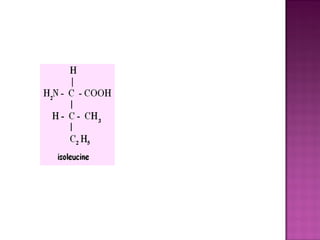Isomerism refers to compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. There are several types of isomerism:
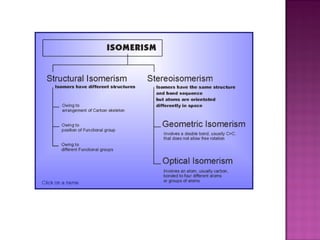
1. Structural isomers have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. This includes chain isomers, positional isomers, and functional isomers.
2. Stereoisomers have the same structure and bond order but different spatial arrangements. This includes geometric isomers, enantiomers, and diastereomers.
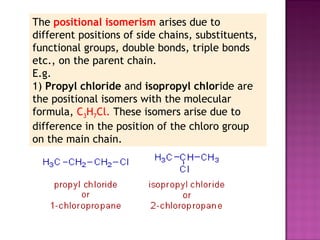
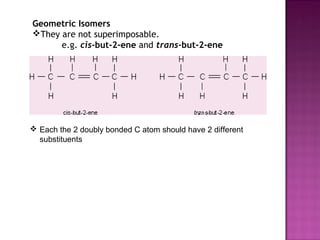
3. Geometric isomers involve double bonds that do not allow free rotation, giving cis and trans orientations. Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images, while diastereomers contain at least two chiral carbons and are not







![STEREOISOMERS
Stereoisomers have the same structure and
bond order but their atoms and groups of
atoms are arranged differently in space.
They have different spatial
arrangements and their molecules are
not superimposable.
Types of Stereisomers:
1] Geometric Isomerism (GI)
Involves a double bond, usually C=C, that does
not allow free rotation about the double bond
(unlike a C-C single bond).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isomerismprsnttn-130116063745-phpapp02/85/Isomerism-prsnttn-14-320.jpg)


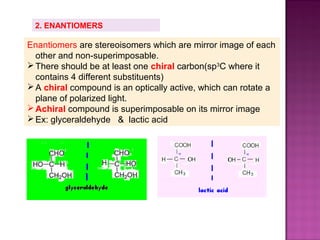
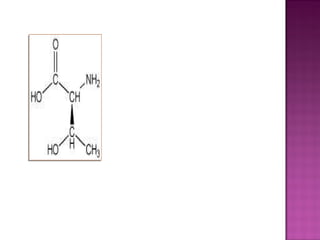
![3] DIASTEREOMERS
isomers that are non-mirror compounds
but contains at least 2 chiral carbons within
the molecule.
No.of Stereoisomers = 2n
where n is the no, of chiral carbon
Ex: 2,3-dichloropentane
CH3–CH–CH –CH2 – CH3
│ │
Cl Cl
No. of stereoisomers= 22 = 4 isomers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isomerismprsnttn-130116063745-phpapp02/85/Isomerism-prsnttn-20-320.jpg)