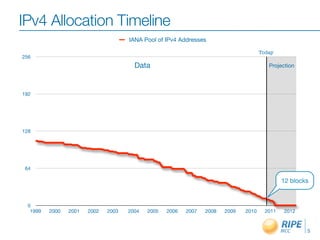
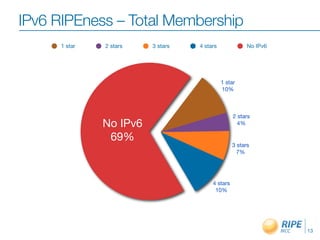
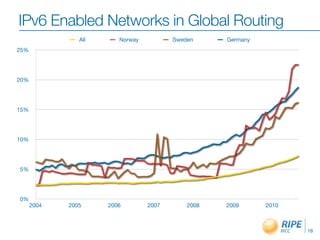
The document discusses the need for organizations to adopt IPv6 before the depletion of IPv4 addresses. It notes that IPv4 addresses are projected to be exhausted in April 2011, while only 5% remain unallocated. The Regional Internet Registry RIPE NCC works to raise awareness of this issue and help organizations obtain IPv6 allocations. It also engages stakeholders through various forums and meetings to facilitate the transition to IPv6.