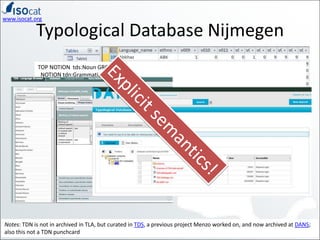
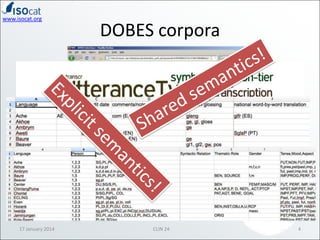
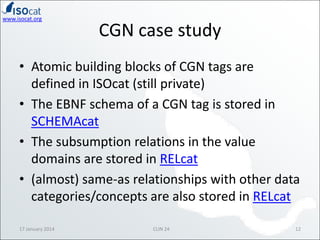
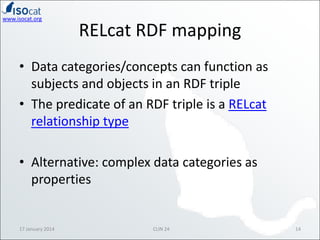
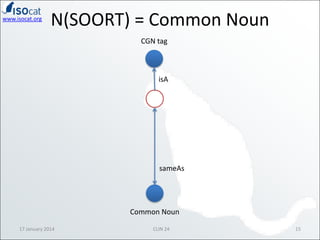
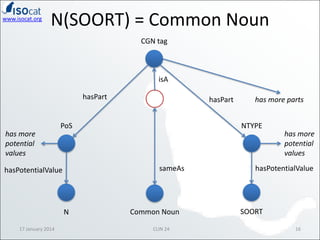
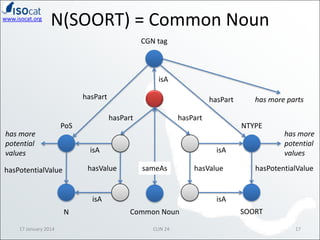
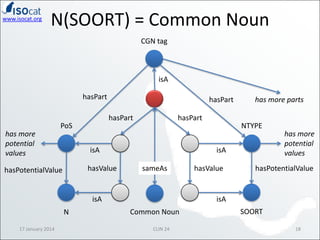
The document discusses the ISOCAT and RELCAT registries, emphasizing their role in mapping data categories and concepts for explicit semantics in linguistic resources. It outlines issues related to theoretical frameworks, granularity, and relationships between various data categories, illustrated through case studies and examples. Conclusions include the need for user support and integration of ISOCAT and RELCAT for improved semantic clarity.









![www.isocat.org
Other examples
• “JJR” -> “POS=adjective & degree=comparative”
• “Transitive” -> “thetavp=vp120 & synvps=[synNP] &
caseAssigner=True”
• “VVIMP” -> “POS= verb & main verb & mood=imperative”
17 January 2014
CLIN 24
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isocat-relcat-coop-sr-final-140120022728-phpapp01/85/ISOcat-and-RELcat-two-cooperating-semantic-registries-21-320.jpg)