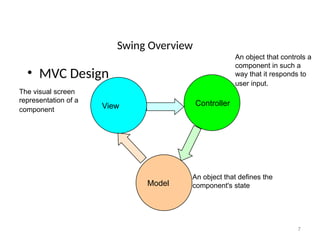
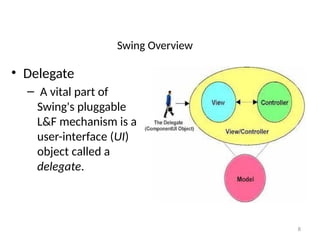
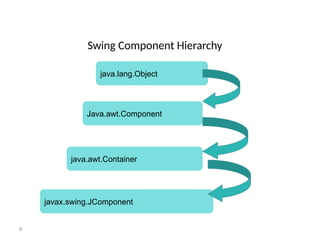
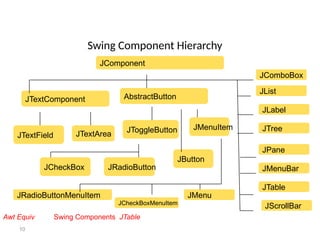
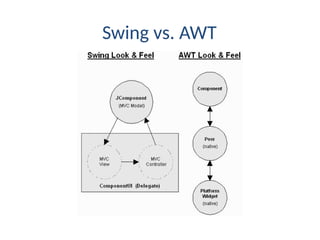
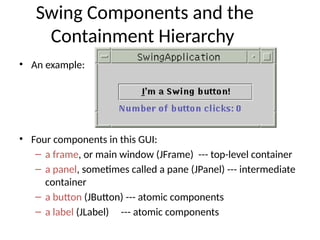
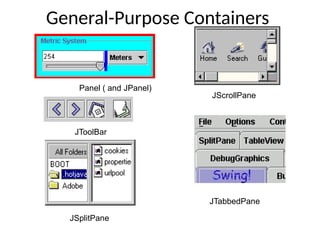
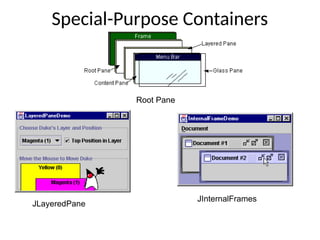
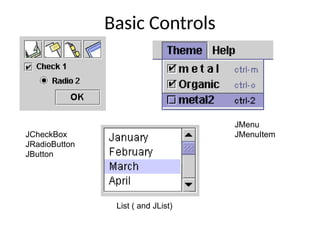
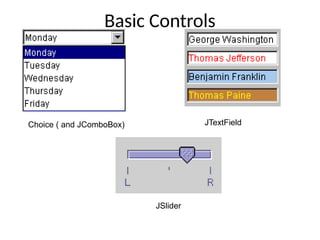
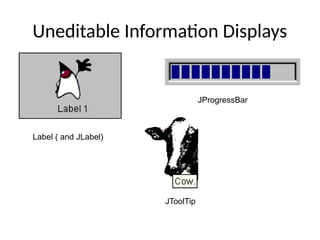
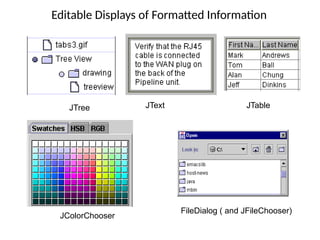
The document provides an overview of Java Swing components, highlighting their advantages over AWT, including improved functionality and a pluggable look and feel. It covers the architecture of JDBC and the various types of drivers, statements, and result sets. Additionally, it details the hierarchy of Swing components and their relationship with the MVC architecture.