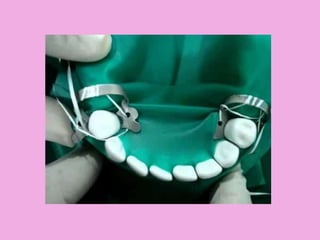
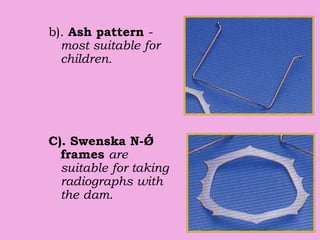
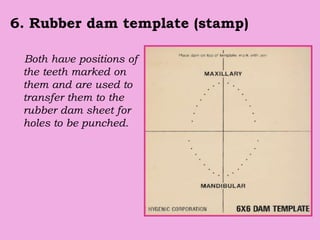
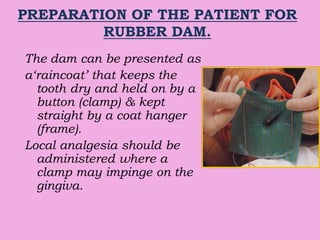
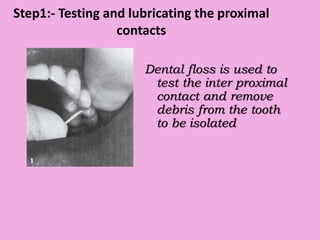
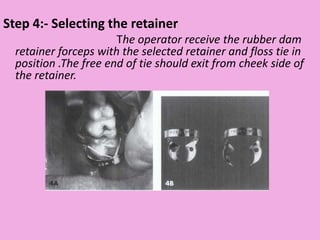
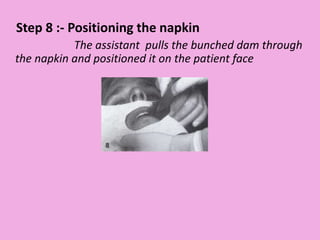
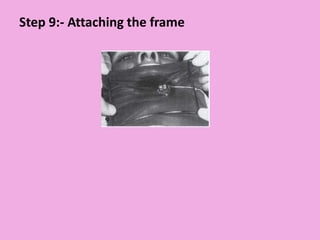
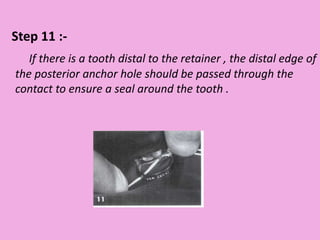
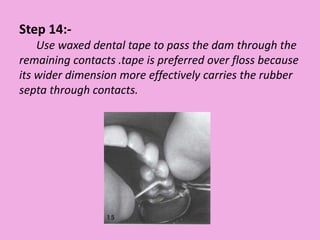
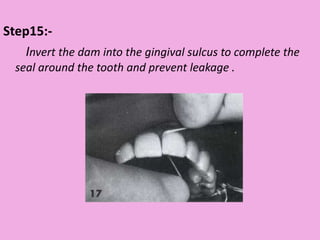
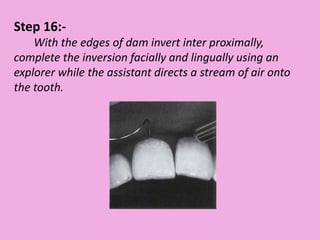
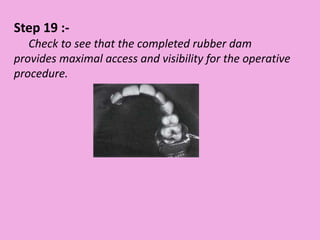
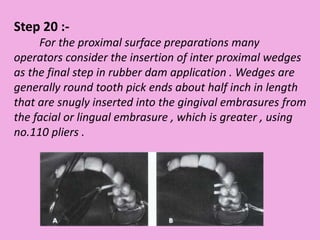
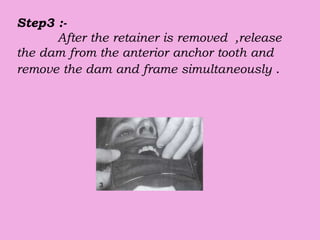
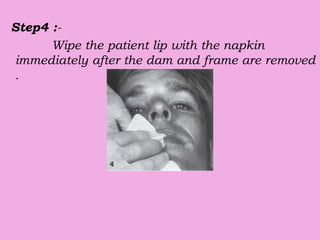
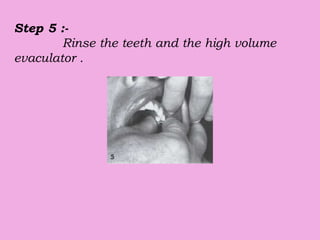
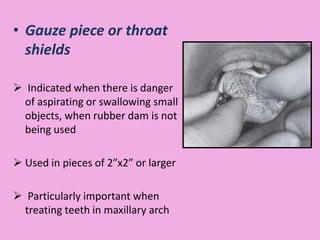
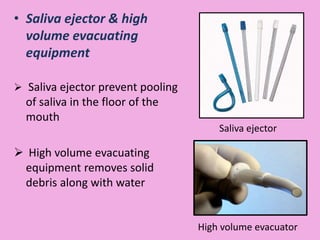
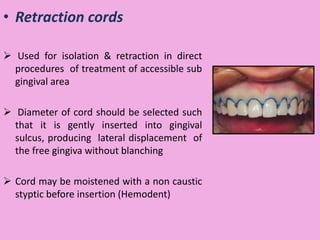
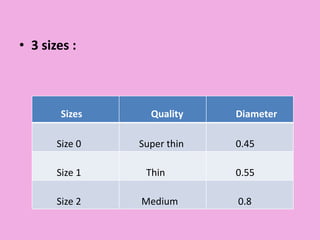
This document discusses methods of isolation in dentistry. Direct isolation methods include rubber dams, cotton rolls, cellulose wafers, Dri-angles, gauze, suction devices, and retraction cords. The rubber dam provides the best isolation and was introduced in 1864. It isolates teeth from oral fluids to create a dry field. Advantages include a clean operating field, improved access and visibility, soft tissue retraction and protection, and reduced cross-contamination. Application and removal of the rubber dam is described in 20 steps. Other isolation methods like cotton rolls provide some retraction but do not create as dry a field as the rubber dam.