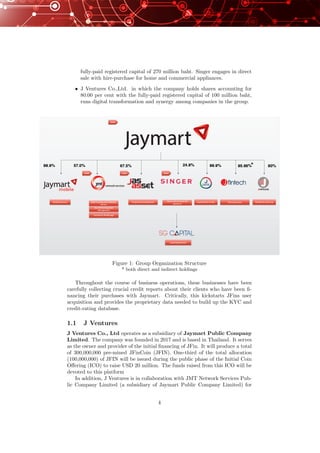
The document is a whitepaper for JFinCoin, which aims to create a decentralized digital lending platform and ecosystem to provide financial services to the unbanked and underbanked populations of Southeast Asia. It notes that over 72% of Southeast Asia's population lacks access to basic banking services. The platform will use blockchain technology and smart contracts to enable peer-to-peer lending in a decentralized network, reducing costs and inefficiencies of traditional centralized lending. An Initial Coin Offering of the JFinCoin utility token will raise $20 million to fund the platform's development.



![debt management and collection based in Thailand. This ensures that loan
defaults and non-performing loans (NPL) are taken care of efficiently. Credit
recovery is made through analysis and approval of proper recovery strategies
i.e. restructuring and legal proceedings.
We firmly believe that the competitive advantage of the synergy among our
subsidies will bring forth financial services that will successfully disrupt the
existing financial services in Thailand and around the globe. Crucially, it will
pioneer new approaches in extending financial inclusion to the unbanked and
underbanked in Thailand and the rest of Southeast Asia.
2 The Problem and Opportunities
Over 72% of Southeast Asias population are unbanked or underbanked lacking
access to basic financial services such as cash deposits, money transfers or loans.
The majority of the people in Indochina are no exception, and what is crucially
needed by them are basic banking services such as deposit, withdrawal, and
most importantly micro loans.
However, due to inefficiencies in the current financial system, it is too costly
for established banks to provide such services to the 72% of the population
who remain unbanked or underbanked. Further, all of this assumes that the
applicants have the documents and transaction histories required to apply for a
loan which is seldom the case for those in rural areas with poor records keeping
or migrant workers. According to the Thailand Ministry of Labour, there are
approximately 4 million migrant workers in Thailand.
The traditional loan process is slow and tedious. It requires lot of paperwork
and a long lead time from a day to a month to complete the whole process. The
process includes application, know-your-customer (KYC), credit checking, ap-
proval, and money transfer. In the worst case, after a long wait, the application
may be rejected due to various reasons.
Apart from the prolonged processes, the rejection rates for personal loan is
high. According to Ayudhya Capital Services, the personal loan rejection rate
was at 61% in September 2017. It increased from 57% in the previous month,
due to the new regulation that each person can only take personal loan from a
maximum of 3 companies at a time [3].
With limited access to the money that they need, loan applicants become
desperate and inevitably take higher risks by seeking illegal loans from so-called
loan sharks. These loan sharks mitigate their risks of non-performing loans/bad
debts is by offering loans that charge more than 150% in interest per year which
puts good borrowers at the receiving end while bad borrowers escape through
vaious means. As a result, the household debt in Thailand has been increasing
every year. According to Kasikorn Research Center, household debt in Thailand
is more than 16 trillion baht (0.5 trillion USD)[11].
Additionally, the interest rate gap in financing markets is vast, due to the
fact that banks offer low interest rates for savings account but take high interest
rates for loans. In Thailand, deposit and bond interest rate can be as low as
0.5% per year, compared to the interest rate for a personal loan at 20-28% per
year [10]. Without a good KYC process and centralised or totally decentralised
credit rating system, banks take the most conservative approach (similar to loan
sharks) by increasing the interest rate and letting good borrowers bear the brunt
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jfincoin-whitepaper-180203062649/85/Jfincoin-whitepaper-5-320.jpg)


![Figure 3: JFin Ecosystem
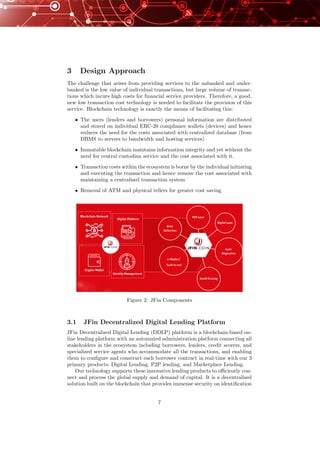
3.1.1 Loan Origination
Loan Origination is a process by which a borrower applies for a new loan, which
typically includes the series of steps taken by the lender/bank from the point the
customer shows interest in a loan product all the way to disbursal of the funds.
The JFin Loan Origination platform will allow borrowers to complete documents
digitally, make online payments, and view their loan status at anytime during
the process.
3.1.2 Credit Scoring
The evaluation of individual loan requests is performed automatically via credit
scoring technique. Each borrower will be determined by the weight and calcula-
tions from the information given as well as their past financial and non-financial
records from other sources, such as payment history, social network interaction,
transaction history in JFin’s DDLP, etc. The information inputs are used for
calculating a maximum total credit limit, interest rate for a specific loan request,
and payment terms. Criteria for calculation of creditworthy of the borrowers
are determined dynamically by machine learning techniques.
Furthermore, as Jaymart has been in the space of consumer sales and finance
for decades, it has collected sufficient data on the ability of repayment for many
individuals (Jaymart customers). This is data that is uniquely Jaymarts and
allows it to develop a non-traditional credit scoring model. With the inclusion of
mobile top up history data, coupled with state-of-the-art machine learning algo-
rithms to better predict their ability for repayment, these individuals now have
their own credit-worthiness encoded in the blockchain, supported by their own
sound data analytics on their historical repayment capabilities, thus allowing
them to borrow effectively at lower interest rates.
Several machine learning and statistics techniques are used to evaluate indi-
vidual credit scoring, for example, k-nearest neighbors-classifier, logistic classi-
fier, and random forest [6][5][7]. We performed back-testings by sampling credit
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jfincoin-whitepaper-180203062649/85/Jfincoin-whitepaper-9-320.jpg)


![The users of JFin are needed to provides KYC documents registered in a
digital form. All the information will be confidentially retained. The informa-
tion will be used to calculate credit scoring once required. The KYC procedures
are a critical function to assess and monitor customer risk and a legal require-
ment to comply with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws. After complete the
process, the Wallet ID will then be created.
3.1.9 JFin Wallet Management
JFin Wallet will be created for individual after JFin KYC is completed. It is a
secured digital wallet that holds an amount of funds that allows to be used to
purchase in store, cash out, or pay utility services.
The mobile application includes a JFin wallet that can be used to securely
hold money in various currencies. It has an ability to perform an international
money transfers, simple payments, fast withdrawal payouts and instant online
payments with low fees through the blockchain network.
Money return and collection according to loan terms are done via JFin Wallet
by top-up money back to the wallet prior to the due date. The blockchain
contract will enforce money transfer back automatically via blockchain network.
In case of NPL or loan defaults, debt collection agents will perform necessary
procedures to recover funds that are past due or accounts that are in default,
according to the Debt Collection Act.
3.1.10 JFin Decentralized Network
The JFin Decentralized Network (JDN) is a layer built on top of the blockchain.
The blockchain technology serves as a decentralized and distributed digital
ledger that records every transactions between two parties in the network in
a verifiable and permanent way [1] [8]. Once records are written in the block of
data, they cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all blocks
prior to the current block. Blockchains are secure by design and are an ex-
ample of a distributed computing system with high Byzantine fault tolerance.
Decentralized consensus has therefore been achieved with a blockchain[12].
We implement smart contracts in order to operate a lending service. Smart
Contracts are self-executing contracts written into lines of code to ensure the
terms and agreement between two parties. The code and the agreement are
contained and distributed in the JDN network. Smart Contracts allow transac-
tions and agreements to be carried out in a trust manner on trust-less networks
and parties. They deliver transactions with transparency, trace-ability, and
permanence[13].
We will use Tendermint or other proof-of-stake algorithms as a consensus
engine in the JDN that enables Byzantine fault tolerance on machines spread
across the globe, with strong security guarantees [4]. One possible example
is the use of Tendermint. Tendermint consensus algorithm provides benefit
such as speed, security, and scalability, as opposed to using Proof-Of-Work
systems, [2] [9]. Tendermint blocks can commit to finality in the order of 1
second. TendermintCore can handle transaction volume at the rate of 10,000
transactions per second for 250byte transactions. The algorithm can scale to
hundreds or thousands of validators unlike Proof-Of-Work technique [4].
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jfincoin-whitepaper-180203062649/85/Jfincoin-whitepaper-12-320.jpg)









![References
[1] Blockchain. Investopedia URL: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/blockchain.asp.
Retrieved 2017-01-01.
[2] Byzantine consensus algorithm. URL:
https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/wiki/Byzantine-Consensus-
Algorithm. Retrieved 2017-12-01.
[3] Personal loan rejection rate soars from new regulation from bot. URL:
https://www.posttoday.com/economy/finance/514932. Retrieved 2017-12-
01.
[4] Tendermint. URL: https://github.com/tendermint/tendermint/wiki/. Re-
trieved 2017-12-01.
[5] N. S. Altman. An introduction to kernel and nearest-neighbor nonpara-
metric regression. The American Statistician, 46(3):175–185, August 1992.
[6] David A. Freedman. Statistical Models: Theory and Practice. Cambridge
University Press, 2009.
[7] Tin Kam Ho. Random decision forests. Proceedings of the 3rd International
Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Montreal, QC 14-16,
page 278282., 1995.
[8] Karim R. Iansiti, Marco; Lakhani. The truth about blockchain, January
2017.
[9] Jae Kwon. Tendermint: Consensus without mining. Draft v. 0.6, fall, 2014.
[10] Bank of Thailand. Interest rate statistic. URL:
https://www.bot.or.th/thai/statistics/ layouts/application/interest rate/in rate.aspx.
Retrieved 2017-12-01.
[11] The Secretariat of the House of Representatives. Loan shark issues and
way to overcome. Hot Issue, 2016.
[12] Siraj Raval. Decentralized Applications: Harnessing Bitcoin’s Blockchain
Technology. O’Reilly Media, Inc., 2016.
[13] Melanie Swan. Blockchain: Blueprint for a New Economy. O’Reilly Media,
Inc., 2015.
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jfincoin-whitepaper-180203062649/85/Jfincoin-whitepaper-23-320.jpg)
