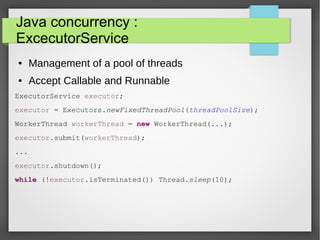
This document provides an introduction to Java concurrency and the ExecutorService API. It discusses parallelism and threads in Java, shows how to create and manage thread pools using ExecutorService, and emphasizes that ExecutorService is now preferred over directly starting and managing threads. The goal is to give a simple overview of Java concurrency basics and how ExecutorService can help manage threads.