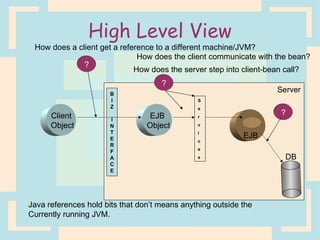
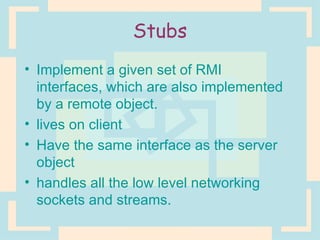
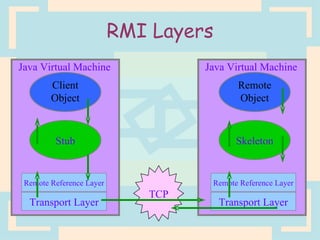
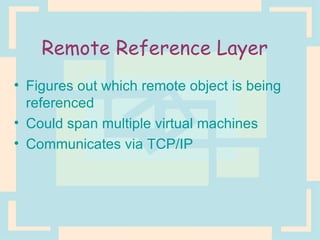
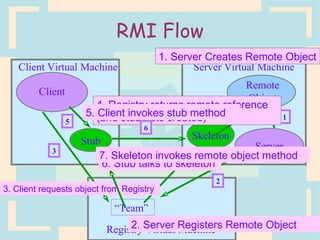
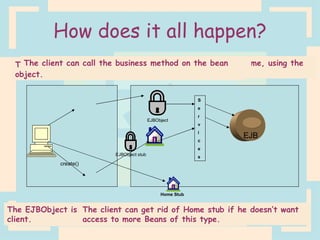
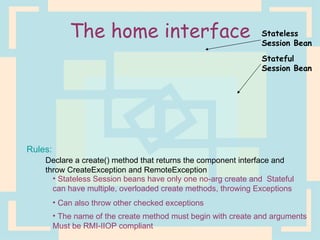
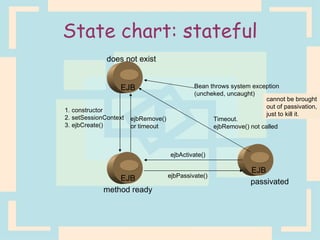
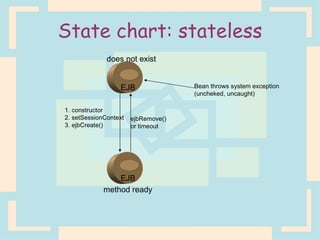
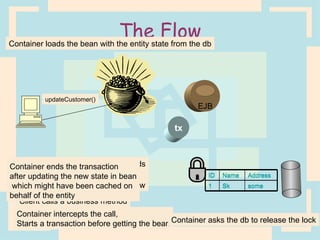
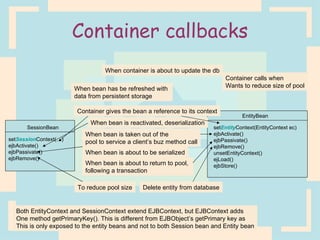
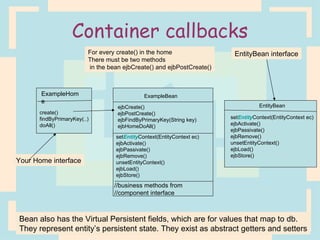
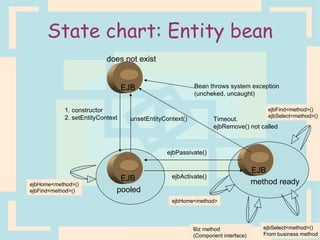
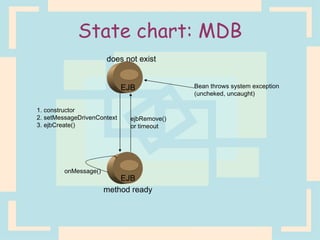
The document discusses Enterprise Java Beans (EJBs), which allow reusable business logic components in Java. EJBs handle transaction management, security, and other services so developers can focus on business logic. Clients access EJBs through remote interfaces using RMI. There are three types of EJBs: session beans for transient client requests, entity beans for persistent data, and message-driven beans for asynchronous messaging. The document explains the EJB architecture, lifecycles, and how clients interact with EJBs through remote interfaces.