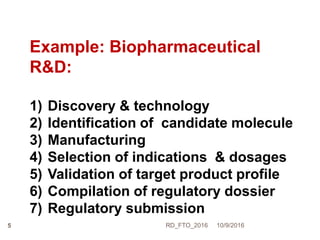
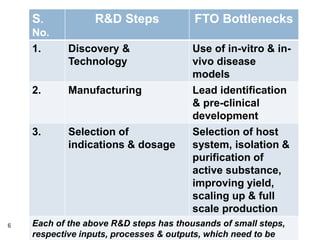
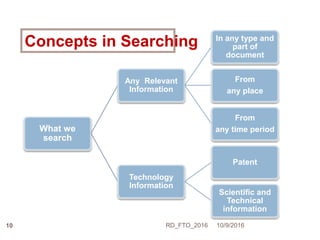
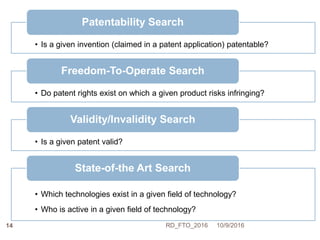
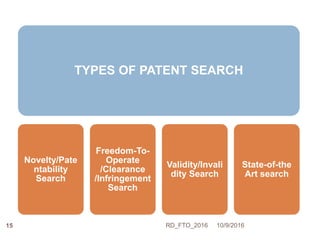
Dr. Ravi Dhar discusses the importance of freedom to operate (FTO) in intellectual property. He explains that FTO is the ability to commercialize an invention without challenges from other patent holders. He outlines different types of patent searches conducted for FTO clearance including patentability, freedom-to-operate, validity, and state-of-the-art searches. Key bottlenecks in biopharmaceutical research and development that require FTO analysis are also described. Strategies for addressing FTO obstacles like licensing, technology exchanges, and patent sharing are presented. Dr. Dhar emphasizes the importance of only using legal means to resolve any FTO issues.