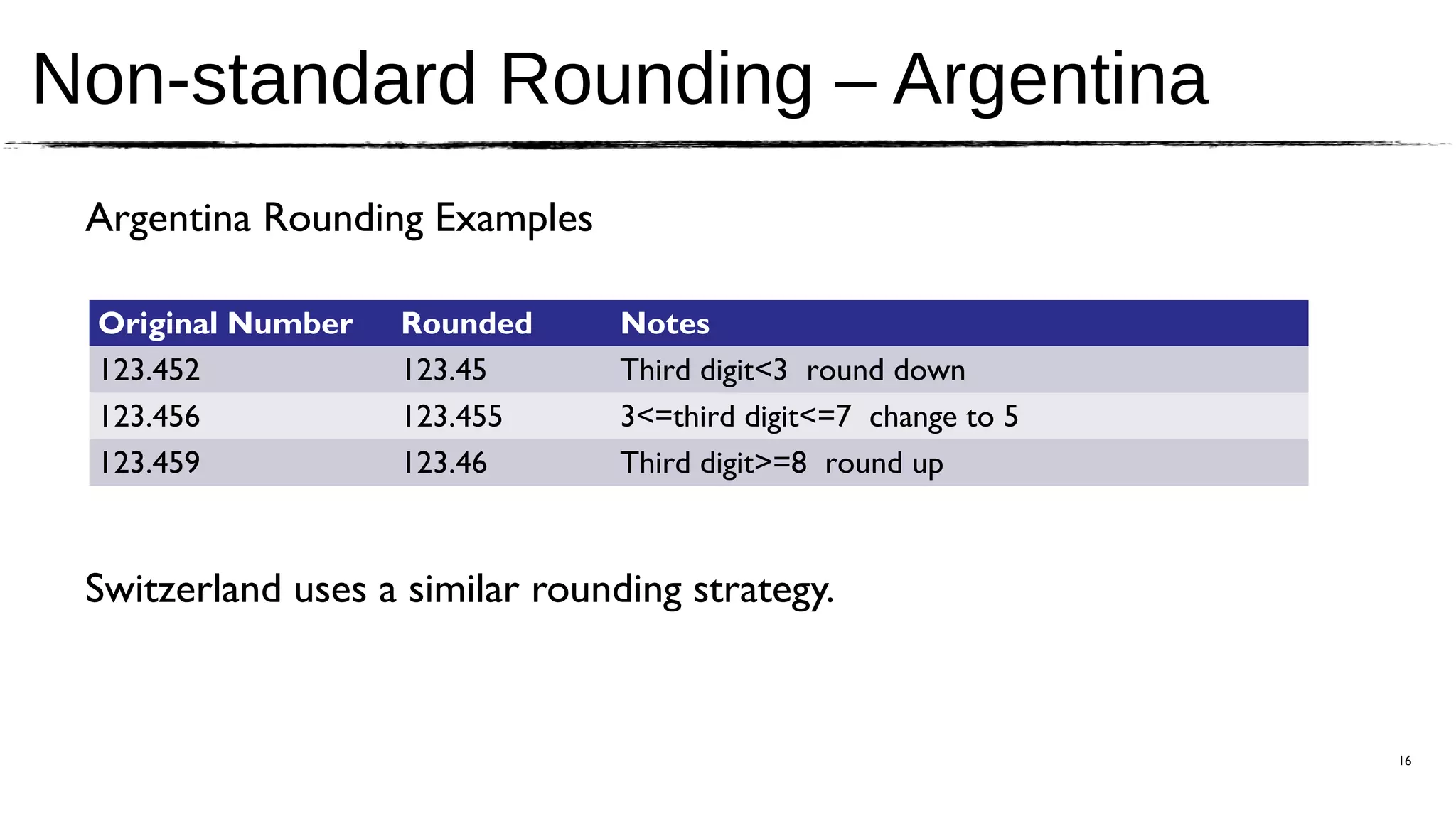
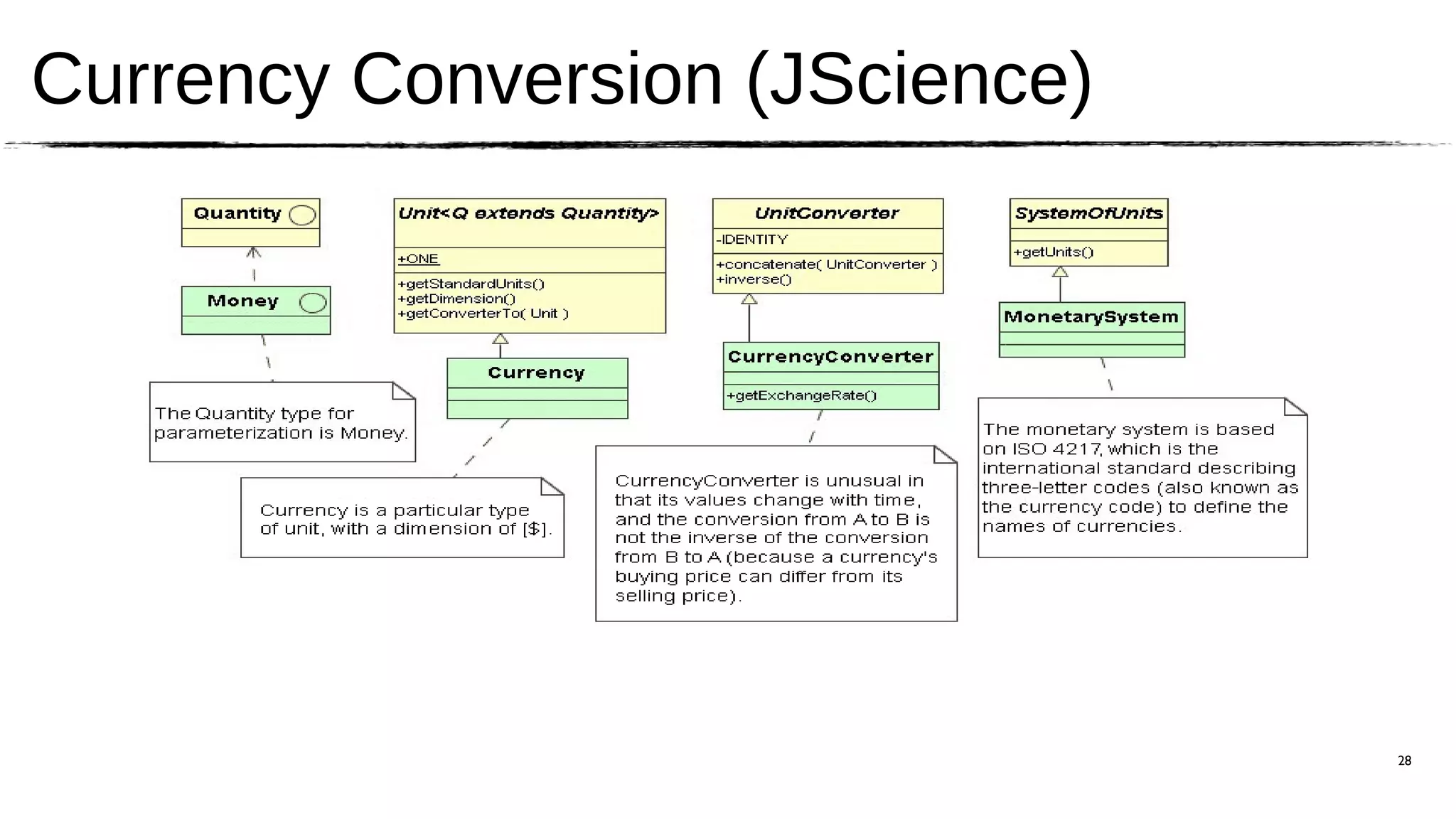
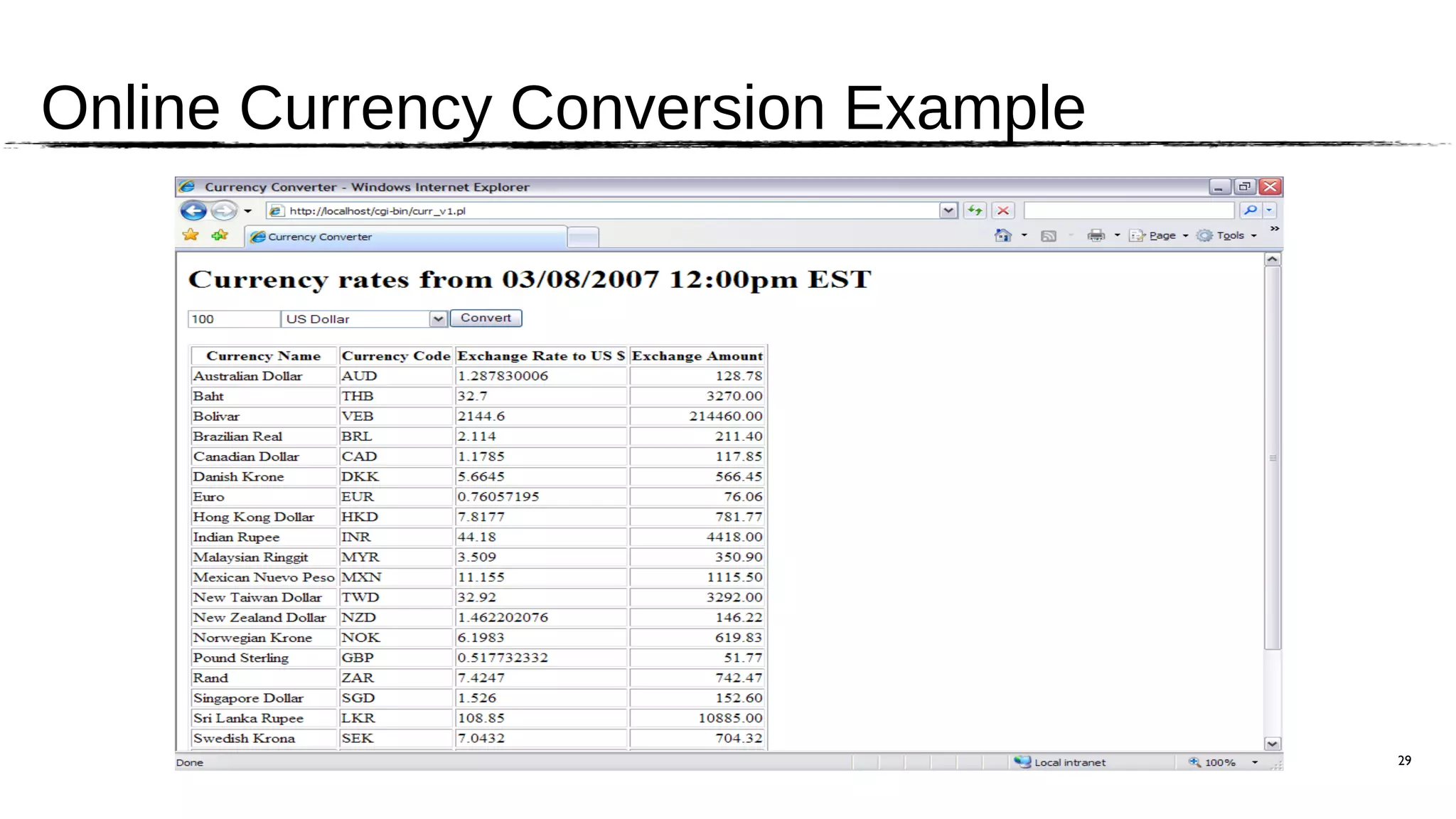
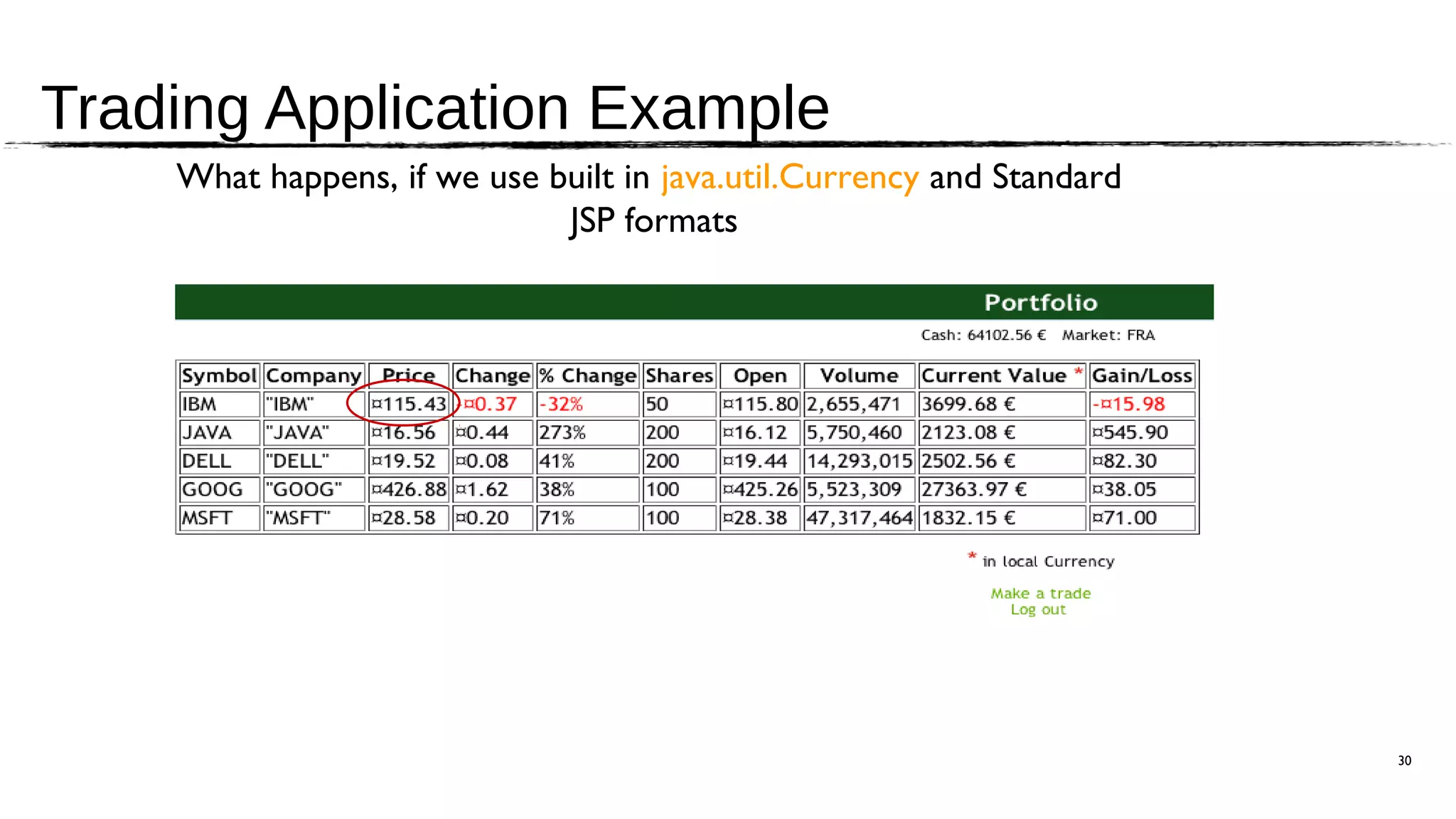
The document discusses the JSR 354, which aims to create a Java Money and Currency API to address the limitations of the current java.util.Currency class by providing a first-class representation of monetary amounts, including support for standard and custom currencies. It highlights various challenges such as currency arithmetic, formatting, non-standard rounding rules, and the need for high precision in financial applications. The expert group involved includes members from major financial institutions and aims for the API to be adopted broadly across Java platforms.