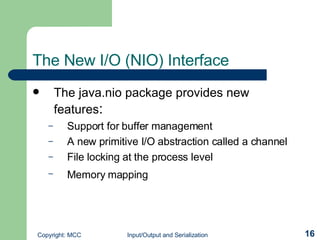
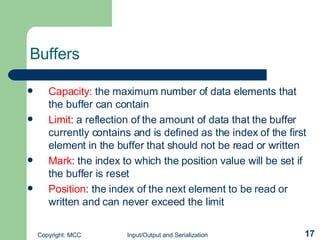
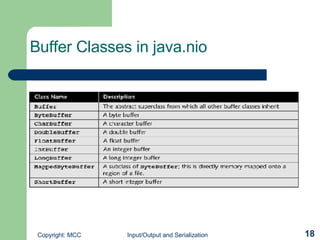
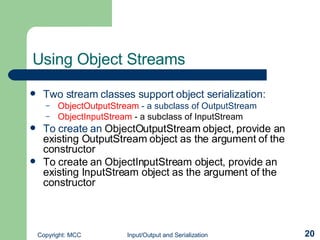
The document discusses input/output (I/O) and serialization in Java. It covers the core I/O packages that support console and file I/O, as well as the new I/O package. It also describes object serialization which allows objects to be written to streams and read back without defining additional methods, enabling object transmission over networks. Key I/O classes include InputStream, OutputStream, Reader and Writer.


![Input Methods Input methods of the java.io.InputStream class: int available() void close() void mark( int readlimit ) boolean markSupported() int read() int read(byte[] buffer ) int read( byte[] buffer , int offset , int length ) void reset() long skip(long bytecount )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/io-and-serialization-1197644391166414-4/85/IO-and-serialization-6-320.jpg)
![Output Methods Output methods of the java.io.OutputStream class: void close() void flush() void write( int b ) void write(byte[] buffer ) void write( byte[] buffer , int offset , int length )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/io-and-serialization-1197644391166414-4/85/IO-and-serialization-7-320.jpg)

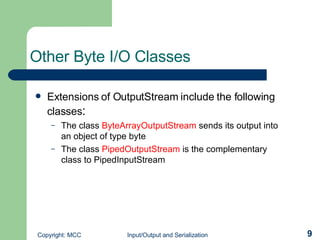


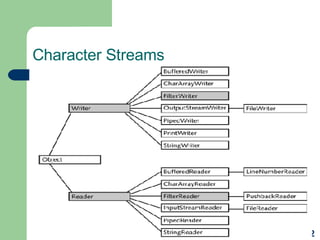

![Using Other Character I/O Classes Extensions of the Writer object include the following: The class CharArrayWriter sends its output into an object of type char[] The class StringWriter lets you write to a StringBuffer object as though it were a Writer object The class PipedWriter is the complementary class to PipedReader The class PrintWriter is the character I/O equivalent of the PrintStream class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/io-and-serialization-1197644391166414-4/85/IO-and-serialization-15-320.jpg)